Related Research Articles

Hausa is a Chadic language that is spoken by the Hausa people in the northern parts of Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon, Benin and Togo, and the southern parts of Niger, and Chad, with significant minorities in Ivory Coast. A small number of speakers also exist in Sudan.
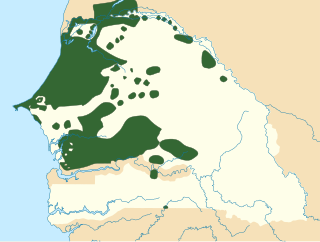
Wolof is a Niger–Congo language spoken by the Wolof people in much of West African subregion of Senegambia that is split between the countries of Senegal, Mauritania, and the Gambia. Like the neighbouring languages Serer and Fula, it belongs to the Senegambian branch of the Niger–Congo language family. Unlike most other languages of its family, Wolof is not a tonal language.
Zenaga is a Berber language on the verge of extinction currently spoken in Mauritania and northern Senegal by a few hundred people. Zenaga Berber is spoken as a mother tongue from the town of Mederdra in southwestern Mauritania to the Atlantic coast and in northern Senegal. The language is recognized by the Mauritanian government.

The Songhay, Songhai or Ayneha languages are a group of closely related languages/dialects centred on the middle stretches of the Niger River in the West African countries of Mali, Niger, Benin, Burkina Faso and Nigeria. In particular, they are spoken in the cities of Timbuktu, Djenné, Niamey and Gao. They have been widely used as a lingua franca in that region ever since the era of the Songhai Empire. In Mali, the government has officially adopted the dialect of Gao as the dialect to be used as a medium of primary education.
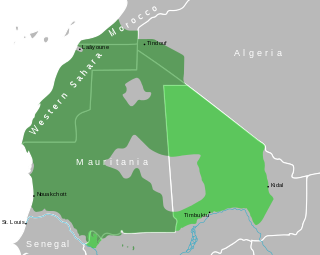
Hassaniya Arabic is a variety of Maghrebi Arabic spoken by Mauritanian Arabs and the Sahrawi people. It was spoken by the Beni Ḥassān Bedouin tribes of Yemeni origin who extended their authority over most of Mauritania and Morocco's southeastern and Western Sahara between the 15th and 17th centuries. Hassaniya Arabic was the language spoken in the pre-modern region around Chinguetti.
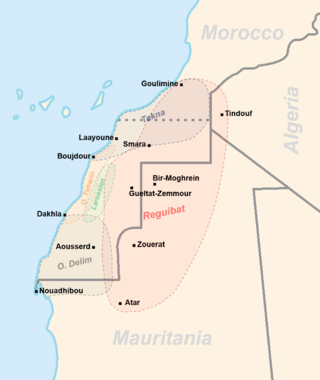
The Sahrawis, or Sahrawi people, are an ethnic group native to the western part of the Sahara desert, which includes the Western Sahara, southern Morocco, much of Mauritania, and along the southwestern border of Algeria. They are of mixed Hassani Arab and Sanhaji Berber descent, as well as West African and other indigenous populations.

Mali is a multilingual country of about 21.9 million people. The languages spoken there reflect ancient settlement patterns, migrations, and its long history. Ethnologue counts more than 80 languages. Of these, Bambara, Bobo, Bozo, Dogon, Fula, Hassaniya, Kassonke, Maninke, Minyanka, Senufo, Songhay languages, Soninke and Tamasheq are official languages. French is the working language.
Bakel is a town of approximately 15,000 inhabitants located in the eastern part of Senegal, West Africa. The town is located on the left bank of the Sénégal River, 65 kilometers (40 mi) from the Malian border and linked by canoe ferry to the village of Gouraye in Mauritania.

Fula, also known as Fulani or Fulah, is a Senegambian language spoken by around 36.8 million people as a set of various dialects in a continuum that stretches across some 18 countries in West and Central Africa. Along with other related languages such as Serer and Wolof, it belongs to the Atlantic geographic group within Niger–Congo, and more specifically to the Senegambian branch. Unlike most Niger-Congo languages, Fula does not have tones.

The Sanhaja were once one of the largest Berber tribal confederations, along with the Zanata and Masmuda confederations. Many tribes in Algeria, Burkina Faso, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Senegal, Tunisia and Western Sahara bore and still carry this ethnonym, especially in its Berber form. Other names for the population include Zenaga, Znaga, Sanhája, Sanhâdja and Senhaja.

Algerian Arabic, natively known as Dziria, Darja or Derja, is a dialectal variety of Arabic spoken in Algeria. It belongs to the Maghrebi Arabic dialect continuum and is mostly intelligible with the Tunisian and Moroccan dialects.
Bozo is a Mande language spoken by the Bozo people of the Inner Niger Delta in Mali. For Fishing, many Bozo are also found in other West African countries where there are Rivers and Dams, such as Nigeria, Burkina Faso and the Ivory Coast. According to the 2000 census, the Bozo people number about 132,100. Bozo is considered a dialect cluster, but there is a quite a bit of diversity. Ethnologue recognises four languages on the basis of requirements for literacy materials. Bozo is part of the northwestern branch of the Mande languages; the closest linguistic relative is Soninke, a major language spoken in the northwestern section of southern Mali, in eastern Senegal, and in southern Mauritania. The Bozo often speak one or more regional languages such as Bambara, Fula, or Western Songhay. The language is tonal, with three lexical tones.
Lugbara, or Lugbarati, is the language of the Lugbara people. It is spoken in the West Nile region in northwestern Uganda, as well as the Democratic Republic of the Congo's Orientale Province with a little extension to the South Sudan as the Zande or Azande people.
Mefele is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in northern Cameroon. Dialects are Mefele, Muhura, Serak, and Shugule. Blench (2006) considers Shugule (Shügule) a separate language.
Tetserret (Tin-Sert) is a Western Berber language spoken by the Ait-Awari and Kel Eghlal Tuareg tribes of the Akoubounou (Akabinu) commune in Niger. This main speech area is located between Abalak, Akoubounou and Shadwanka. The variant spoken by the Kel Eghlal is called taməsəɣlalt. The Tamasheq equivalent šin-sart / šin-sar / tin-sar is used in some older literature. Popular understanding among some Ait-Awari derives the name tet-serret, and its Tamasheq equivalent šin-sart, from expressions meaning 'the (language) of Sirte'.

Mauritania, officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a sovereign country in Northwest Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to the north and northwest, Algeria to the northeast, Mali to the east and southeast, and Senegal to the southwest. By land area Mauritania is the 11th-largest country in Africa and 28th-largest in the world; 90% of its territory is in the Sahara. Most of its population of some 4.3 million lives in the temperate south of the country, with roughly a third concentrated in the capital and largest city, Nouakchott, on the Atlantic coast.

The languages of Mauritania include the official language, Arabic, three national languages, Pular, Soninke and Wolof, and French, a former official language which is still the language of working language, education and administration.
The Karamojong language is a Nilotic language spoken by the Karamojong people in Northeast Uganda.
Rangi or Langi is a Bantu language spoken by the Rangi people of Kondoa District in the Dodoma Region of Central Tanzania. Whilst the language is known as Rangi in English and Kirangi in the dominant Swahili spoken throughout the African Great Lakes, the self-referent term is Kilaangi.
The Koma language is a language cluster belonging to the Duru branch of Savannas languages of Cameroon. Blench (2004) includes three varieties separated in Ethnologue, Koma Ndera, Gɨmne, and Gɨmnɨme; within Koma Ndera, speakers of the marginal dialects, Gomnome and Ndera, can scarcely understand one another, though both understand the central dialect, Gomme.
References
- 1 2 Hassaniyya at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Christopher Moseley, Encyclopedia of the World's Endangered Languages, Routledge, 2007, ISBN 978-0-7007-1197-0 p. 623: No data exists on this language. It is not unlikely that the language can be linked to Azer, Zenaga, Soninke and/or Hassaniya
- ↑ Muriel Devey, La Mauritanie, KARTHALA Editions, 2005 ISBN 978-2-84586-583-9, p.39: "leur langue est un mélange d'hassaniya, de zenaga et d'azer"
- ↑ Nemadi entry in the Languages of Mali Archived 2007-09-29 at the Wayback Machine , 13th edition (1996)