Microsoft Access is a database management system (DBMS) from Microsoft that combines the relational Access Database Engine (ACE) with a graphical user interface and software-development tools. It is a member of the Microsoft 365 suite of applications, included in the Professional and higher editions or sold separately.
In computing, Microsoft's ActiveX Data Objects (ADO) comprises a set of Component Object Model (COM) objects for accessing data sources. A part of MDAC, it provides a middleware layer between programming languages and OLE DB. ADO allows a developer to write programs that access data without knowing how the database is implemented; developers must be aware of the database for connection only. No knowledge of SQL is required to access a database when using ADO, although one can use ADO to execute SQL commands directly.
In computing, Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a standard application programming interface (API) for accessing database management systems (DBMS). The designers of ODBC aimed to make it independent of database systems and operating systems. An application written using ODBC can be ported to other platforms, both on the client and server side, with few changes to the data access code.
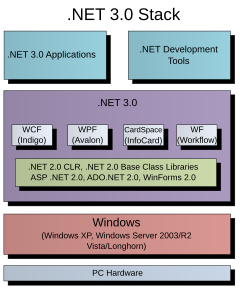
WinFS was the code name for a canceled data storage and management system project based on relational databases, developed by Microsoft and first demonstrated in 2003. It was intended as an advanced storage subsystem for the Microsoft Windows operating system, designed for persistence and management of structured, semi-structured and unstructured data.
Hibernate ORM is an object–relational mapping tool for the Java programming language. It provides a framework for mapping an object-oriented domain model to a relational database. Hibernate handles object–relational impedance mismatch problems by replacing direct, persistent database accesses with high-level object handling functions.
OLE DB, an API designed by Microsoft, allows accessing data from a variety of sources in a uniform manner. The API provides a set of interfaces implemented using the Component Object Model (COM); it is otherwise unrelated to OLE. Microsoft originally intended OLE DB as a higher-level replacement for, and successor to, ODBC, extending its feature set to support a wider variety of non-relational databases, such as object databases and spreadsheets that do not necessarily implement.
A GIS software program is a computer program to support the use of a geographic information system, providing the ability to create, store, manage, query, analyze, and visualize geographic data, that is, data representing phenomena for which location is important. The GIS software industry encompasses a broad range of commercial and open-source products that provide some or all of these capabilities within various information technology architectures.
The Access Database Engine is a database engine on which several Microsoft products have been built. The first version of Jet was developed in 1992, consisting of three modules which could be used to manipulate a database.

Microsoft Data Access Components is a framework of interrelated Microsoft technologies that allows programmers a uniform and comprehensive way of developing applications that can access almost any data store. Its components include: ActiveX Data Objects (ADO), OLE DB, and Open Database Connectivity (ODBC). There have been several deprecated components as well, such as the Jet Database Engine, MSDASQL, and Remote Data Services (RDS). Some components have also become obsolete, such as the former Data Access Objects API and Remote Data Objects.
Microsoft SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) is an online analytical processing (OLAP) and data mining tool in Microsoft SQL Server. SSAS is used as a tool by organizations to analyze and make sense of information possibly spread out across multiple databases, or in disparate tables or files. Microsoft has included a number of services in SQL Server related to business intelligence and data warehousing. These services include Integration Services, Reporting Services and Analysis Services. Analysis Services includes a group of OLAP and data mining capabilities and comes in two flavors multidimensional and tabular, where the difference between the two is how the data is presented. In a tabular model, the information is arranged in two-dimensional tables which can thus be more readable for a human. A multidimensional model can contain information with many degrees of freedom, and must be unfolded to increase readability by a human.

NHibernate is an object–relational mapping (ORM) solution for the Microsoft .NET platform. It provides a framework for mapping an object-oriented domain model to a traditional relational database. Its purpose is to relieve the developer from a significant portion of relational data persistence-related programming tasks. NHibernate is free and open-source software that is distributed under the GNU Lesser General Public License. NHibernate is a port of Hibernate.
In ADO.NET, a DataReader is a broad category of objects used to sequentially read data from a data source. DataReaders provide a very efficient way to access data, and can be thought of as a Firehose cursor from ASP Classic, except that no server-side cursor is used. A DataReader parses a Tabular Data Stream from Microsoft SQL Server, and other methods of retrieving data from other sources.
Entity Framework (EF) is an open source object–relational mapping (ORM) framework for ADO.NET. It was originally shipped as an integral part of .NET Framework, however starting with Entity Framework version 6.0 it has been delivered separately from the .NET Framework.
Microsoft SQL Server Compact is a discontinued relational database produced by Microsoft for applications that run on mobile devices and desktops. Prior to the introduction of the desktop platform, it was known as SQL Server for Windows CE and SQL Server Mobile Edition.
Language Integrated Query is a Microsoft .NET Framework component that adds native data querying capabilities to .NET languages, originally released as a major part of .NET Framework 3.5 in 2007.
Microsoft SQL Server is a proprietary relational database management system developed by Microsoft. As a database server, it is a software product with the primary function of storing and retrieving data as requested by other software applications—which may run either on the same computer or on another computer across a network. Microsoft markets at least a dozen different editions of Microsoft SQL Server, aimed at different audiences and for workloads ranging from small single-machine applications to large Internet-facing applications with many concurrent users.
An embedded database system is a database management system (DBMS) which is tightly integrated with an application software; it is embedded in the application. It is a broad technology category that includes:
Quick Objects is an object–relational mapping tool for the Microsoft .NET Framework, a built in framework for business logic and validation. The architecture for Quick Objects differs from other ORM tools. The focus of Quick Objects is to provide the advantages of code reuse, code generation and object relational mapping in a single tool set.

db4o was an embeddable open-source object database for Java and .NET developers. It was developed, commercially licensed and supported by Actian. In October 2014, Actian declined to continue to actively pursue and promote the commercial db4o product offering for new customers.
nHydrate is an object-relational mapping (ORM) solution for the Microsoft .NET platform providing a framework for a relational database to be mapped to .NET objects. It is designed to alleviate the drudgery software developers experience writing persistence domains.