In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (−OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, C
6H
5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.
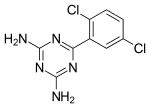
1,3,5-Triazine, also called s-triazine, is an organic chemical compound with the formula (HCN)3. It is a six-membered heterocyclic aromatic ring, one of several isomeric triazines. S-triazine—the "symmetric" isomer—and its derivatives are useful in a variety of applications.
Dimethoxyamphetamine (DMA) is a series of six lesser-known psychedelic drugs similar in structure to the three isomers of methoxyamphetamine and six isomers of trimethoxyamphetamine. The isomers are 2,3-DMA, 2,4-DMA, 2,5-DMA, 2,6-DMA, 3,4-DMA, and 3,5-DMA. Three of the isomers were characterized by Alexander Shulgin in his book PiHKAL. Little is known about their dangers or toxicity.

Cycloguanil is a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor, and is a metabolite of the antimalarial drug proguanil; its formation in vivo has been thought to be primarily responsible for the antimalarial activity of proguanil. However, more recent work has indicated that, while proguanil is synergistic with the drug atovaquone, cycloguanil is in fact antagonistic to the effects of atovaquone, suggesting that, unlike cycloguanil, proguanil may have an alternative mechanism of antimalarial action besides dihydrofolate reductase inhibition.

Triflubazam is a drug which is a 1,5-benzodiazepine derivative, related to clobazam. It has sedative and anxiolytic effects, with a long half-life and duration of action.

Amrubicin is an anthracycline used in the treatment of lung cancer. It is marketed in Japan since 2002 by Sumitomo under the brand name Calsed.

DPI-221 is an opioid drug that is used in scientific research. It is a highly selective agonist for the δ-opioid receptor, which produces fewer convulsions than most drugs from this family.

NESS-0327 is a drug used in scientific research which acts as an extremely potent and selective antagonist of the cannabinoid receptor CB1. It is much more potent an antagonist, and more selective for the CB1 receptor over CB2, than the more commonly used ligand rimonabant, with a Ki at CB1 of 350fM (i.e. 0.00035nM) and a selectivity of over 60,000x for CB1 over CB2. Independently, two other groups have described only modest nanomolar CB1 affinity for this compound (125nM and 18.4nM). Also unlike rimonabant, NESS-0327 does not appear to act as an inverse agonist at higher doses, instead being a purely neutral antagonist which blocks the CB1 receptor but does not produce any physiological effect of its own.

Surinabant (SR147778) is a cannabinoid receptor type 1 antagonist developed by Sanofi-Aventis. It is being investigated as a potential treatment for nicotine addiction, to assist smoking cessation. It may also be developed as an anorectic drug to assist with weight loss, however there are already several CB1 antagonists or inverse agonists on the market or under development for this application, so surinabant is at present mainly being developed as an anti-smoking drug, with possible application in the treatment of other addictive disorders such as alcoholism. Other potential applications such as treatment of ADHD have also been proposed.

VCHSR is a drug used in scientific research which acts as a selective antagonist of the cannabinoid receptor CB1. It is derived from the widely used CB1 antagonist rimonabant, and has similar potency and selectivity for the CB1 receptor, but has been modified to remove the hydrogen bonding capability in the C-3 substituent region, which removes the inverse agonist effect that rimonabant produces at high doses, so that VCHSR instead acts as a neutral antagonist, blocking the receptor but producing no physiological effect of its own.
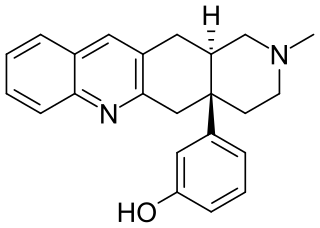
TAN-67 (SB-205,607) is an opioid drug used in scientific research that acts as a potent and selective δ-opioid agonist, selective for the δ1 subtype. It has analgesic properties and induces dopamine release in nucleus accumbens. It also protects both heart and brain tissue from hypoxic tissue damage through multiple mechanisms involving among others an interaction between δ receptors and mitochondrial K(ATP) channels.

SB-612,111 is an opioid receptor ligand which is a potent and selective antagonist for the nociceptin receptor (ORL-1), several times more potent than the older drug J-113,397. It does not have analgesic effects in its own right, but prevents the development of hyperalgesia, and also shows antidepressant effects in animal studies.

Bropirimine is an experimental drug with anti-cancer and antiviral properties. It is an orally effective immunomodulator and is being tried in bladder cancers.

TM-38837 is a small molecule inverse agonist/antagonist of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor, with peripheral selectivity. It is being developed for the treatment of obesity and metabolic disorders by 7TM Pharma. The company has announced phase I clinical trials.
An uncoupler or uncoupling agent is a molecule that disrupts oxidative phosphorylation in prokaryotes and mitochondria or photophosphorylation in chloroplasts and cyanobacteria by dissociating the reactions of ATP synthesis from the electron transport chain. The result is that the cell or mitochondrion expends energy to generate a proton-motive force, but the proton-motive force is dissipated before the ATP synthase can recapture this energy and use it to make ATP. Because the intracellular supply of protons is replenished, uncouplers actually stimulate cellular metabolism. Uncouplers are capable of transporting protons through mitochondrial and lipid membranes.

O-1269 is a drug that is a diarylpyrazole derivative, related to potent cannabinoid antagonist drugs such as rimonabant and surinabant. However O-1269 and several related drugs were unexpectedly found to act as full or partial agonists at the cannabinoid receptors rather than antagonists, and so produce the usual effects expected of cannabinoid agonists in animal tests, such as sedation and analgesic effects. The N-heptyl homolog O-1270 and the N-propyl homolog O-1399 also act as cannabinoid agonists with similar potency in vivo, despite weaker binding affinity at cannabinoid receptors compared to the pentyl homolog O-1269. Agonist-like and atypical cannabinoid activity has also been observed with a number of related compounds.

Leptophos (O-(4-bromo-2,5-dichlorophenyl) O-methyl phenylphosphonothioate) belongs to the organophosphates and at room temperature it is a stable white solid. It is also known as Phosvel, Abar and Vcs 506. Leptophos was primarily used as a pesticide and fungicide. for rice, cotton, fruit and vegetables until its use was discontinued in 1975 in USA, but still sold in South-Eastern Asia in 1981.
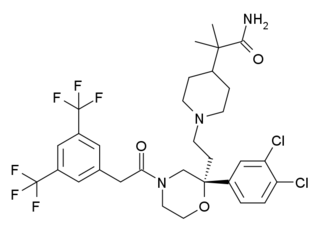
Burapitant (SSR-240,600) is a drug developed by Sanofi-Aventis which was one of the first compounds developed that acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the NK1 receptor. While burapitant itself did not proceed beyond early clinical trials and was never developed for clinical use in humans, promising animal results from this and related compounds have led to a number of novel drugs from this class that have now been introduced into medical use.

GSK1016790A is a drug developed by GlaxoSmithKline which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the TRPV4 receptor. It has been used to study the role of TRPV4 receptors in the function of smooth muscle tissue, particularly that lining blood vessels, lymphatic system, and the bladder.