Nevada is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, the 32nd-most populous, and the 9th-least densely populated of the U.S. states. Nearly three-quarters of Nevada's people live in Clark County, which contains the Las Vegas–Paradise metropolitan area, including three of the state's four largest incorporated cities. Nevada's capital is Carson City. Las Vegas is the largest city in the state.

The Four Corners Monument marks the quadripoint in the Southwestern United States where the states of Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah meet. It is the only point in the United States shared by four states, leading to the area being named the Four Corners region. The monument also marks the boundary between two semi-autonomous Native American governments, the Navajo Nation, which maintains the monument as a tourist attraction, and the Ute Mountain Ute Tribe Reservation.

The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that includes Arizona and New Mexico, along with adjacent portions of California, Colorado, Nevada, Oklahoma, Texas, and Utah. The largest cities by metropolitan area are Phoenix, Las Vegas, El Paso, Albuquerque, and Tucson. Before 1848, in the historical region of Santa Fe de Nuevo México as well as parts of Alta California and Coahuila y Tejas, settlement was almost non-existent outside of Nuevo México's Pueblos and Spanish or Mexican municipalities. Much of the area had been a part of New Spain and Mexico until the United States acquired the area through the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 and the smaller Gadsden Purchase in 1854.

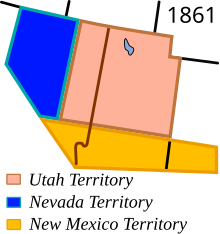
The Territory of New Mexico was an organized incorporated territory of the United States from September 9, 1850, until January 6, 1912. It was created from the U.S. provisional government of New Mexico, as a result of Nuevo México becoming part of the American frontier after the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. It existed with varying boundaries until the territory was admitted to the Union as the U.S. state of New Mexico. This jurisdiction was an organized, incorporated territory of the US for nearly 62 years, the longest period of any territory in the contiguous United States.

The Mexican Cession is the region in the modern-day southwestern United States that Mexico originally controlled, then ceded to the United States in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 after the Mexican–American War. This region had not been part of the areas east of the Rio Grande that had been claimed by the Republic of Texas, though the Texas annexation resolution two years earlier had not specified the southern and western boundary of the new state of Texas. At roughly 529,000 square miles (1,370,000 km2), the Mexican Cession was the third-largest acquisition of territory in U.S. history, surpassed only by the 827,000-square-mile (2,140,000 km2) Louisiana Purchase and the 586,000-square-mile (1,520,000 km2) Alaska Purchase.

The State of Deseret was a proposed state of the United States, proposed in 1849 by settlers from the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in Salt Lake City. The provisional state existed for slightly over two years, but was never recognized by the United States government. The name derives from the word for "honeybee" in the Book of Mormon.

The Territory of Utah was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from September 9, 1850, until January 4, 1896, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Utah, the 45th state. At its creation, the Territory of Utah included all of the present-day State of Utah, most of the present-day state of Nevada save for Southern Nevada, much of present-day western Colorado, and the extreme southwest corner of present-day Wyoming.

The Territory of Arizona was a territory of the United States that existed from February 24, 1863, until February 14, 1912, when the remaining extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the state of Arizona. It was created from the western half of the New Mexico Territory during the American Civil War.

The territory of the United States and its overseas possessions has evolved over time, from the colonial era to the present day. It includes formally organized territories, proposed and failed states, unrecognized breakaway states, international and interstate purchases, cessions, and land grants, and historical military departments and administrative districts. The last section lists informal regions from American vernacular geography known by popular nicknames and linked by geographical, cultural, or economic similarities, some of which are still in use today.

The Provisional Government of the Territory of Jefferson was an extralegal and unrecognized United States territory that existed in the Pike's Peak mining region from October 24, 1859, until it yielded to the new Territory of Colorado on June 6, 1861. The Jefferson Territory, named for Founding Father and third United States president Thomas Jefferson, included land officially part of the Kansas Territory, the Nebraska Territory, the New Mexico Territory, the Utah Territory, and the Washington Territory, but the region was remote from the governments of those five territories.
Roop County, known until 1862 as Lake County, was a county of Nevada Territory in the United States from 1861 until 1864. It was created in 1861 as one of the original nine counties of Nevada. In 1864 it was succeeded by Lassen County, California and Washoe County, Nevada.
The 37th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 37 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, the Mediterranean Sea, Africa, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.

The Nataqua Territory was a short-lived, unofficial territory of the United States. It consisted of a portion of what is now northeastern California and northwestern Nevada. Nataqua Territory was the first incarnation of the proposed "State of Jefferson". In 1849, the border between California and the Utah Territory was defined by geographical coordinates that were not surveyed. On April 26, 1856, local residents took advantage of this ambiguity and justified their resistance to tax collectors from Plumas County, California, by proclaiming themselves part of a new "Territory of Nataqua." The twenty men of the Susanville convention who announced the Nataqua Territory had defined a rectangle-shaped territory by latitude and longitude, which inadvertently did not include their own Honey Lake Valley but did encompass most of what soon became western Nevada, along with 600 unsuspecting inhabitants. The Territory of Nataqua was a frontier land club or claim association, designed to protect the property rights of individual settlers until regular government reached the area. The movement was led by Peter Lassen and Isaac Roop. Association with the Utah Territory was unpalatable to the residents due to anti-Mormonism.

The parallel 36°30′ north is a circle of latitude that is 36 and one-half degrees north of the equator of the Earth. This parallel of latitude is particularly significant in the history of the United States as the line of the Missouri Compromise, which was used to divide the prospective slave and free states west of the Mississippi River, with the exception of Missouri, which is mostly north of this parallel.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the U.S. state of Nevada:

The 1872 California-Nevada State Boundary Marker marks the initial point for the 1872 survey delineation of the state line between California and Nevada. It is listed in the National Register of Historic Places.
This timeline is a chronology of significant events in the history of the U.S. State of Colorado and the historical area now occupied by the state.

The Von Schmidt State Boundary Monument was designated a California Historic Landmark (No.859) on April 26, 1973. In 1873 San Francisco civil engineer Allexey W. Von Schmidt built the State Boundary Monument in San Bernardino County, California, near Needles, California. In 1872 and 1873 Von Schmidt did a survey of the border between California and Nevada/Arizona. The California Historic marker is on the dirt road, Pew Road, also called River Road, 2.6 Miles South of the State Line; 14 Miles North of Needles. The marker is not at the current state boundary, as Von Schmidt made an error in his survey. A new survey in 1893 showed that the Von Schmidt line was 1,600 to 1,800 feet off to the west. The marker is at the southern end of the California-Arizona State boundary. In 1872, a dispute arose between Nevada and California about the location of the state's boundary. Nevada wanted the state divide to be the same as the Sierra Nevada mountain range divide. California wanted the line to the east of the mountain range. When California attained statehood in 1850, it adopted 120 degrees west longitude as its eastern border. Between 1855 and 1900 there were six surveys to locate 120 degrees, with each locating 120 degrees of longitude differently. Von Schmidt applied for and was granted the contract to survey the state's frontier border east of the Sierra Nevada. In 1872 Von Schmidt using only a compass, a sextant and dead reckoning process set out with his crew to define the boundary. Von Schmidt was charged to measure and mark the boundary. Von Schmidt and his crew built stone markers and installed cast iron markers about one mile apart on the length of the state's boundary. Not many of the markers had foundations, so fewer remain today. A new survey in 1893 showed that the Von Schmidt line was 1,600 to 1,800 feet west of the actual 120 degrees. However, California and Nevada both recognize the 1872 Von Schmidt survey and the 1893 survey as the state line. Later the 1893 line was used. The exact location of the north-south California-Nevada border, between Lake Tahoe and the intersection of the southern boundary of Oregon at the 42nd parallel, was contentious and was surveyed and re-surveyed many time. One of the few iron markers that has survived is a near Verdi, Nevada, this is a National Historic Landmark called the 1872 California-Nevada State Boundary Marker.
Rio Virgen County is a former county in the U.S. state of Utah. It was established by the Territory of Utah on February 1869.