
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a plant in the botanical class of Cannabis sativa cultivars grown specifically for industrial and consumable use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest growing plants on Earth. It was also one of the first plants to be spun into usable fiber 50,000 years ago. It can be refined into a variety of commercial items, including paper, rope, textiles, clothing, biodegradable plastics, paint, insulation, biofuel, food, and animal feed.

Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid discovered in 1940. It is one of 113 identified cannabinoids in cannabis plants, along with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and accounts for up to 40% of the plant's extract. As of 2022, clinical research on CBD included studies related to the treatment of anxiety, addiction, psychosis, movement disorders, and pain, but there is insufficient high-quality evidence that cannabidiol is effective for these conditions. CBD is also sold as a herbal dietary supplement promoted with unproven claims of particular therapeutic effects.

In the United States, the removal of cannabis from Schedule I of the Controlled Substances Act is a proposed legal and administrative change in cannabis-related law at the federal level. It has been proposed repeatedly since 1972. The category is the most tightly restricted category reserved for drugs that have "no currently accepted medical use."
The Hemp Industries Association (HIA) is a non-profit trade group representing hemp companies, researchers and supporters in the United States and Canada. The group petitions for fair and equal treatment of industrial hemp. Since 1994, the HIA has been dedicated to education, industry development, and the accelerated expansion of hemp world market supply and demand.
Alex White Plume is the former vice president and president of the Oglala Sioux Tribe of the Pine Ridge Reservation, located on South Dakota of the United States. He served as president from June 30, 2006 to November 2006 after Cecilia Fire Thunder was impeached.
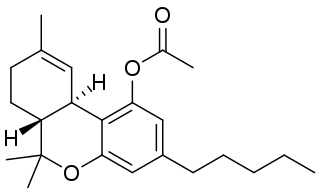
THC-O-acetate is the acetate ester of THC. The term THC-O-acetate and its variations are commonly used for two types of the substance, dependent on which cannabinoid it is synthesized from. The difference between Δ8-THC and Δ9-THC is bond placement on the cyclohexene ring.

In the United States, increased restrictions and labeling of cannabis as a poison began in many states from 1906 onward, and outright prohibitions began in the 1920s. By the mid-1930s cannabis was regulated as a drug in every state, including 35 states that adopted the Uniform State Narcotic Drug Act. The first national regulation was the Marihuana Tax Act of 1937.

The use, sale, and possession of cannabis containing over 0.3% THC by dry weight in the United States, despite laws in many states permitting it under various circumstances, is illegal under federal law. As a Schedule I drug under the federal Controlled Substances Act (CSA) of 1970, cannabis containing over 0.3% THC by dry weight is considered to have "no accepted medical use" and a high potential for abuse and physical or psychological dependence. Cannabis use is illegal for any reason, with the exception of FDA-approved research programs. However, individual states have enacted legislation permitting exemptions for various uses, including medical, industrial, and recreational use.

Cannabis in Oregon is legal for both medical and recreational use. In recent decades, the U.S. state of Oregon has had a number of legislative, legal, and cultural events surrounding use of cannabis. Oregon was the first state to decriminalize the possession of small amounts of cannabis, and among the first to authorize its use for medical purposes. An attempt to recriminalize possession of small amounts of cannabis was turned down by Oregon voters in 1997.
The Industrial Hemp Farming Act of 2009, introduced during the 111th United States Congress by House Republican Ron Paul of Texas) and House Democrat Barney Frank of Massachusetts) on April 2, 2009, sought to clarify the differences between marijuana and industrial hemp as well as repeal federal laws that prohibit cultivation of industrial, but only for research facilities of higher education from conducting research. Industrial hemp is the non-psychoactive, low-THC, oil-seed and fibers varieties of, predominantly, the cannabis sativa plant. Hemp is a sustainable resource that can be used to create thousands of different products including fuel, fabrics, paper, household products, and food and has been used for hundreds of centuries by civilizations around the world. If H.R.1866 passes American farmers will be permitted to compete in global hemp markets. On March 10, 2009, both Paul and Frank wrote a letter to their Congressional colleagues urging them to support the legislation. This bill was previously introduced in 2005 under the title of Industrial Hemp Farming Act of 2005.

Hash oil or cannabis oil is an oleoresin obtained by the extraction of cannabis or hashish. It is a cannabis concentrate containing many of its resins and terpenes – in particular, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD), and other cannabinoids. Hash oil is usually consumed by smoking, vaporizing or eating. Preparations of hash oil may be solid or semi-liquid colloids depending on both production method and temperature and are usually identified by their appearance or characteristics. Color most commonly ranges from transparent golden or light brown, to tan or black. There are various extraction methods, most involving a solvent, such as butane or ethanol.

Kentucky was the greatest producer of hemp in the United States during the 19th and 20th centuries, when it was the source of three fourths of U.S. hemp fiber. Production started to decline after World War I due to the rise of tobacco as the cash crop in Kentucky and the foreign competition of hemp fibers and finished products. In 1970, federal policies virtually banned the production of industrial hemp during the war on drugs saying all Cannabis sativa is a Schedule I controlled substance. Federal law under the Agricultural Act of 2014 allowed research back into hemp. Kentucky began production again with 33 acres in 2014. As of the 2016 harvest season, only two U.S. states other than Kentucky had over 100 acres (40 ha) in hemp production: Colorado and Tennessee. The first 500-acre commercial crop was planted in Harrison County in 2017, and research permits were issued for over 12,000 acres (4,900 ha) that year. The 2016 documentary Harvesting Liberty concerns the 21st century Kentucky hemp industry.
The legal status of cannabis in North Korea is unclear due to the lack of sources available to the outside world. Cannabis for industrial purposes (hemp), which has a low THC, is legal and is widely used in the country for the production of consumer goods. As a result of the lack of reliable information on North Korea, myths suggesting the legal or widespread use of marijuana have been spread by some media outlets.
Cannabis in Italy is currently legal for medical and industrial uses, although it is strictly regulated, while it is decriminalized for recreational uses. In particular, the possession of small amounts of marijuana for personal use is a civil infraction. The possible sanctions for possession vary from the issuing of a diffida to first offenders, that is an injunction not to use the drug again; to the temporary suspension of certain personal documents for repeat offenders. Conversely, the unauthorized sale of cannabis-related products is illegal and punishable with imprisonment, as is the unlicensed cultivation of cannabis, although recent court cases have effectively established the legality of cultivating small amounts of cannabis for exclusively personal use. The licensed cultivation of cannabis for medical and industrial purposes requires the use of certified seeds; however, there is no need for authorization to plant certified seeds with minimal levels of psychoactive compounds.

The Donald Trump administration took positions against marijuana and against the easing of laws regarding marijuana. Although Trump indicated during his 2016 presidential campaign that he favored leaving the issue of legalization of marijuana to the states, his administration subsequently upheld the federal prohibition of cannabis, and Trump's 2021 fiscal budget proposal included removing protections for state medical marijuana laws.

Terms related to cannabis include:
The Hemp Farming Act of 2018 was a proposed law to remove hemp from Schedule I controlled substances and making it an ordinary agricultural commodity. Its provisions were incorporated in the 2018 United States farm bill that became law on December 20, 2018.
Hemp in the U.S. state of Washington has emerged as an experimental crop in the 21st century.
Hemp Industries Association v. Drug Enforcement Administration, often shortened to HIA v. DEA, refers to two lawsuits concerning the legality of cannabis extracts and other products from the hemp plant that have very low or nonexistent natural THC levels, including CBD oil, in the United States. The first is from 2004 and the second is from 2018.

The 2018 farm bill or Agriculture Improvement Act of 2018 is an enacted United States farm bill that reauthorized $867 billion for many expenditures approved in the prior farm bill. The bill was passed by the Senate and House on December 11 and 12, 2018, respectively. On December 20, 2018, it was signed into law by President Donald Trump.










