
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.

Video CD is a home video format and the first format for distributing films on standard 120 mm (4.7 in) optical discs. The format was widely adopted in Southeast Asia, South Asia, Greater China, Central Asia and West Asia, superseding the VHS and Betamax systems in the regions until DVD-Video finally became affordable in the first decade of the 21st century.

Computer operating systems (OSes) provide a set of functions needed and used by most application programs on a computer, and the links needed to control and synchronize computer hardware. On the first computers, with no operating system, every program needed the full hardware specification to run correctly and perform standard tasks, and its own drivers for peripheral devices like printers and punched paper card readers. The growing complexity of hardware and application programs eventually made operating systems a necessity for everyday use.
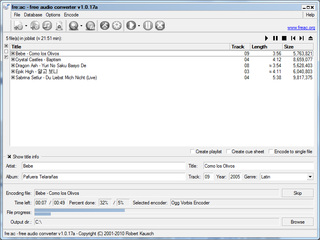
A CD ripper, CD grabber, or CD extractor is software that rips raw digital audio in Compact Disc Digital Audio (CD-DA) format tracks on a compact disc to standard computer sound files, such as WAV or MP3.

A CD player is an electronic device that plays audio compact discs, which are a digital optical disc data storage format. CD players were first sold to consumers in 1982. CDs typically contain recordings of audio material such as music or audiobooks. CD players may be part of home stereo systems, car audio systems, personal computers, or portable CD players such as CD boomboxes. Most CD players produce an output signal via a headphone jack or RCA jacks. To use a CD player in a home stereo system, the user connects an RCA cable from the RCA jacks to a hi-fi and loudspeakers for listening to music. To listen to music using a CD player with a headphone output jack, the user plugs headphones or earphones into the headphone jack.

In computing, an optical disc drive is a disc drive that uses laser light or electromagnetic waves within or near the visible light spectrum as part of the process of reading or writing data to or from optical discs. Some drives can only read from certain discs, but recent drives can both read and record, also called burners or writers. Compact discs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs are common types of optical media which can be read and recorded by such drives.

A live CD is a complete bootable computer installation including operating system which runs directly from a CD-ROM or similar storage device into a computer's memory, rather than loading from a hard disk drive. A live CD allows users to run an operating system for any purpose without installing it or making any changes to the computer's configuration. Live CDs can run on a computer without secondary storage, such as a hard disk drive, or with a corrupted hard disk drive or file system, allowing data recovery.
LEON is a radiation-tolerant 32-bit central processing unit (CPU) microprocessor core that implements the SPARC V8 instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Sun Microsystems. It was originally designed by the European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC), part of the European Space Agency (ESA), without any involvement by Sun. Later versions have been designed by Gaisler Research, under a variety of owners. It is described in synthesizable VHSIC Hardware Description Language (VHDL). LEON has a dual license model: An GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) and GNU General Public License (GPL) free and open-source software (FOSS) license that can be used without licensing fee, or a proprietary license that can be purchased for integration in a proprietary product. The core is configurable through VHDL generics, and is used in system on a chip (SOC) designs both in research and commercial settings.

Copy Control was the generic name of a copy prevention system, used from 2001 until 2006 on several digital audio disc releases by EMI Group and Sony BMG Music Entertainment in several regions. It should not be confused with the CopyControl computer software copy protection system introduced by Microcosm Ltd in 1989.

GD-ROM is a proprietary optical disc format originally used for the Dreamcast video game console, as well as its arcade counterpart, the Sega NAOMI and select Triforce arcade board titles. It was developed by Yamaha to curb piracy common to standard CDs and to offer increased storage capacity without the expense of the fledgling DVD-ROM. It is similar to the standard CD-ROM except that the pits on the disc are packed more closely together, resulting in a higher storage capacity of 1 gigabyte, a 30% increase over a conventional CD's capacity of 700 megabytes.
CD/DVD copy protection is a blanket term for various methods of copy protection for CDs and DVDs. Such methods include DRM, CD-checks, Dummy Files, illegal tables of contents, over-sizing or over-burning the CD, physical errors and bad sectors. Many protection schemes rely on breaking compliance with CD and DVD standards, leading to playback problems on some devices.

Exact Audio Copy (EAC) is a CD ripping program for Microsoft Windows. The program has been developed by Andre Wiethoff since 1998. Wiethoff's motivation for creating the program was that other such software only performed jitter correction while scratched CDs often produced distortion.
In computing, data recovery is a process of retrieving deleted, inaccessible, lost, corrupted, damaged, or formatted data from secondary storage, removable media or files, when the data stored in them cannot be accessed in a usual way. The data is most often salvaged from storage media such as internal or external hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), USB flash drives, magnetic tapes, CDs, DVDs, RAID subsystems, and other electronic devices. Recovery may be required due to physical damage to the storage devices or logical damage to the file system that prevents it from being mounted by the host operating system (OS).
A cue sheet, or cue file, is a metadata file which describes how the tracks of a CD or DVD are laid out. Cue sheets are stored as plain text files and commonly have a .cue filename extension. CDRWIN first introduced cue sheets, which are now supported by many optical disc authoring applications and media players.
In computing, ioctl is a system call for device-specific input/output operations and other operations which cannot be expressed by regular file semantics. It takes a parameter specifying a request code; the effect of a call depends completely on the request code. Request codes are often device-specific. For instance, a CD-ROM device driver which can instruct a physical device to eject a disc would provide an ioctl request code to do so. Device-independent request codes are sometimes used to give userspace access to kernel functions which are only used by core system software or still under development.
A C2 error, also known as E32 error, is a read error of a Compact Disc. C2 errors can to a degree be recovered by the hardware error detection and correction scheme. A CD drive can have extraction errors when the data on the disc is not readable due to scratches or smudges. The drive can compensate by supplying a "best guess" of what the missing data was, then supplying the missing data. C2 error correction is an analysis over many interleaved frames, an improvement over C1 error correction, which analyzed just one frame, resulting in more accurate data correction. C2 error correction codes are also used by the Digital Audio Tape (DAT) format.
Cactus Data Shield (CDS) is a form of CD/DVD copy protection for audio compact discs developed by Israeli company Midbar Technologies. It has been used extensively by EMI, BMG and their subsidiaries. CDS relies on two components: Erroneous Disc Navigation and Data Corruption.

A CD-ROM is a type of read-only memory consisting of a pre-pressed optical compact disc that contains data computers can read—but not write or erase—CD-ROMs. Some CDs, called enhanced CDs, hold both computer data and audio with the latter capable of being played on a CD player, while data is only usable on a computer.

fre:ac is a free audio converter and CD extractor for Windows, Linux, macOS, and FreeBSD, distributed under the GPL-2.0-or-later.










