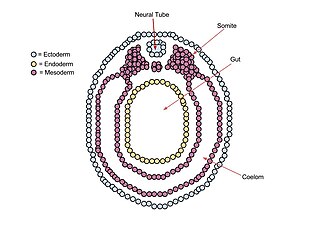
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.

A body cavity is any space or compartment, or potential space, in an animal body. Cavities accommodate organs and other structures; cavities as potential spaces contain fluid.
The amniotic sac, also called the bag of waters or the membranes, is the sac in which the embryo and later fetus develops in amniotes. It is a thin but tough transparent pair of membranes that hold a developing embryo until shortly before birth. The inner of these membranes, the amnion, encloses the amniotic cavity, containing the amniotic fluid and the embryo. The outer membrane, the chorion, contains the amnion and is part of the placenta. On the outer side, the amniotic sac is connected to the yolk sac, the allantois, and via the umbilical cord, the placenta.

The amnion is a membrane that closely covers human and various other embryos when they first form. It fills with amniotic fluid, which causes the amnion to expand and become the amniotic sac that provides a protective environment for the developing embryo. The amnion, along with the chorion, the yolk sac and the allantois protect the embryo. In birds, reptiles and monotremes, the protective sac is enclosed in a shell. In marsupials and placental mammals, it is enclosed in a uterus.

The chorion is the outermost fetal membrane around the embryo in mammals, birds and reptiles (amniotes). It develops from an outer fold on the surface of the yolk sac, which lies outside the zona pellucida, known as the vitelline membrane in other animals. In insects, it is developed by the follicle cells while the egg is in the ovary. Some mollusks also have chorions as part of their eggs. For example, fragile octopus eggs have only a chorion as their envelope.
A germ layer is a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans produce two or three primary germ layers. Some animals, like cnidarians, produce two germ layers making them diploblastic. Other animals such as bilaterians produce a third layer between these two layers, making them triploblastic. Germ layers eventually give rise to all of an animal's tissues and organs through the process of organogenesis.
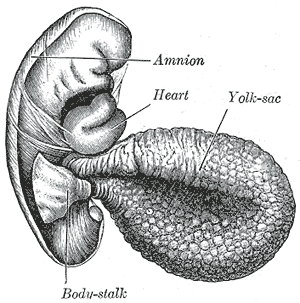
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though yolk sac is far more widely used. In humans, the yolk sac is important in early embryonic blood supply, and much of it is incorporated into the primordial gut during the fourth week of embryonic development.
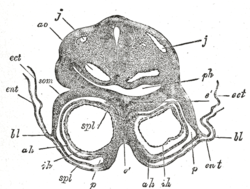
A neurula is a vertebrate embryo at the early stage of development in which neurulation occurs. The neurula stage is preceded by the gastrula stage; consequentially, neurulation is preceded by gastrulation. Neurulation marks the beginning of the process of organogenesis.
The primitive node is the organizer for gastrulation in most amniote embryos. In birds it is known as Hensen's node, and in amphibians it is known as the Spemann-Mangold organizer. It is induced by the Nieuwkoop center in amphibians, or by the posterior marginal zone in amniotes including birds.

The primitive streak is a structure that forms in the early embryo in amniotes. In amphibians, the equivalent structure is the blastopore. During early embryonic development, the embryonic disc becomes oval shaped, and then pear-shaped with the broad end towards the anterior, and the narrower region projected to the posterior. The primitive streak forms a longitudinal midline structure in the narrower posterior (caudal) region of the developing embryo on its dorsal side. At first formation, the primitive streak extends for half the length of the embryo. In the human embryo, this appears by stage 6, about 17 days.

Intermediate mesoderm or intermediate mesenchyme is a narrow section of the mesoderm located between the paraxial mesoderm and the lateral plate of the developing embryo. The intermediate mesoderm develops into vital parts of the urogenital system.
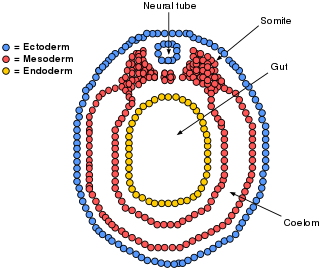
The lateral plate mesoderm is the mesoderm that is found at the periphery of the embryo. It is to the side of the paraxial mesoderm, and further to the axial mesoderm. The lateral plate mesoderm is separated from the paraxial mesoderm by a narrow region of intermediate mesoderm. The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers, between the outer ectoderm and inner endoderm.

In amniote embryonic development, the epiblast is one of two distinct cell layers arising from the inner cell mass in the mammalian blastocyst, or from the blastula in reptiles and birds, the other layer is the hypoblast. It drives the embryo proper through its differentiation into the three primary germ layers, ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, during gastrulation. The amniotic ectoderm and extraembryonic mesoderm also originate from the epiblast.
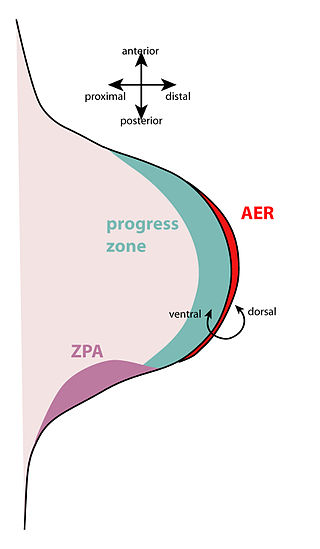
The apical ectodermal ridge (AER) is a structure that forms from the ectodermal cells at the distal end of each limb bud and acts as a major signaling center to ensure proper development of a limb. After the limb bud induces AER formation, the AER and limb mesenchyme—including the zone of polarizing activity (ZPA)—continue to communicate with each other to direct further limb development.

Mesenchyme is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every organ in the developing embryo.

The bilaminar embryonic disc, bilaminar blastoderm or embryonic disc is the distinct two-layered structure of cells formed in an embryo. In the development of the human embryo this takes place by day eight. It is formed when the inner cell mass, also known as the embryoblast, forms a bilaminar disc of two layers, an upper layer called the epiblast and a lower layer called the hypoblast, which will eventually form into fetus. These two layers of cells are stretched between two fluid-filled cavities at either end: the primitive yolk sac and the amniotic sac.
The limb bud is a structure formed early in vertebrate limb development. As a result of interactions between the ectoderm and underlying mesoderm, formation occurs roughly around the fourth week of development. In the development of the human embryo the upper limb bud appears in the third week and the lower limb bud appears four days later.

Human embryonic development or human embryogenesis is the development and formation of the human embryo. It is characterised by the processes of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, the development of the human body entails growth from a one-celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilization occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form the single cell zygote and the germinal stage of development commences. Embryonic development in the human, covers the first eight weeks of development; at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus. The eight weeks have 23 stages.
The development of the digestive system in the human embryo concerns the epithelium of the digestive system and the parenchyma of its derivatives, which originate from the endoderm. Connective tissue, muscular components, and peritoneal components originate in the mesoderm. Different regions of the gut tube such as the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, etc. are specified by a retinoic acid gradient that causes transcription factors unique to each region to be expressed. Differentiation of the gut and its derivatives depends upon reciprocal interactions between the gut endoderm and its surrounding mesoderm. Hox genes in the mesoderm are induced by a Hedgehog signaling pathway secreted by gut endoderm and regulate the craniocaudal organization of the gut and its derivatives. The gut system extends from the oropharyngeal membrane to the cloacal membrane and is divided into the foregut, midgut, and hindgut.
This glossary of developmental biology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts commonly used in the study of developmental biology and related disciplines in biology, including embryology and reproductive biology, primarily as they pertain to vertebrate animals and particularly to humans and other mammals. The developmental biology of invertebrates, plants, fungi, and other organisms is treated in other articles; e.g terms relating to the reproduction and development of insects are listed in Glossary of entomology, and those relating to plants are listed in Glossary of botany.