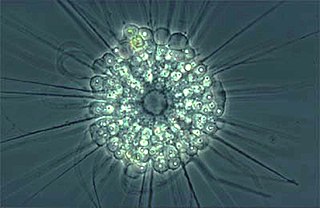
The actinophryids are an order of heliozoa, a polyphyletic array of stramenopiles, having a close relationship with pedinellids and Ciliophrys. They are common in fresh water and occasionally found in marine and soil habitats. Actinophryids are unicellular and roughly spherical in shape, with many axopodia that radiate outward from the cell body. Axopodia are a type of pseudopodia that are supported by hundreds of microtubules arranged in interlocking spirals and forming a needle-like internal structure or axoneme. Small granules, extrusomes, that lie under the membrane of the body and axopodia capture flagellates, ciliates and small metazoa that make contact with the arms.
In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla.

Euglena is a genus of single cell flagellate eukaryotes. It is the best known and most widely studied member of the class Euglenoidea, a diverse group containing some 54 genera and at least 200 species. Species of Euglena are found in fresh water and salt water. They are often abundant in quiet inland waters where they may bloom in numbers sufficient to color the surface of ponds and ditches green (E. viridis) or red (E. sanguinea).
Protozoology is the study of protozoa, the "animal-like" protists. The Protozoa are considered to be a subkingdom of Protista. They are free-living organisms that are found in almost every habitat. All humans have protozoan found living on their body, and many people may be infected with one or more throughout their life.

Yellow-green algae or the Xanthophyceae (xanthophytes) are an important group of heterokont algae. Most live in fresh water, but some are found in marine and soil habitats. They vary from single-celled flagellates to simple colonial and filamentous forms. Xanthophyte chloroplasts contain the photosynthetic pigments chlorophyll a, chlorophyll c, β-carotene, and the carotenoid diadinoxanthin. Unlike other Stramenopiles (heterokonts), their chloroplasts do not contain fucoxanthin, which accounts for their lighter colour. Their storage polysaccharide is chrysolaminarin. Xanthophyte cell walls are produced of cellulose and hemicellulose. They appear to be the closest relatives of the brown algae.
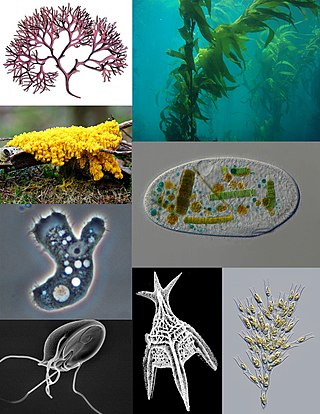
A protist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. Protists, along with other eukaryotes, all descend from the last eukaryotic common ancestor. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade; any unicellular eukaryote may be described as a protist, in addition to some cases of multicellular protists such as slime molds, brown algae and xenophyophorean forams. Protists represent an extremely large, undiscovered diversity in the process of being defined. The study of protists is termed protistology.

Protozoa are a polyphyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals", because they often possess animal-like behaviours, such as motility and predation, and lack a cell wall, as found in plants and many algae.

Holozoa is a group of organisms that includes animals and their closest single-celled (protist) relatives, but excludes fungi and all other organisms. It is a monophyletic group or clade, a lineage consisting of all descendants of a common ancestor. Among these descendants, the protists are of high interest because of their close relationship to animals: in the search for the genes responsible for animal multicellularity within these protists, they help elucidate the nature of the unicellular ancestor of animals.
Seymour Herbert Hutner (1911–2003) was a microbiologist specializing in the nutritional biochemistry of protists. Born in Brooklyn, New York in 1911, he obtained a bachelor's degree from the City College of New York (CCNY) in 1931 and a Ph.D. at Cornell University in 1937, where he worked with the Nobel laureate James B. Sumner.

Frontonia is a genus of free-living unicellular ciliate protists, belonging to the order Peniculida. As Peniculids, the Frontonia are closely related to members of the genus Paramecium. However, whereas Paramecia are mainly bacterivores, Frontonia are capable of ingesting large prey such as diatoms, filamentous algae, testate amoebas, and even, in some circumstances, members of their own species. In bacteria-rich saprobic conditions, Frontonia leucas can live as a facultative bacterivore.

Peranema is a genus of free-living phagotrophic euglenids. There are more than 20 nominal species, varying in size between 8 and 200 micrometers. Peranema cells are gliding flagellates found in freshwater lakes, ponds and ditches, and are often abundant at the bottom of stagnant pools rich in decaying organic material. Although they belong to the class Euglenoidea, and are morphologically similar to the green Euglena, Peranema have no chloroplasts, and do not conduct autotrophy. Instead, they capture live prey, such as yeast, bacteria and other flagellates, consuming them with the help of a rigid feeding apparatus called a "rod-organ." Unlike the green euglenids, they lack both an eyespot (stigma), and the paraflagellar body (photoreceptor) that is normally coupled with that organelle. However, while Peranema lack a localized photoreceptor, they do possess the light-sensitive protein rhodopsin, and respond to changes in light with a characteristic "curling behaviour."
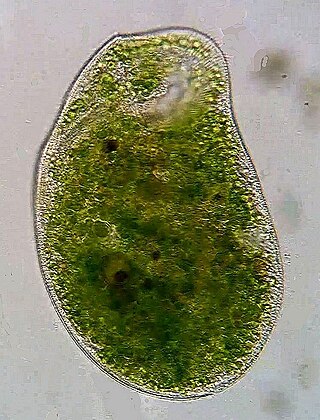
Climacostomum virens is a species of unicellular ciliate protists. It is one of just two formally described species in the genus Climacostomum.
A mucron is an attachment organelle found in archigregarines - an order of epicellular parasitic Conoidasida.

An amoeba, often called an amoeboid, is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopods. Amoebae do not form a single taxonomic group; instead, they are found in every major lineage of eukaryotic organisms. Amoeboid cells occur not only among the protozoa, but also in fungi, algae, and animals.
Bronisław M. Honigberg was a Polish-born American zoologist. Born in Warsaw, he settled in the United States as a refugee during World War II. He was Professor of parasitology at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. His research centered on unicellular organisms such as Trichomonadida and Kinetoplastida, the name which he invented. He was a leading authority on the naming system (systematics) of protozoans. He led the Committee on Taxonomy and Taxonomical Problems of the Society of Protozoologists and made a new Systematics of Protozoa in 1964.
The initial version of a classification system of life by British zoologist Thomas Cavalier-Smith appeared in 1978. This initial system continued to be modified in subsequent versions that were published until he died in 2021. As with classifications of others, such as Carl Linnaeus, Ernst Haeckel, Robert Whittaker, and Carl Woese, Cavalier-Smith's classification attempts to incorporate the latest developments in taxonomy., Cavalier-Smith used his classifications to convey his opinions about the evolutionary relationships among various organisms, principally microbial. His classifications complemented his ideas communicated in scientific publications, talks, and diagrams. Different iterations might have a wider or narrow scope, include different groupings, provide greater or lesser detail, and place groups in different arrangements as his thinking changed. His classifications has been a major influence in the modern taxonomy, particularly of protists.

Condylostoma is a genus of unicellular ciliate protists, belonging to the class Heterotrichea.
Dorothy Riggs Pitelka was an American zoologist, protistologist, cancer researcher, and pioneer in applications of electron microscopy to zoology and protistology, known for her 1963 book Electron-Microscopic Structure of Protozoa.
Renate Radek is a protistologist and an associate professor at the Freie Universität Berlin.

Marine protists are defined by their habitat as protists that live in marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. Life originated as marine single-celled prokaryotes and later evolved into more complex eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are the more developed life forms known as plants, animals, fungi and protists. Protists are the eukaryotes that cannot be classified as plants, fungi or animals. They are mostly single-celled and microscopic. The term protist came into use historically as a term of convenience for eukaryotes that cannot be strictly classified as plants, animals or fungi. They are not a part of modern cladistics because they are paraphyletic.











