Highway engineering is a professional engineering discipline branching from the civil engineering subdiscipline of transportation engineering that involves the planning, design, construction, operation, and maintenance of roads, highways, streets, bridges, and tunnels to ensure safe and effective transportation of people and goods. Highway engineering became prominent towards the latter half of the 20th century after World War II. Standards of highway engineering are continuously being improved. Highway engineers must take into account future traffic flows, design of highway intersections/interchanges, geometric alignment and design, highway pavement materials and design, structural design of pavement thickness, and pavement maintenance.

Crumple zones, crush zones, or crash zones are a structural safety feature used in vehicles, mainly in automobiles, to increase the time over which a change in velocity occurs from the impact during a collision by a controlled deformation; in recent years, it is also incorporated into trains and railcars.

A road surface or pavement is the durable surface material laid down on an area intended to sustain vehicular or foot traffic, such as a road or walkway. In the past, gravel road surfaces, macadam, hoggin, cobblestone and granite setts were extensively used, but these have mostly been replaced by asphalt or concrete laid on a compacted base course. Asphalt mixtures have been used in pavement construction since the beginning of the 20th century and are of two types: metalled (hard-surfaced) and unmetalled roads. Metalled roadways are made to sustain vehicular load and so are usually made on frequently used roads. Unmetalled roads, also known as gravel roads or dirt roads, are rough and can sustain less weight. Road surfaces are frequently marked to guide traffic.

A crash test is a form of destructive testing usually performed in order to ensure safe design standards in crashworthiness and crash compatibility for various modes of transportation or related systems and components.

Road traffic safety refers to the methods and measures used to prevent road users from being killed or seriously injured. Typical road users include pedestrians, cyclists, motorists, vehicle passengers, and passengers of on-road public transport.

Asphalt concrete is a composite material commonly used to surface roads, parking lots, airports, and the core of embankment dams. Asphalt mixtures have been used in pavement construction since the beginning of the twentieth century. It consists of mineral aggregate bound together with bitumen, laid in layers, and compacted.

A Jersey barrier, Jersey wall, or Jersey bump is a modular concrete or plastic barrier employed to separate lanes of traffic. It is designed to minimize vehicle damage in cases of incidental contact while still preventing vehicle crossovers resulting in a likely head-on collision. Jersey barriers are also used to reroute traffic and protect pedestrians and workers during highway construction. They are named after the U.S. state of New Jersey which first started using the barriers as separators between lanes of a highway in the 1950s.

Rumble strips are a road safety feature to alert inattentive drivers of potential danger, by causing a tactile fuzzy vibration and audible rumbling transmitted through the wheels into the vehicle interior. A rumble strip is applied along the direction of travel following an edgeline or centerline, to alert drivers when they drift from their lane. Rumble strips may also be installed in a series across the direction of travel, to warn drivers of a stop or slowdown ahead, or of an approaching danger spot.

Guard rails, guardrails, railings or protective guarding, in general, are a boundary feature and may be a means to prevent or deter access to dangerous or off-limits areas while allowing light and visibility in a greater way than a fence. Common shapes are flat, rounded edge, and tubular in horizontal railings, whereas tetraform spear-headed or ball-finialled are most common in vertical railings around homes. Park and garden railings commonly in metalworking feature swirls, leaves, plate metal areas and/or motifs particularly on and beside gates.

A curb, or kerb, is the edge where a raised sidewalk or road median/central reservation meets a street or other roadway.

The M5 is an expressway in the City of Cape Town Metropolitan Municipality, South Africa. It connects Milnerton on the Western Seaboard in the north to Muizenberg in the south, and crosses both the N1 and the N2. For part of its length, from the N1 interchange to Plumstead, it is a limited-access freeway (motorway). From Mowbray to Muizenberg it is parallel to the M4 Main Road.

Roadway noise is the collective sound energy emanating from motor vehicles. It consists chiefly of road surface, tire, engine/transmission, aerodynamic, and braking elements. Noise of rolling tires driving on pavement is found to be the biggest contributor of highway noise and increases with higher vehicle speeds.
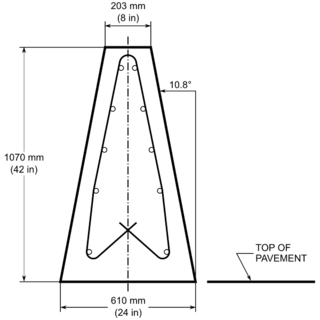
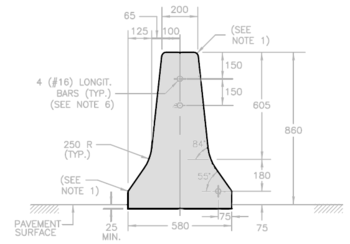
A constant slope barrier is a traffic barrier made of reinforced concrete and designed with a single slope that is used to separate lanes of vehicular traffic. Its advantages compared to more complex shapes arise because its performance is not as affected by changes in the height of the roadbed during repaving.

Traffic barriers keep vehicles within their roadway and prevent them from colliding with dangerous obstacles such as boulders, sign supports, trees, bridge abutments, buildings, walls, and large storm drains, or from traversing steep (non-recoverable) slopes or entering deep water. They are also installed within medians of divided highways to prevent errant vehicles from entering the opposing carriageway of traffic and help to reduce head-on collisions. Some of these barriers, designed to be struck from either side, are called median barriers. Traffic barriers can also be used to protect vulnerable areas like school yards, pedestrian zones, and fuel tanks from errant vehicles.
Road surface textures are deviations from a planar and smooth surface, affecting the vehicle/tyre interaction. Pavement texture is divided into: microtexture with wavelengths from 0 mm to 0.5 millimetres (0.020 in), macrotexture with wavelengths from 0.5 millimetres (0.020 in) to 50 millimetres (2.0 in) and megatexture with wavelengths from 50 millimetres (2.0 in) to 500 millimetres (20 in).

A concrete step barrier is a safety barrier used on the central reservation of motorways and dual carriageways as an alternative to the standard steel crash barrier.

A cable barrier, sometimes referred to as guard cable or wire rope safety barrier (WRSB), is a type of roadside or median safety traffic barrier/guard rail. It consists of steel wire ropes mounted on weak posts. As is the case with any roadside barrier, its primary purpose is to prevent a vehicle from leaving the traveled way and striking a fixed object or terrain feature that is less forgiving than itself. Also similar to most roadside barriers, cable barriers function by capturing and/or redirecting the errant vehicle.

A roadway departure is a type of incident that occurs when a vehicle leaves the roadway. Such incidents can lead to a single-vehicle collision.

The geometric design of roads is the branch of highway engineering concerned with the positioning of the physical elements of the roadway according to standards and constraints. The basic objectives in geometric design are to optimize efficiency and safety while minimizing cost and environmental damage. Geometric design also affects an emerging fifth objective called "livability," which is defined as designing roads to foster broader community goals, including providing access to employment, schools, businesses and residences, accommodate a range of travel modes such as walking, bicycling, transit, and automobiles, and minimizing fuel use, emissions and environmental damage.

The Transportation Research Center (TRC) is North America's largest multi-user automotive proving ground. It is operated by TRC Inc. The center occupies 4,500 acres in East Liberty, Ohio, about 40 miles northwest of Columbus, Ohio. These 4,500 acres are split between the main TRC property and a rural road/ATV course located approximately 2.5 miles from the main property.