
The 2000 United States presidential election was the 54th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 7, 2000. Republican Texas Governor George W. Bush, the eldest son of George H. W. Bush, narrowly defeated incumbent Democratic Vice President Al Gore. It was the fourth of five U.S. presidential elections, and the first since 1888, in which the winning candidate lost the popular vote, and is considered one of the closest U.S. presidential elections, with long-standing controversy about the result. Gore conceded the election on December 13.

The 2000 presidential campaign of George W. Bush, then governor of Texas, was formally launched on June 14, 1999 as Governor Bush, the eldest son of former President George H. W. Bush, announced his intention to seek the Republican Party nomination for the presidency of the United States in the 2000 presidential election.

The New Hampshire presidential primary is the first in a series of nationwide party primary elections and the second party contest, the first being the Iowa caucuses, held in the United States every four years as part of the process of choosing the delegates to the Democratic and Republican national conventions which choose the party nominees for the presidential elections to be held in November. Although only a few delegates are chosen in the New Hampshire primary, its real importance comes from the massive media coverage it receives, along with the first caucus in Iowa.

From January 29 to June 4, 1996, voters of the Republican Party chose its nominee for president in the 1996 United States presidential election. Senator Bob Dole of Kansas, the former Senate majority leader, was selected as the nominee through a series of primary elections and caucuses culminating in the 1996 Republican National Convention held from August 12 to 15, 1996, in San Diego, California. Dole resigned from the Senate in June 1996 once he became the presumptive nominee to concentrate on his presidential campaign. He chose Jack Kemp as his running mate.

The South Carolina presidential primary is an open primary election which has become one of several key early-state presidential primaries in the process of the Democratic and Republican Parties choosing their respective general election nominees for President of the United States. South Carolina has cemented its place as the "First in the South" primary for both parties.
The 2000 presidential campaign of John McCain, the United States Senator from Arizona, began in September 1999. He announced his run for the Republican Party nomination for the presidency of the United States in the 2000 presidential election.

Electoral history of Bob Dole, United States Senator from Kansas (1969–1996), Senate Majority Leader, Senate Minority Leader (1987–1995), 1976 Republican Party vice presidential nominee and 1996 presidential nominee.

This is the electoral history of Alan Keyes, a frequent candidate. He has never been elected to office.

The 2000 Iowa Republican presidential caucuses took place on January 24, 2000. The Iowa Republican caucuses are an unofficial primary, with the delegates to the state convention selected proportionally via a straw poll. The Iowa caucuses marked the traditional formal start of the delegate selection process for the 2000 United States presidential election.

The Mackinac Republican Leadership Conference, also known as the Midwest Mackinac Republican Leadership Conference, is a biennial United States Republican Party political conference held on Mackinac Island, Michigan.

The 2012 United States Senate election in Utah took place on November 6, 2012, concurrently with the 2012 U.S. presidential election as well as other elections to the United States Senate and House of Representatives and as various state and local elections. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator Orrin Hatch won re-election to a seventh term against the Democratic candidate, former state Senator and IBM executive Scott Howell, in a rematch of the 2000 Senate election. This would be the last time Hatch was elected to the Senate before his retirement in 2018.
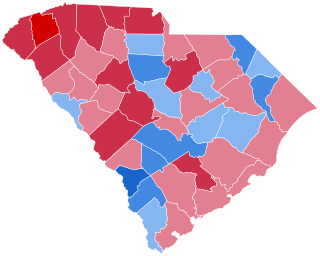
The 2000 United States presidential election in South Carolina took place on November 7, 2000, and was part of the 2000 United States presidential election. Voters chose 8 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
This article contains the list of candidates associated with the 2016 Republican Party presidential primaries for the 2016 United States presidential election.

The 2018 United States Senate election in Utah took place on November 6, 2018, to elect a member of the United States Senate to represent the State of Utah, concurrently with other elections to the United States Senate, elections to the United States House of Representatives, and various state and local elections. The primaries took place on June 26.
Since 1980, the Republican Party of the United States has held debates between candidates for the Republican nomination in presidential elections during the primary election season. Unlike debates between party-nominated candidates, which have been organized by the bi-partisan Commission on Presidential Debates since 1988, debates between candidates for party nomination are organized by mass media outlets.

The 2000 presidential campaign of Alan Keyes, former Assistant Secretary of State for International Organization Affairs from Maryland began when he formed an exploratory committee, simply called Keyes 2000, on June 17, 1999, with a formal announcement on September 21, 1999 in Bedford, New Hampshire. He ran in the 2000 presidential primaries, opposing Texas governor George W. Bush and Arizona Senator John McCain for his party's nomination. Keyes campaigned as a more ideologically consistent candidate than John McCain, taking right-wing positions on issues, including abortion, gun control, and government spending.

The 2000 presidential campaign of Orrin Hatch, a U.S. senator from Utah, officially began on July 1, 1999, with the establishment of an exploratory committee. Hatch had been a senator since 1977 and at the time of his announcement he was a high-ranking official on several Senate committees, most notably the chairman for the Senate Judiciary Committee. He had established himself as a conservative Republican who was known to work with liberal Democrats on major bipartisan bills, such as the 1997 Children's Health Insurance Program bill. From the beginning of his campaign, Hatch stressed his experience in federal government and attacked the perceived lack of experience of the Republican frontrunner, Texas governor George W. Bush. However, numerous commentators noted that Hatch's campaign was unlikely to succeed, due to his late entry into the race and Bush's dominant position in fundraising and opinion polling. Throughout his campaign, Hatch struggled to raise money and consistently polled in the single digits. In January 2000, he came in last place in the Iowa caucuses and announced on January 26 that he was ending his campaign, supporting eventual nominee Bush, who would go on to win the 2000 United States presidential election. Hatch remained in the Senate for several more years following his campaign and in 2015, as the most senior member of the Senate, he became the president pro tempore. In 2019, he decided to retire, ending his 42-year career as the most senior Republican senator ever before dying in 2022.

The 2000 Texas Republican presidential primary was held on March 14, 2000, as part of the 2000 presidential primaries for the 2000 presidential election. 124 delegates to the 2000 Republican National Convention were allocated to the presidential candidates, the contest was held alongside primaries in Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi, Oklahoma and Tennessee.































