
Endodontics is the dental specialty concerned with the study and treatment of the dental pulp.

Toothache, also known as dental pain, is pain in the teeth or their supporting structures, caused by dental diseases or pain referred to the teeth by non-dental diseases. When severe it may impact sleep, eating, and other daily activities.

The pulp is the part in the centre of a tooth made up of living connective tissues and odontoblasts. The pulp is a part of the dentin–pulp complex (endodontium). The vitality of the dentin-pulp complex, both during health and after injury, depends on pulp cell activity and the signalling processes that regulate the cell's behaviour.
Pulpitis is inflammation of dental pulp tissue. The pulp contains the blood vessels, the nerves, and connective tissue inside a tooth and provides the tooth’s blood and nutrients. Pulpitis is mainly caused by bacterial infection which itself is a secondary development of caries. It manifests itself in the form of a toothache.
A dental emergency is an issue involving the teeth and supporting tissues that is of high importance to be treated by the relevant professional. Dental emergencies do not always involve pain, although this is a common signal that something needs to be looked at. Pain can originate from the tooth, surrounding tissues or can have the sensation of originating in the teeth but be caused by an independent source. Depending on the type of pain experienced an experienced clinician can determine the likely cause and can treat the issue as each tissue type gives different messages in a dental emergency.

Veterinary dentistry is the field of dentistry applied to the care of animals. It is the art and science of prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of conditions, diseases, and disorders of the oral cavity, the maxillofacial region, and its associated structures as it relates to animals.
A pulp polyp, also known as chronic hyperplastic pulpitis, is a "productive" inflammation of dental pulp in which the development of granulation tissue is seen in response to persistent, low-grade mechanical irritation and bacterial invasion of the pulp.
Dens evaginatus is a rare odontogenic developmental anomaly that is found in teeth where the outer surface appears to form an extra bump or cusp.
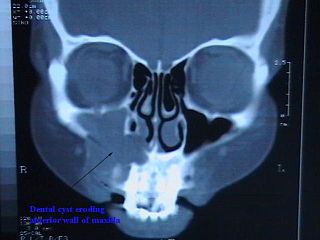
Commonly known as a dental cyst, the periapical cyst is the most common odontogenic cyst. It may develop rapidly from a periapical granuloma, as a consequence of untreated chronic periapical periodontitis.

A dental abscess is a localized collection of pus associated with a tooth. The most common type of dental abscess is a periapical abscess, and the second most common is a periodontal abscess. In a periapical abscess, usually the origin is a bacterial infection that has accumulated in the soft, often dead, pulp of the tooth. This can be caused by tooth decay, broken teeth or extensive periodontal disease. A failed root canal treatment may also create a similar abscess.

Root canal treatment is a treatment sequence for the infected pulp of a tooth which is intended to result in the elimination of infection and the protection of the decontaminated tooth from future microbial invasion. Root canals, and their associated pulp chamber, are the physical hollows within a tooth that are naturally inhabited by nerve tissue, blood vessels and other cellular entities. Together, these items constitute the dental pulp.
Apical periodontitis is typically the body's defense response to the threat of microbial invasion from the root canal. Primary among the members of the host defense mechanism is the polymorphonuclear leukocyte, otherwise known as the neutrophil. The task of the neutrophil is to locate and destroy microbes that intrude into the body – anywhere in the body – and they represent the hallmark of acute inflammation.
Pulpotomy is a minimally invasive procedure performed in children on a primary tooth with extensive caries but without evidence of root pathology. The minimally invasive endodontic techniques of vital pulp therapy (VPT) are based on improved understanding of the capacity of pulp (nerve) tissues to heal and regenerate plus the availability of advanced endodontic materials. During the caries removal, this results in a carious or mechanical pulp exposure (bleeding) from the cavity. During pulpotomy, the inflamed/diseased pulp tissue is removed from the coronal pulp chamber of the tooth leaving healthy pulp tissue which is dressed with a long-term clinically-successful medicament that maintains the survival of the pulp and promotes repair. There are various types of medicament placed above the vital pulp such as Buckley’s Solution of formocresol, ferric sulfate, calcium hydroxide or mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA). MTA is a more recent material used for pulpotomies with a high rate of success, better than formocresol or ferric sulfate. It is also recommended to be the preferred pulpotomy agent in the future. After the coronal pulp chamber is filled, the tooth is restored with a filling material that seals the tooth from microleakage, such as a stainless steel crown which is the most effective long-term restoration. However, if there is sufficient remaining supporting tooth structure, other filling materials such as amalgam or composite resin can provide a functional alternative when the primary tooth has a life span of two years or less. The medium- to long-term treatment outcomes of pulpotomy in symptomatic permanent teeth with caries, especially in young people, indicate that pulpotomy can be a potential alternative to root canal therapy (RCT).
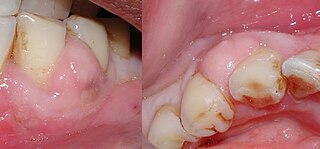
A periodontal abscess, is a localized collection of pus within the tissues of the periodontium. It is a type of dental abscess. A periodontal abscess occurs alongside a tooth, and is different from the more common periapical abscess, which represents the spread of infection from a dead tooth. To reflect this, sometimes the term "lateral (periodontal) abscess" is used. In contrast to a periapical abscess, periodontal abscesses are usually associated with a vital (living) tooth. Abscesses of the periodontium are acute bacterial infections classified primarily by location.
Combined periodontic-endodontic lesions are localized, circumscribed areas of bacterial infection originating from either dental pulp, periodontal tissues surrounding the involved tooth or teeth or both.
Pulp necrosis is a clinical diagnostic category indicating the death of the pulp and nerves of the pulp chamber and root canal of a tooth which may be due to bacterial sequelae, trauma and chemical or mechanical irritation. It is often the end result of many cases of dental trauma, caries and irreversible pulpitis.

Periapical periodontitis or apical periodontitis (AP) is an acute or chronic inflammatory lesion around the apex of a tooth root, most commonly caused by bacterial invasion of the pulp of the tooth. It is a likely outcome of untreated dental caries, and in such cases it can be considered a sequela in the natural history of tooth decay, irreversible pulpitis and pulpal necrosis. Other causes can include occlusal trauma due to 'high spots' after restoration work, extrusion from the tooth of root filling material, or bacterial invasion and infection from the gums. Periapical periodontitis may develop into a periapical abscess, where a collection of pus forms at the end of the root, the consequence of spread of infection from the tooth pulp, or into a periapical cyst, where an epithelial lined, fluid-filled structure forms.

Regenerative endodontic procedures is defined as biologically based procedures designed to replace damaged structures such as dentin, root structures, and cells of the pulp-dentin complex. This new treatment modality aims to promote normal function of the pulp. It has become an alternative to heal apical periodontitis. Regenerative endodontics is the extension of root canal therapy. Conventional root canal therapy cleans and fills the pulp chamber with biologically inert material after destruction of the pulp due to dental caries, congenital deformity or trauma. Regenerative endodontics instead seeks to replace live tissue in the pulp chamber. The ultimate goal of regenerative endodontic procedures is to regenerate the tissues and the normal function of the dentin-pulp complex.
In the dental specialty of endodontics, periradicular surgery is surgery to the external root surface. Examples of periradicular surgery include apicoectomy, root resection, repair of root perforation or resorption defects, removal of broken fragments of the tooth or a filling material, and exploratory surgery to look for root fractures.
Periapical granuloma, also sometimes referred to as a radicular granuloma or apical granuloma, is an inflammation at the tip of a dead (nonvital) tooth. It is a lesion or mass that typically starts out as an epithelial lined cyst, and undergoes an inward curvature that results in inflammation of granulation tissue at the root tips of a dead tooth. This is usually due to dental caries or a bacterial infection of the dental pulp. Periapical granuloma is an infrequent disorder that has an occurrence rate between 9.3 to 87.1 percent. Periapical granuloma is not a true granuloma due to the fact that it does not contain granulomatous inflammation; however, periapical granuloma is a common term used.










