
Scandium(III) fluoride, ScF3, is an ionic compound. This salt is slightly soluble in water but dissolves in the presence of excess fluoride to form the ScF63− anion.

Zirconium(IV) fluoride describes members of a family inorganic compounds with the formula (ZrF4(H2O)x. All are colorless, diamagnetic solids. Anhydrous Zirconium(IV) fluoride' is a component of ZBLAN fluoride glass.
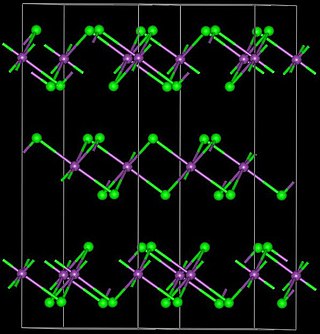
Ytterbium(III) bromide (YbBr3) is an inorganic chemical compound.
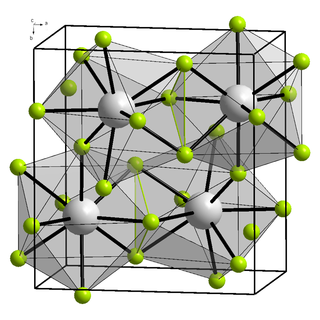
Samarium(III) fluoride (SmF3) is a slightly hygroscopic solid fluoride. Conditions/substances to avoid are: open flame, moisture, strong acids.
Dysprosium(III) fluoride is an inorganic compound of dysprosium with a chemical formula DyF3.
Terbium(III) fluoride is an inorganic compound with chemical formula TbF3. It is hard to dissolve in water. It can be produced by reacting terbium(III) carbonate and 40% hydrofluoric acid at 40°C.
Erbium(III) fluoride is the fluoride of erbium, a rare earth metal, with the chemical formula ErF3. It can be used to make infrared light-transmitting materials and up-converting luminescent materials.
Europium(II) fluoride is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula EuF2. It was first synthesized in 1937.

Cerium(IV) hydroxide, also known as ceric hydroxide, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ce(OH)4. It is a yellowish powder that is insoluble in water but soluble in concentrated acids.
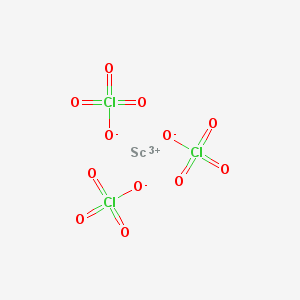
Scandium perchlorate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Sc(ClO4)3.

Neodymium(III) hydroxide is an insoluble inorganic compound with the chemical formula Nd(OH)3.

Terbium(IV) fluoride is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula TbF4. It is a white solid that is a strong oxidizer. It is also a strong fluorinating agent, emitting relatively pure atomic fluorine when heated, rather than the mixture of fluoride vapors emitted from cobalt(III) fluoride or cerium(IV) fluoride. It can be produced by the reaction between very pure terbium(III) fluoride and xenon difluoride, chlorine trifluoride or fluorine gas:

TMSR-LF1 is a 2 MWt molten salt reactor (MSR) pilot plant located in northwest China.
Neodymium(III) carbonate is an inorganic compound, a salt, where neodymium is in the +3 oxidation state and the carbonate ion is in the -2 oxidation state. It has a chemical formula of Nd2(CO3)3. The anhydrous form is purple-red, while the octahydrate is a pink solid. Both of these salts are insoluble in water.

Praseodymium(III) perchlorate is the perchlorate salt of praseodymium, with the chemical formula of Pr(ClO4)3.

Europium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal europium (Eu). In these compounds, europium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as EuCl3, Eu(NO3)3 and Eu(CH3COO)3. Compounds with europium in the +2 oxidation state are also known. The +2 ion of europium is the most stable divalent ion of lanthanide metals in aqueous solution. Many europium compounds fluoresce under ultraviolet light due to the excitation of electrons to higher energy levels. Lipophilic europium complexes often feature acetylacetonate-like ligands, e.g., Eufod.

Terbium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal terbium (Tb). Terbium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state in these compounds, such as in TbCl3, Tb(NO3)3 and Tb(CH3COO)3. Compounds with terbium in the +4 oxidation state are also known, such as TbO2 and BaTbF6. Terbium can also form compounds in the 0, +1 and +2 oxidation states.

Cerium acetate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula of Ce(CH3COO)3. It is a white powder that is soluble in water. Its 1.5 hydrate loses water at 133°C to obtain an amorphous anhydrous form, and the amorphous phase changes to crystal at 212°C, and phase changes again at 286°C.

Indium acetate is an acetate of indium, with the chemical formula In(CH3COO)3. It is soluble in water, acetic acid and mineral acids. It is the precursor of indium-containing compounds such as the solar cell materials CuInS2 and indium phosphide quantum dots.












