The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord, the retina and optic nerve, and the olfactory nerve and epithelia. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral to caudal axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain, though precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets.

The sense of balance or equilibrioception is the perception of balance and spatial orientation. It helps prevent humans and nonhuman animals from falling over when standing or moving. Equilibrioception is the result of a number of sensory systems working together; the eyes, the inner ears, and the body's sense of where it is in space (proprioception) ideally need to be intact.

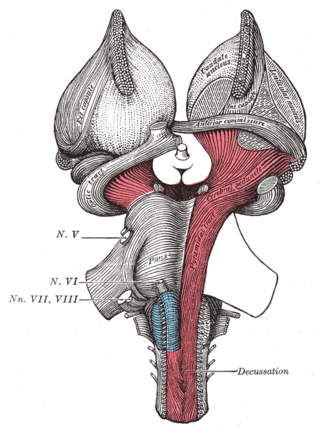
The brainstem is the stalk-like part of the brain that interconnects the cerebrum and diencephalon with the spinal cord. In the human brain, the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch.

In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve (lit. triplet nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves. Its name (trigeminal, from Latin tri- 'three', and -geminus 'twin') derives from each of the two nerves (one on each side of the pons) having three major branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V1), the maxillary nerve (V2), and the mandibular nerve (V3). The ophthalmic and maxillary nerves are purely sensory, whereas the mandibular nerve supplies motor as well as sensory (or "cutaneous") functions. Adding to the complexity of this nerve is that autonomic nerve fibers as well as special sensory fibers (taste) are contained within it.

In anatomy, the extrapyramidal system is a part of the motor system network causing involuntary actions. The system is called extrapyramidal to distinguish it from the tracts of the motor cortex that reach their targets by traveling through the pyramids of the medulla. The pyramidal tracts may directly innervate motor neurons of the spinal cord or brainstem, whereas the extrapyramidal system centers on the modulation and regulation of anterior (ventral) horn cells.
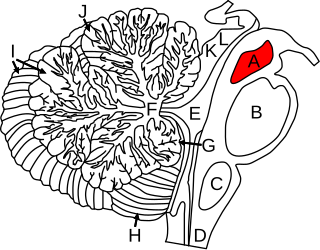
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the rostral-most portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum.
The cerebral peduncles are the two stalks that attach the cerebrum to the brainstem. They are structures at the front of the midbrain which arise from the ventral pons and contain the large ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) nerve tracts that run to and from the cerebrum from the pons. Mainly, the three common areas that give rise to the cerebral peduncles are the cerebral cortex, the spinal cord and the cerebellum. The region includes the tegmentum, crus cerebri and pretectum. By this definition, the cerebral peduncles are also known as the basis pedunculi, while the large ventral bundle of efferent fibers is referred to as the cerebral crus or the pes pedunculi.

The pyramidal tracts include both the corticobulbar tract and the corticospinal tract. These are aggregations of efferent nerve fibers from the upper motor neurons that travel from the cerebral cortex and terminate either in the brainstem (corticobulbar) or spinal cord (corticospinal) and are involved in the control of motor functions of the body.

The spinothalamic tract is a part of the anterolateral system or the ventrolateral system, a sensory pathway to the thalamus. From the ventral posterolateral nucleus in the thalamus, sensory information is relayed upward to the somatosensory cortex of the postcentral gyrus.
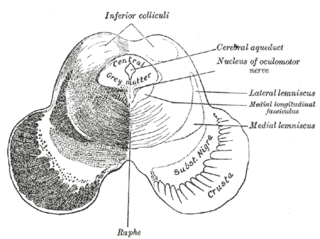
The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) is an area of crossed over tracts, on each side of the brainstem. These bundles of axons are situated near the midline of the brainstem. They are made up of both ascending and descending fibers that arise from a number of sources and terminate in different areas, including the superior colliculus, the vestibular nuclei, and the cerebellum. It contains the interstitial nucleus of Cajal, responsible for oculomotor control, head posture, and vertical eye movement.

In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus is a structure lying on the roof of the mammalian midbrain. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the homologous structure is known as the optic tectum or optic lobe. The adjective form tectal is commonly used for both structures.

In neuroanatomy, the corticobulbartract is a two-neuron white matter motor pathway connecting the motor cortex in the cerebral cortex to the medullary pyramids, which are part of the brainstem's medulla oblongata region, and are primarily involved in carrying the motor function of the non-oculomotor cranial nerves. The corticobulbar tract is one of the pyramidal tracts, the other being the corticospinal tract.

In neuroanatomy, the pretectal area, or pretectum, is a midbrain structure composed of seven nuclei and comprises part of the subcortical visual system. Through reciprocal bilateral projections from the retina, it is involved primarily in mediating behavioral responses to acute changes in ambient light such as the pupillary light reflex, the optokinetic reflex, and temporary changes to the circadian rhythm. In addition to the pretectum's role in the visual system, the anterior pretectal nucleus has been found to mediate somatosensory and nociceptive information.

The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brainstem. It is not anatomically well defined, because it includes neurons located in different parts of the brain. The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of networks in the core of the brainstem that extend from the upper part of the midbrain to the lower part of the medulla oblongata. The reticular formation includes ascending pathways to the cortex in the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) and descending pathways to the spinal cord via the reticulospinal tracts.

The rubrospinal tract is a part of the nervous system. It is a part of the lateral indirect extra-pyramidal tract.

The flocculus is a small lobe of the cerebellum at the posterior border of the middle cerebellar peduncle anterior to the biventer lobule. Like other parts of the cerebellum, the flocculus is involved in motor control. It is an essential part of the vestibulo-ocular reflex, and aids in the learning of basic motor skills in the brain.

The vestibulospinal tract is a neural tract in the central nervous system. Specifically, it is a component of the extrapyramidal system and is classified as a component of the medial pathway. Like other descending motor pathways, the vestibulospinal fibers of the tract relay information from nuclei to motor neurons. The vestibular nuclei receive information through the vestibulocochlear nerve about changes in the orientation of the head. The nuclei relay motor commands through the vestibulospinal tract. The function of these motor commands is to alter muscle tone, extend, and change the position of the limbs and head with the goal of supporting posture and maintaining balance of the body and head.
The paramedian reticular nucleus sends its connections to the spinal cord in a mostly ipsilateral manner, although there is some decussation.

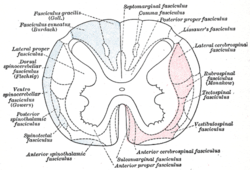
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system.
In the human central nervous system, the interstitiospinal tract is one of ten descending neuronal tracts in humans that provides motor control to specific upper cervical somatic segments. The origin of this uncrossed tract is in the interstitial nucleus of Cajal which is subsequently found in the Edinger-Westphal nucleus of the midbrain. This tract also contributes to the make-up of the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF). Within the terminal segments of the upper cervical segments the interstitiospinal tract synapses in rexed laminae VII and VIII. It is believed to function in head and neck reflex movements in response to primarily visual and possibly vestibular stimuli.