
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.
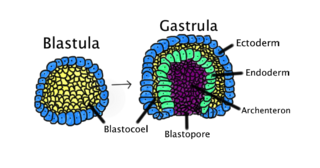
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula, or in mammals the blastocyst, is reorganized into a two-layered or three-layered embryo known as the gastrula. Before gastrulation, the embryo is a continuous epithelial sheet of cells; by the end of gastrulation, the embryo has begun differentiation to establish distinct cell lineages, set up the basic axes of the body, and internalized one or more cell types including the prospective gut.

Somitogenesis is the process by which somites form. Somites are bilaterally paired blocks of paraxial mesoderm that form along the anterior-posterior axis of the developing embryo in segmented animals. In vertebrates, somites give rise to skeletal muscle, cartilage, tendons, endothelium, and dermis.
The Wnt signaling pathways are a group of signal transduction pathways which begin with proteins that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptors. The name Wnt is a portmanteau created from the names Wingless and Int-1. Wnt signaling pathways use either nearby cell-cell communication (paracrine) or same-cell communication (autocrine). They are highly evolutionarily conserved in animals, which means they are similar across animal species from fruit flies to humans.
The primitive node is the organizer for gastrulation in most amniote embryos. In birds it is known as Hensen's node, and in amphibians it is known as the Spemann-Mangold organizer. It is induced by the Nieuwkoop center in amphibians, or by the posterior marginal zone in amniotes including birds.

Intermediate mesoderm or intermediate mesenchyme is a narrow section of the mesoderm located between the paraxial mesoderm and the lateral plate of the developing embryo. The intermediate mesoderm develops into vital parts of the urogenital system.

In amniote embryonic development, the epiblast is one of two distinct cell layers arising from the inner cell mass in the mammalian blastocyst, or from the blastula in reptiles and birds, the other layer is the hypoblast. It drives the embryo proper through its differentiation into the three primary germ layers, ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, during gastrulation. The amniotic ectoderm and extraembryonic mesoderm also originate from the epiblast.
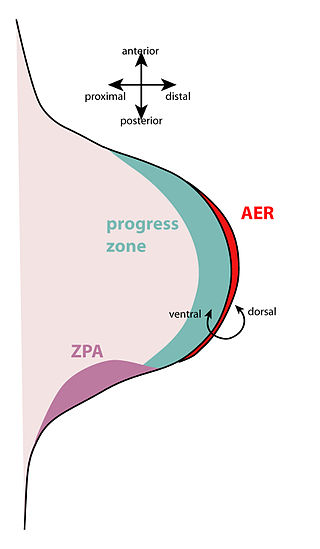
The apical ectodermal ridge (AER) is a structure that forms from the ectodermal cells at the distal end of each limb bud and acts as a major signaling center to ensure proper development of a limb. After the limb bud induces AER formation, the AER and limb mesenchyme—including the zone of polarizing activity (ZPA)—continue to communicate with each other to direct further limb development.
In developmental biology, the cells that give rise to the gametes are often set aside during embryonic cleavage. During development, these cells will differentiate into primordial germ cells, migrate to the location of the gonad, and form the germline of the animal.
The limb bud is a structure formed early in vertebrate limb development. As a result of interactions between the ectoderm and underlying mesoderm, formation occurs roughly around the fourth week of development. In the development of the human embryo the upper limb bud appears in the third week and the lower limb bud appears four days later.
In the field of developmental biology, regional differentiation is the process by which different areas are identified in the development of the early embryo. The process by which the cells become specified differs between organisms.
Cripto is an EGF-CFC or epidermal growth factor-CFC, which is encoded by the Cryptic family 1 gene. Cryptic family protein 1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFC1B gene. Cryptic family protein 1B acts as a receptor for the TGF beta signaling pathway. It has been associated with the translation of an extracellular protein for this pathway. The extracellular protein which Cripto encodes plays a crucial role in the development of left and right division of symmetry.
Growth differentiation factors (GDFs) are a subfamily of proteins belonging to the transforming growth factor beta superfamily that have functions predominantly in development.

Growth differentiation factor-3 (GDF3), also known as Vg-related gene 2 (Vgr-2) is protein that in humans is encoded by the GDF3 gene. GDF3 belongs to the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) superfamily. It has high similarity to other TGF-β superfamily members including Vg1 and GDF1.

The development of fishes is unique in some specific aspects compared to the development of other animals.

Cerberus is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CER1 gene. Cerberus is a signaling molecule which contributes to the formation of the head, heart and left-right asymmetry of internal organs. This gene varies slightly from species to species but its overall functions seem to be similar.

In amniote embryology, the hypoblast is one of two distinct layers arising from the inner cell mass in the mammalian blastocyst, or from the blastodisc in reptiles and birds. The hypoblast gives rise to the yolk sac, which in turn gives rise to the chorion.

Nodal homolog is a secretory protein that in humans is encoded by the NODAL gene which is located on chromosome 10q22.1. It belongs to the transforming growth factor beta superfamily. Like many other members of this superfamily it is involved in cell differentiation in early embryogenesis, playing a key role in signal transfer from the primitive node, in the anterior primitive streak, to lateral plate mesoderm (LPM).

In avian gastrulation, Koller's sickle is a local thickening of cells at the posterior edge of the upper layer of the area pellucida called the epiblast. Koller's sickle is crucial for avian development, due to its critical role in inducing the differentiation of various avian body parts. Koller's sickle induces primitive streak and Hensen's node, which are major components of avian gastrulation. Avian gastrulation is a process by which developing cells in an avian embryo move relative to one another in order to form the three germ layers.
The Nodal signaling pathway is a signal transduction pathway important in regional and cellular differentiation during embryonic development.

















