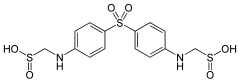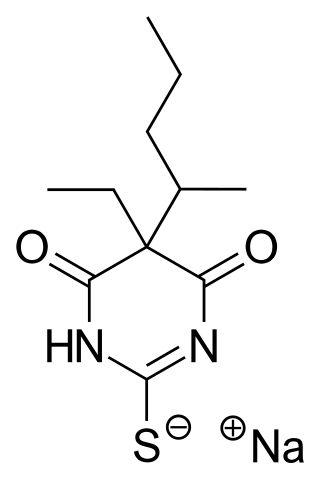
Sodium thiopental, also known as Sodium Pentothal, thiopental, thiopentone, or Trapanal, is a rapid-onset short-acting barbiturate general anesthetic. It is the thiobarbiturate analog of pentobarbital, and an analog of thiobarbital. Sodium thiopental was a core medicine in the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, but was supplanted by propofol. Despite this, thiopental is listed as an acceptable alternative to propofol, depending on local availability and cost of these agents. It was previously the first of three drugs administered during most lethal injections in the United States, but the US manufacturer Hospira stopped manufacturing the drug in 2011 and the European Union banned the export of the drug for this purpose. Although thiopental abuse carries a dependency risk, its recreational use is rare.

Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a long-term infection by the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae or Mycobacterium lepromatosis. Infection can lead to damage of the nerves, respiratory tract, skin, and eyes. This nerve damage may result in a lack of ability to feel pain, which can lead to the loss of parts of a person's extremities from repeated injuries or infection through unnoticed wounds. An infected person may also experience muscle weakness and poor eyesight. Leprosy symptoms may begin within one year, but, for some people, symptoms may take 20 years or more to occur.
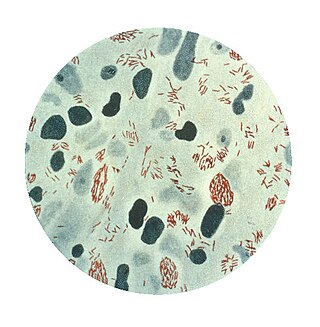
Mycobacterium leprae is one of the two species of bacteria that cause Hansen’s disease (leprosy), a chronic but curable infectious disease that damages the peripheral nerves and targets the skin, eyes, nose, and muscles.

Sodium benzoate also known as benzoate of soda is the sodium salt of benzoic acid, widely used as a food preservative (with an E number of E211) and a pickling agent. It appears as a white crystalline chemical with the formula C6H5COONa.

Alginic acid, also called algin, is a naturally occurring, edible polysaccharide found in brown algae. It is hydrophilic and forms a viscous gum when hydrated. With metals such as sodium and calcium, its salts are known as alginates. Its colour ranges from white to yellowish-brown. It is sold in filamentous, granular, or powdered forms.

Clofazimine, sold under the brand name Lamprene, is a medication used together with rifampicin and dapsone to treat leprosy. It is specifically used for multibacillary (MB) leprosy and erythema nodosum leprosum. Evidence is insufficient to support its use in other conditions though a retrospective study found it 95% effective in the treatment of Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) when administered with a macrolide and ethambutol, as well as the drugs amikacin and clarithromycin. However, in the United States, clofazimine is considered an orphan drug, is unavailable in pharmacies, and its use in the treatment of MAC is overseen by the Food and Drug Administration. It is taken orally.

Sodium oxybate, sold under the brand name Xyrem or Alcover among others, is a medication used to treat three symptoms of narcolepsy: sudden muscle weakness and excessive daytime sleepiness and alcohol dependence. It is used sometimes in France and Italy as an anesthetic given intravenously; it is also approved and used in Italy and in Austria to treat alcohol dependence and alcohol withdrawal syndrome.

Sir Leonard Rogers was a founder member of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, and its President from 1933 to 1935.
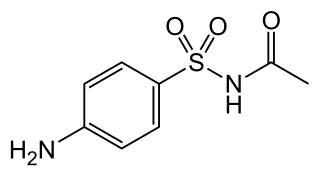
Sulfacetamide is a sulfonamide antibiotic.

Fosfestrol, sold under the brand name Honvan and also known as diethylstilbestrol diphosphate (DESDP), is an estrogen medication which is used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. It is given by slow intravenous infusion once per day to once per week or by mouth once per day.

Pilsicainide (INN) is an antiarrhythmic agent. It is marketed in Japan as サンリズム (Sunrythm). It was developed by Suntory Holdings Limited and first released in 1991. The JAN applies to the hydrochloride salt, pilsicainide hydrochloride.

Acedapsone (INN) is an antimicrobial drug, which also has antimalarial activity.

Prasterone sulfate, also known as dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S), is a naturally occurring androstane steroid which is marketed and used in Japan and other countries as a labor inducer in the treatment of insufficient cervical ripening and dilation during childbirth. It is the C3β sulfate ester of prasterone, and is known to act as a prohormone of DHEA and by extension of androgens and estrogens, although it also has its own activity as a neurosteroid. Prasterone sulfate is used medically as the sodium salt via injection and is referred to by the name sodium prasterone sulfate (JAN).

Acetrizoic acid is a pharmaceutical drug that was used as an iodinated contrast medium for X-ray imaging. It was applied in form of its salt, sodium acetrizoate, but is no longer in clinical use.
Leprosy stigma is a type of social stigma, a strong negative feeling towards a person with leprosy relating to their moral status in society. It is also referred to as leprosy-related stigma, leprostigma, and stigma of leprosy. Since ancient times, leprosy instilled the practice of fear and avoidance in many societies because of the associated physical disfigurement and lack of understanding behind its cause. Because of the historical trauma the word "leprosy" invokes, the disease is now referred to as Hansen's disease, named after Gerhard Armauer Hansen who discovered Mycobacterium leprae, the bacterial agent that causes Hansen's disease. Those who have suffered from Hansen's disease describe the impact of social stigma as far worse than the physical manifestations despite it being only mildly contagious and pharmacologically curable. This sentiment is echoed by Weis and Ramakrishna, who noted that "the impact of the meaning of the disease may be a greater source of suffering than symptoms of the disease".
Hydnocarpus wightianus or chaulmoogra is a tree in the Achariaceae family. Hydnocarpus wightiana seed oil has been widely used in traditional Indian medicine, especially in Ayurveda, and in Chinese traditional medicine for the treatment of leprosy. It entered early Western medicine in the nineteenth century before the era of sulfonamides and other antibiotics for the treatment of several skin diseases and leprosy. The oil was prescribed for leprosy as a mixture suspended in gum or as an emulsion.

Promin, or sodium glucosulfone is a sulfone drug that was investigated for the treatment of malaria, tuberculosis and leprosy. It is broken down in the body to dapsone, which is the therapeutic form.

The history of leprosy was traced to its origins by an international team of 22 geneticists using comparative genomics of the worldwide distribution of Mycobacterium leprae. Monot et al. (2005) determined that leprosy originated in East Africa or the Near East and traveled with humans along their migration routes, including those of trade in goods and slaves. The four strains of M. leprae are based in specific geographic regions where each predominantly occurs:

Sodium nitroprusside (SNP), sold under the brand name Nitropress among others, is a medication used to lower blood pressure. This may be done if the blood pressure is very high and resulting in symptoms, in certain types of heart failure, and during surgery to decrease bleeding. It is used by continuous injection into a vein. Onset is nearly immediate and effects last for up to ten minutes.
Ernest Muir FRCS, CIE, CMG was a Scottish medical missionary and educator in British-controlled India and Nigeria most noted for his work with Hansen's disease (leprosy).