
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin calx "lime", which was obtained from heating limestone.

Phosphine (IUPAC name: phosphane) is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic compound with the chemical formula PH3, classed as a pnictogen hydride. Pure phosphine is odorless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphane (P2H4). With traces of P2H4 present, PH3 is spontaneously flammable in air (pyrophoric), burning with a luminous flame. Phosphine is a highly toxic respiratory poison, and is immediately dangerous to life or health at 50 ppm. Phosphine has a trigonal pyramidal structure.
Calcium fluoride is the inorganic compound of the elements calcium and fluorine with the formula CaF2. It is a white solid that is practically insoluble in water. It occurs as the mineral fluorite (also called fluorspar), which is often deeply coloured owing to impurities.

Calcium peroxide or calcium dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula CaO2. It is the peroxide (O22−) salt of Ca2+. Commercial samples can be yellowish, but the pure compound is white. It is almost insoluble in water.

In chemistry, hypochlorite, or chloroxide is an anion with the chemical formula ClO−. It combines with a number of cations to form hypochlorite salts. Common examples include sodium hypochlorite and calcium hypochlorite. The Cl-O distance in ClO− is 1.69 Å.

In chemistry, a phosphide is a compound containing the P3− ion or its equivalent. Many different phosphides are known, with widely differing structures. Most commonly encountered on the binary phosphides, i.e. those materials consisting only of phosphorus and a less electronegative element. Numerous are polyphosphides, which are solids consisting of anionic chains or clusters of phosphorus. Phosphides are known with the majority of less electronegative elements with the exception of Hg, Pb, Sb, Bi, Te, and Po. Finally, some phosphides are molecular.
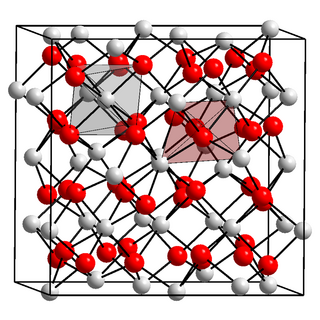
Calcium nitride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca3N2. It exists in various forms (isomorphs), α-calcium nitride being more commonly encountered.

Calcium phosphide (CP) is the inorganic compound with the formula Ca3P2. It is one of several phosphides of calcium, being described as the salt-like material composed of Ca2+ and P3−. Other, more exotic calcium phosphides have the formula CaP / Ca2P2, CaP3, and Ca5P8.
Calcium hypochlorite is an inorganic compound with chemical formula Ca(ClO)2, also written as Ca(OCl)2. It is a white solid, although commercial samples appear yellow. It strongly smells of chlorine, owing to its slow decomposition in moist air. This compound is relatively stable as a solid and solution and has greater available chlorine than sodium hypochlorite. "Pure" samples have 99.2% active chlorine. Given common industrial purity, an active chlorine content of 65-70% is typical. It is the main active ingredient of commercial products called bleaching powder, used for water treatment and as a bleaching agent.

Calcium bromide is the name for compounds with the chemical formula CaBr2(H2O)x. Individual compounds include the anhydrous material (x = 0), the hexahydrate (x = 6), and the rare dihydrate (x = 2). All are white powders that dissolve in water, and from these solutions crystallizes the hexahydrate. The hydrated form is mainly used in some drilling fluids.

Calcium disilicide (CaSi2) is an inorganic compound, a silicide of calcium. It is a whitish or dark grey to black solid matter with melting point 1033 °C. It is insoluble in water, but may decompose when subjected to moisture, evolving hydrogen and producing calcium hydroxide. It decomposes in hot water, and is flammable and may ignite spontaneously in air.

Group 2 organometallic chemistry refers to the chemistry of compounds containing carbon bonded to any group 2 element. By far the most common group 2 organometallic compounds are the magnesium-containing Grignard reagents which are widely used in organic chemistry. Other organometallic group 2 compounds are rare and are typically limited to academic interests.

Diphosphane, or diphosphine, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula P2H4. This colourless liquid is one of several binary phosphorus hydrides. It is the impurity that typically causes samples of phosphine to ignite in air.

Calcium sulfite, or calcium sulphite, is a chemical compound, the calcium salt of sulfite with the formula CaSO3·x(H2O). Two crystalline forms are known, the hemihydrate and the tetrahydrate, respectively CaSO3·½(H2O) and CaSO3·4(H2O). All forms are white solids. It is most notable as the product of flue-gas desulfurization.
Triphosphane or triphosphine is an inorganic compound having the chemical formula HP(PH2)2. It can be generated from diphosphine but is highly unstable at room temperature:

Calcium copper titanate (also abbreviated CCTO, for calcium copper titanium oxide) is an inorganic compound with the formula CaCu3Ti4O12. It is noteworthy for its extremely large dielectric constant (effective relative permittivity) of over 10,000 at room temperature.
Uranium monophosphide is a compound of uranium and phosphorus, synthesized from heating metal uranium and white phosphorus:
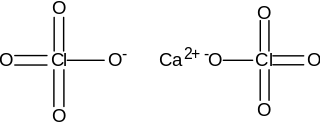
Calcium perchlorate is classified as a metal perchlorate salt with the molecular formula Ca(ClO4)2. It is an inorganic compound that is a yellow-white crystalline solid in appearance. As a strong oxidizing agent, it reacts with reducing agents when heated to generate heat and products that may be gaseous. Calcium perchlorate has been categorized as having explosive reactivity. Ca(ClO4)2 is a common chemical on the soil of planet Mars, counting for almost 1% of the Martian dust, by weight.
Praseodymium monophosphide is an inorganic compound of praseodymium and phosphorus with the chemical formula PrP. The compound forms crystals.
Samarium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal samarium (Sm). In these compounds, samarium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as SmCl3, Sm(NO3)3 and Sm(C2O4)3. Compounds with samarium in the +2 oxidation state are also known, for example SmI2.


















