Caesium is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of 28.5 °C (83.3 °F), which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at or near room temperature. Caesium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of rubidium and potassium. The most reactive of all metals, it is pyrophoric and reacts with water even at −116 °C (−177 °F). It is the least electronegative element, with a value of 0.79 on the Pauling scale. It has only one stable isotope, caesium-133. Caesium is mined mostly from pollucite, while the radioisotopes, especially caesium-137, a fission product, are extracted from waste produced by nuclear reactors.

Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+
and hydroxide anions OH−
.
The chloride ion is the anion Cl−. It is formed when the element chlorine gains an electron or when a compound such as hydrogen chloride is dissolved in water or other polar solvents. Chloride salts such as sodium chloride are often very soluble in water. It is an essential electrolyte located in all body fluids responsible for maintaining acid/base balance, transmitting nerve impulses and regulating liquid flow in and out of cells. Less frequently, the word chloride may also form part of the "common" name of chemical compounds in which one or more chlorine atoms are covalently bonded. For example, methyl chloride, with the standard name chloromethane is an organic compound with a covalent C−Cl bond in which the chlorine is not an anion.

Brine is a high-concentration solution of salt (NaCl) in water (H2O). In diverse contexts, brine may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawater, on the lower end of that of solutions used for brining foods) up to about 26% (a typical saturated solution, depending on temperature). Brine forms naturally due to evaporation of ground saline water but it is also generated in the mining of sodium chloride. Brine is used for food processing and cooking (pickling and brining), for de-icing of roads and other structures, and in a number of technological processes. It is also a by-product of many industrial processes, such as desalination, so it requires wastewater treatment for proper disposal or further utilization (fresh water recovery).

Sodium chloride, commonly known as salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. With molar masses of 22.99 and 35.45 g/mol respectively, 100 g of NaCl contains 39.34 g Na and 60.66 g Cl. Sodium chloride is the salt most responsible for the salinity of seawater and of the extracellular fluid of many multicellular organisms. In its edible form of table salt, it is commonly used as a condiment and food preservative. Large quantities of sodium chloride are used in many industrial processes, and it is a major source of sodium and chlorine compounds used as feedstocks for further chemical syntheses. A second major application of sodium chloride is de-icing of roadways in sub-freezing weather.

Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, and is commonly called caustic potash.

Calcium chloride is an inorganic compound, a salt with the chemical formula CaCl2. It is a white crystalline solid at room temperature, and it is highly soluble in water. It can be created by neutralising hydrochloric acid with calcium hydroxide.
A drain cleaner is a chemical product that unblocks sewer pipes or clogged wastewater drains. The term may also refer to a mechanical device such as a plumber's snake, drain auger, toilet plunger, or similar device. Occasionally, the term is applied to a plumber or other individual who performs the drain cleaning and hygiene.
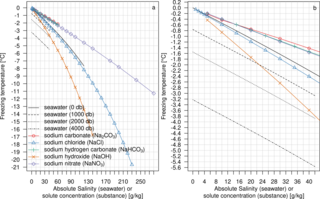
Freezing-point depression is a drop in the temperature at which a substance freezes, caused when a smaller amount of another, non-volatile substance is added. Examples include adding salt into water, alcohol in water, ethylene or propylene glycol in water, adding copper to molten silver, or the mixing of two solids such as impurities into a finely powdered drug.

Bischofite is a hydrous magnesium chloride mineral with formula MgCl2·6H2O. It belongs to halides and is a sea salt concentrate. It contains many macro- and micro-elements vital for human health, in much higher concentrations than can be found in sea or ocean salt. The main bischofite compound is magnesium chloride (up to 350 g/L), moreover, it contains about 70 other elements as impurities, including potassium, sodium, bromine, boron, calcium, silicon, molybdenum, silver, zinc, iron and copper.
The chloralkali process is an industrial process for the electrolysis of sodium chloride solutions. It is the technology used to produce chlorine and sodium hydroxide, which are commodity chemicals required by industry. 35 million tons of chlorine were prepared by this process in 1987. The chlorine and sodium hydroxide produced in this process are widely used in the chemical industry.

Snow removal or snow clearing is the job of removing snow after a snowfall to make travel easier and safer. This is done by both individual households and by governments and institutions.

De-icing is the process of removing snow, ice or frost from a surface. Anti-icing is understood to be the application of chemicals that not only de-ice but also remain on a surface and continue to delay the reformation of ice for a certain period of time, or prevent adhesion of ice to make mechanical removal easier.
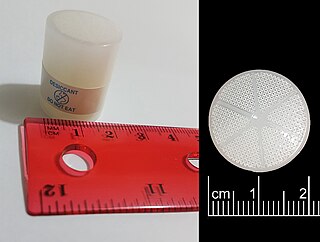
A molecular sieve is a material with pores of uniform size. These pore diameters are similar in size to small molecules, and thus large molecules cannot enter or be adsorbed, while smaller molecules can. As a mixture of molecules migrate through the stationary bed of porous, semi-solid substance referred to as a sieve, the components of highest molecular weight leave the bed first, followed by successively smaller molecules. Some molecular sieves are used in size-exclusion chromatography, a separation technique that sorts molecules based on their size. Other molecular sieves are used as desiccants.

Potassium acetate (CH3COOK) is the potassium salt of acetic acid. It is a hygroscopic solid at room temperature.

Sodium formate, HCOONa, is the sodium salt of formic acid, HCOOH. It usually appears as a white deliquescent powder.
Calcium magnesium acetate (CMA) is a deicer and can be used as an alternative to road salt. It is approximately as corrosive as normal tap water, and in varying concentrations can be effective in stopping road ice from forming down to around −27.5 °C (−17.5 °F) (its eutectic temperature). CMA can also be used as an H2S capture agent.
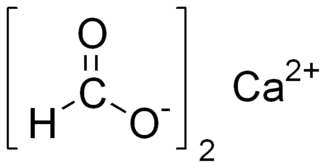
Calcium formate is the calcium salt of formic acid. It is also known as E238. Under this E number it is used as an animal feed preservative within EU, but not in foods intended for people.

High-temperature corrosion is a mechanism of corrosion that takes place when gas turbines, diesel engines, furnaces or other machinery come in contact with hot gas containing certain contaminants. Fuel sometimes contains vanadium compounds or sulfates which can form compounds during combustion having a low melting point. These liquid melted salts are strongly corrosive for stainless steel and other alloys normally inert against the corrosion and high temperatures. Other high-temperature corrosions include high-temperature oxidation, sulfidation and carbonization. High temperature oxidation and other corrosion types are commonly modelled using the Deal-Grove model to account for diffusion and reaction processes.
Chlorine gas can be produced by extracting from natural materials, including the electrolysis of a sodium chloride solution (brine) and other ways.