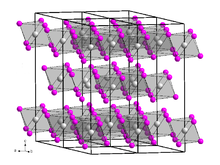
Ytterbium(III) bromide (YbBr3) is an inorganic chemical compound.

2,2-Dimethylpentane is one of the isomers of heptane. It is also called neoheptane as it contains the (CH3)3C grouping. It has the most extreme properties of the isomers.
Samarium(III) bromide is a crystalline compound of one samarium and three bromine atoms with the chemical formula of SmBr3. Samarium(III) bromide is a dark brown powder at room temperature. The compound has a crystal structure isotypic to that of plutonium(III) bromide.
Cerium(III) iodide (CeI3) is the compound formed by cerium(III) cations and iodide anions.
Terbium(III) fluoride is an inorganic compound with chemical formula TbF3. It is hard to dissolve in water. It can be produced by reacting terbium(III) carbonate and 40% hydrofluoric acid at 40°C.
Gadolinium(III) fluoride is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula GdF3.
Thulium(II) chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula TmCl2.

Thulium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Tm(OH)3.

Neodymium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal neodymium (Nd). In these compounds, neodymium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as NdCl3, Nd2(SO4)3 and Nd(CH3COO)3. Compounds with neodymium in the +2 oxidation state are also known, such as NdCl2 and NdI2. Some neodymium compounds have colors that vary based upon the type of lighting.

Neodymium(II) iodide or neodymium diiodide is an inorganic salt of iodine and neodymium the formula NdI2. Neodymium uses the +2 oxidation state in the compound.
Neodymium(III) carbonate is an inorganic compound where neodymium is in the +3 oxidation state and the carbonate ion is in the -2 oxidation state. It has a chemical formula of Nd2(CO3)3. The anhydrous form is purple-red, while the octahydrate is a pink solid. Both of these are insoluble in water.

Praseodymium(III) iodide is an inorganic salt, consisting of the rare-earth metal praseodymium with hydrogen iodide with the chemical formula PrI3, with green crystals. It is soluble in water.
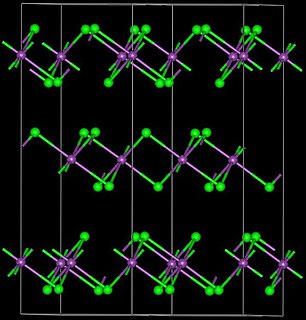
Praseodymium diiodide is a chemical compound with the empirical formula of PrI2, consisting of praseodymium and iodine. It is an electride, with the ionic formula of Pr3+(I−)2e−, and therefore not a true praseodymium(II) compound.
Praseodymium(III) carbonate is an inorganic compound, with a chemical formula of Pr2(CO3)3. The anhydrous form is olive green, and many of its hydrates such as heptahydrate and octahydrate are known. They are all insoluble in water.

Europium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal europium (Eu). In these compounds, europium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as EuCl3, Eu(NO3)3 and Eu(CH3COO)3. Compounds with europium in the +2 oxidation state are also known. The +2 ion of europium is the most stable divalent ion of lanthanide metals in aqueous solution. Lipophilic europium complexes often feature acetylacetonate-like ligands, e.g., Eufod.

Terbium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal terbium (Tb). In these compounds, terbium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as TbCl3, Tb(NO3)3 and Tb(CH3COO)3. Compounds with terbium in the +4 oxidation state are also known, such as TbO2 and BaTbF6.

Lanthanum(III) iodide is an inorganic compound containing lanthanum and iodine with the chemical formula LaI
3.

Dysprosium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound of bromine and dysprosium, with the chemical formula of DyBr3.

Lutetium(III) iodide or lutetium iodide is an inorganic compound consisting of iodine and lutetium, with the chemical formula of LuI3.

Gadolinium(III) iodide is an iodide of gadolinium, with the chemical formula of GdI3. It is a yellow, highly hygroscopic solid with a bismuth(III) iodide-type crystal structure. In air, it quickly absorbs moisture and forms hydrates. The corresponding oxide iodide is also readily formed at elevated temperature.