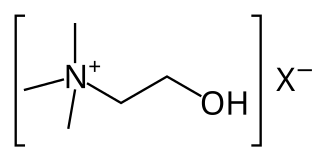
Cholinergic agents are compounds which mimic the action of acetylcholine and/or butyrylcholine. In general, the word "choline" describes the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the N,N,N-trimethylethanolammonium cation. Found in most animal tissues, choline is a primary component of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and functions with inositol as a basic constituent of lecithin. Choline also prevents fat deposits in the liver and facilitates the movement of fats into cells.

The enzyme cholinesterase (EC 3.1.1.8, choline esterase; systematic name acylcholine acylhydrolase) catalyses the hydrolysis of choline-based esters:

Donepezil, sold under the brand name Aricept among others, is a medication used to treat dementia of the Alzheimer's type. It appears to result in a small benefit in mental function and ability to function. Use, however, has not been shown to change the progression of the disease. Treatment should be stopped if no benefit is seen. It is taken by mouth or via a transdermal patch.

Tacrine is a centrally acting acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and indirect cholinergic agonist (parasympathomimetic). It was the first centrally acting cholinesterase inhibitor approved for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, and was marketed under the trade name Cognex. Tacrine was first synthesised by Adrien Albert at the University of Sydney in 1949. It also acts as a histamine N-methyltransferase inhibitor.

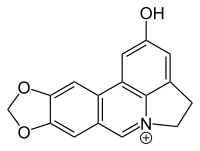
Galantamine is used for the treatment of cognitive decline in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease and various other memory impairments. It is an alkaloid that has been isolated from the bulbs and flowers of Galanthus nivalis, Galanthus caucasicus, Galanthus woronowii, and some other members of the family Amaryllidaceae, such as Narcissus (daffodil), Leucojum aestivum (snowflake), and Lycoris including Lycoris radiata. It can also be produced synthetically.

Huperzine A is a naturally occurring sesquiterpene alkaloid compound found in the firmoss Huperzia serrata and in varying quantities in other food Huperzia species, including H. elmeri, H. carinat, and H. aqualupian. Huperzine A has been investigated as a treatment for neurological conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, but a meta-analysis of those studies concluded that they were of poor methodological quality and the findings should be interpreted with caution. Huperzine A inhibits the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. It is commonly available over the counter as a nutrient supplement, and is marketed as a cognitive enhancer for improving memory and concentration.

Bulbocapnine is an alkaloid found in Corydalis and Dicentra, genera of the plant family Fumariaceae which have caused the fatal poisoning of sheep and cattle. It has been shown to act as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, and inhibits biosynthesis of dopamine via inhibition of the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase. Like apomorphine, it is reported to be an inhibitor of amyloid beta protein (Aβ) fiber formation, whose presence is a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Bulbocapnine is thus a potential therapeutic under the amyloid hypothesis. According to the Dorlands Medical Dictionary, it "inhibits the reflex and motor activities of striated muscle. It has been used in the treatment of muscular tremors and vestibular nystagmus".

Acetylcholinesterase (HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters:

Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation, mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years.

Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase enzyme family.

Cholinesterase inhibitors (ChEIs), also known as anti-cholinesterase, are chemicals that prevent the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine or butyrylcholine. This increases the amount of the acetylcholine or butyrylcholine in the synaptic cleft that can bind to muscarinic receptors, nicotinic receptors and others. This group of inhibitors is divided into two subgroups, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors (BChEIs).

Tenuazonic acid is a mycotoxin produced by Alternaria species. It is a powerful eukaryotic protein synthesis inhibitor. It is a tetrameric acid that is ubiquitous in biological environments and prevents the release of newly synthesized protein from the ribosome. Its toxicity is the highest among all Alternaria mycotoxins and has both phytotoxic and cytotoxic properties. In 1991 Tenuazonic acid was reported to inhibit skin tumor promotion in mice.

Ladostigil (TV-3,326) is a novel neuroprotective agent being investigated for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer's disease, Lewy body disease, and Parkinson's disease. It acts as a reversible acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitor, and an irreversible monoamine oxidase B inhibitor, and combines the mechanisms of action of older drugs like rivastigmine and rasagiline into a single molecule. In addition to its neuroprotective properties, ladostigil enhances the expression of neurotrophic factors like GDNF and BDNF, and may be capable of reversing some of the damage seen in neurodegenerative diseases via the induction of neurogenesis. Ladostigil also has antidepressant effects, and may be useful for treating comorbid depression and anxiety often seen in such diseases as well.

Nerine bowdenii is a species of flowering plant in the family Amaryllidaceae. It is an herbaceous bulbous perennial, growing to 45 cm (18 in) tall by 8 cm (3 in), with strap-shaped leaves and large umbels of lily-like pink flowers in late summer and autumn. The common names of the species are Cornish lily, Cape flower, Guernsey lily, and Bowden lily. However, it is neither a true lily nor from Cornwall or Guernsey, but originates from South Africa. Confusingly the name “Guernsey lily” is also applied to a related species, Nerine sarniensis.

Rivastigmine is a cholinesterase inhibitor used for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. The drug can be administered orally or via a transdermal patch; the latter form reduces the prevalence of side effects, which typically include nausea and vomiting.
Methanesulfonyl fluoride (MSF) has long been known to be a potent inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), the enzyme that regulates acetylcholine, an important neurotransmitter in both the central and peripheral nervous systems.

Phenserine is a synthetic drug which has been investigated as a medication to treat Alzheimer's disease (AD), as the drug exhibits neuroprotective and neurotrophic effects.
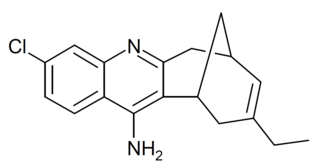
Huprine X is a synthetic cholinergic compound developed as a hybrid between the natural product Huperzine A and the synthetic drug tacrine. It is one of the most potent reversible inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase known, with a binding affinity of 0.026nM, as well as showing direct agonist activity at both nicotinic and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. In animal studies it has nootropic and neuroprotective effects, and is used in research into Alzheimer's disease, and although huprine X itself has not been researched for medical use in humans, a large family of related derivatives have been developed.

Hopeahainol A is a polyphenol acetylcholinesterase inhibitor with the molecular formula C56H42O12. Hopeahainol A has been isolated from the tree Hopea hainanensis. Hopeahainol A may be used for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.

Myrtenal is a bicyclic monoterpenoid with the chemical formula C10H14O. It is a naturally occuring molecule that can be found in numerous plant species including Hyssopus officinalis, Salvia absconditiflora, and Cyperus articulatus.