
Dayton is the sixth-largest city in the U.S. state of Ohio. The county seat of Montgomery County, it anchors the state's fourth-largest metropolitan area. A small part of the city extends into Greene County. As of the 2020 census, the city proper had a population of 137,644, while the Dayton metropolitan area had 814,049 residents. Dayton is located within Ohio's Miami Valley region, 50 miles (80 km) north of Cincinnati and 60 miles (97 km) west of Columbus. It is a principal city of the Dayton–Springfield–Sidney combined statistical area, home to a population of 1,086,512.

Gettysburg is a village in Darke County, Ohio, United States. The population was 463 at the 2020 census.

Xenia is a city in and the county seat of Greene County, Ohio, United States. Located in southwestern Ohio, it is 15 miles (24 km) east of Dayton and is part of the Dayton metropolitan area as well as the Miami Valley region. The name comes from the Greek word Xenia (ξενία), which means "hospitality".

Rockwood is a borough in Somerset County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 850 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Johnstown, Pennsylvania, Metropolitan Statistical Area, and located due north of Pennsylvania's highest peak, Mount Davis, which significantly constricts land travel routing south of the municipality.

Loveland is a city in Hamilton, Clermont, and Warren counties in the southwestern part of the U.S. state of Ohio. The population was 13,307 at the 2020 census. Considered part of the Cincinnati metropolitan area, Loveland is located near exit 52 off Interstate 275, about 15 miles (24 km) northeast of the Cincinnati city limits. It borders Symmes, Miami and Hamilton townships and straddles the Little Miami River. Once a busy railroad town, Loveland is now a major stop along the Little Miami Scenic Trail.

Springboro is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio. A suburb of Cincinnati and Dayton, it is located mostly in Warren County in Clearcreek and Franklin Townships; with a small portion in Miami Township in Montgomery County. The city is part of the Miami Valley. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 19,062.

The Marietta and Cincinnati (M&C) was one of five important east-west railroads of southern Ohio; it was later absorbed by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O). Its original route ran from Marietta through Vincent, Athens, Hamden, Chillicothe, Greenfield, Blanchester, and Loveland. It had two main branches: Blanchester to Hillsboro, which was originally part of the Hillsboro and Cincinnati Railroad; and Hamden to Portsmouth, Ohio, originally part of the Scioto and Hocking Valley Railroad.

The Cincinnati, Lebanon and Northern Railway (CL&N) was a local passenger and freight-carrying railroad in the southwestern part of the U.S. state of Ohio, connecting Cincinnati to Dayton via Lebanon. It was built in the late 19th century to give the town of Lebanon and Warren County better transportation facilities. The railroad was locally known as the "Highland Route", since it followed the ridge between the Little and Great Miami rivers, and was the only line not affected by floods such as the Great Dayton Flood of 1913.

The Cincinnati, Hamilton and Dayton Railway (CH&D) was a railroad based in the U.S. state of Ohio that existed between its incorporation on March 2, 1846, and its acquisition by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad in December 1917. It was originally chartered to build from Cincinnati to Hamilton, Ohio, and then to Dayton, a distance of 59 mi (95 km); further construction and acquisition extended the railroad, and by 1902 it owned or controlled 640 mi (1,030 km) of railroad. Its stock and bond value plunged in late 1905 after "financial mismanagement of the properties" was revealed. The company was reorganized as the Toledo and Cincinnati Railroad in 1917.

The Pittsburgh, Cincinnati, Chicago and St. Louis Railroad, commonly called the Pan Handle Route, was a railroad that was part of the Pennsylvania Railroad system. Its common name came from its main line, which began at Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, crossed the Northern Panhandle of West Virginia, and continued west to Bradford, Ohio, where it split into a northern line to Chicago and a southern one through Indianapolis, Indiana, to East St. Louis, Illinois.

The Peters Cartridge Company was a company located along the Little Miami River in Kings Mills, Ohio, which specialized in gunpowder and ammunition production. Founded in 1887 by Gershom Moore Peters, the company supplied military ammunition to various countries during both world wars. Following its demise in 1944, the site was repurposed by Columbia Records and later Seagram, before being abandoned in 1968 and falling into disrepair. Its historic buildings, built in 1916, were added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1985. A brewery and apartment complex themed to the defunct company was constructed on site in 2020, in which many structures were restored and the company's history was placed on display for guests.

Chauncey Rose was a successful American businessman of the 19th century.
The Cleveland, Columbus and Cincinnati Railroad (CC&C) was a railroad that ran from Cleveland to Columbus in the U.S. state of Ohio in the United States. Chartered in 1836, it was moribund for the first 10 years of its existence. Its charter was revived and amended in 1845, and construction on the line began in November 1847. Construction was completed and the line opened for regular business in February 1851. The CC&C absorbed a small bankrupt railroad in 1861, and in May 1868 merged with the Bellefontaine Railway to form the Cleveland, Columbus, Cincinnati and Indianapolis Railway.

Interstate 75 (I-75) runs from Cincinnati to Toledo by way of Dayton in the US state of Ohio. The highway enters the state running concurrently with I-71 from Kentucky on the Brent Spence Bridge over the Ohio River and into the Bluegrass region. I-75 continues along the Mill Creek Expressway northward to the Butler County line just north of I-275. From there, the freeway runs into the Miami Valley and then passes through the Great Black Swamp before crossing into Michigan.
The Cincinnati Northern Railroad was a railroad that stretched from Franklin, Ohio, north to Jackson, Michigan, a distance of about 186 miles (299 km). It was acquired by the Cleveland, Cincinnati, Chicago and St. Louis Railway in 1901 and the New York Central Railroad several years later. Most of the line has since been abandoned.

Goes Station is a small unincorporated community in northern Xenia Township, Greene County, Ohio, United States. It sits at the intersection of Snively Road and U.S. Route 68 between Xenia and Yellow Springs.

Como is a ghost town in Lyon County, Nevada, in the United States.
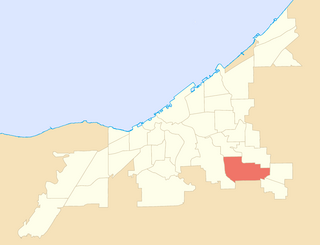
Union–Miles Park is a neighborhood on the Southeast side of Cleveland, Ohio, in the United States. The neighborhood draws its name from Union Avenue, and Miles Park in its far southwest corner.

Stillman Witt was an American railroad and steel industry executive best known for building the Cleveland, Columbus and Cincinnati Railroad, Cleveland, Painesville and Ashtabula Railroad, and the Bellefontaine and Indiana Railroad. Through his banking activities, he played a significant role in the early years of the Standard Oil company. He was also one of the founding investors in the Cleveland Rolling Mill, a major steel firm in the United States.
The Valley Railway was a shortline railroad which operated between the city of Cleveland and small town of Zoarville in the state of Ohio in the United States. The railroad was founded in 1871, but the first segment of track did not open until 1880 and the line was not completed until 1884. The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) obtained a controlling interest in the Valley Railway in 1890. The railroad went bankrupt in 1895, at which time it was reorganized as The Cleveland Terminal and Valley Railroad Company (CT&V). The B&O took over operation of the CT&V in 1909, and the company was merged with the B&O in 1915.


















