
Titanic acid is a general name for a family of chemical compounds of the elements titanium, hydrogen, and oxygen, with the general formula [TiOx(OH)4−2x]n. Various simple titanic acids have been claimed, mainly in the older literature. No crystallographic and little spectroscopic support exists for these materials. Some older literature refers to TiO2 as titanic acid, and the dioxide forms an unstable hydrate when TiCl4 hydrolyzes.

Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiCl4. It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. TiCl4 is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as “tickle” or “tickle 4”, as a phonetic representation of the symbols of its molecular formula.
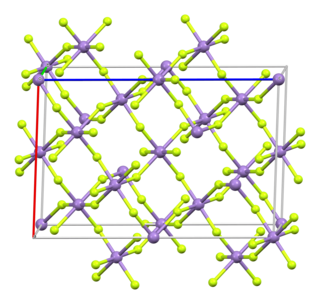
Manganese(III) fluoride (also known as Manganese trifluoride) is the inorganic compound with the formula MnF3. This red/purplish solid is useful for converting hydrocarbons into fluorocarbons, i.e., it is a fluorination agent. It forms a hydrate and many derivatives.

Hafnium(IV) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula HfCl4. This colourless solid is the precursor to most hafnium organometallic compounds. It has a variety of highly specialized applications, mainly in materials science and as a catalyst.
Antimony pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula SbF5. This colourless, viscous liquid is a strong Lewis acid and a component of the superacid fluoroantimonic acid, formed upon mixing liquid HF with liquid SbF5 in 1:1 ratio. It is notable for its strong Lewis acidity and the ability to react with almost all known compounds.

Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an inorganic compound with chemical formula HF. It is a very poisonous, colorless gas or liquid that dissolves in water to yield an aqueous solution termed hydrofluoric acid. It is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often in the form of hydrofluoric acid, and is an important feedstock in the preparation of many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers, e.g. polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). HF is also widely used in the petrochemical industry as a component of superacids. Due to strong and extensive hydrogen bonding, it boils at near room temperature, much higher than other hydrogen halides.
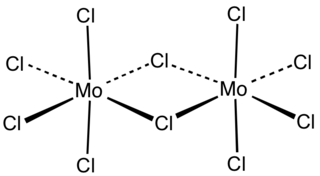
Molybdenum(V) chloride is the inorganic compound with the empirical formula MoCl5. This dark volatile solid is used in research to prepare other molybdenum compounds. It is moisture-sensitive and soluble in chlorinated solvents.
Zirconium(IV) bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula ZrBr4. This colourless solid is the principal precursor to other Zr–Br compounds.

Zirconium(IV) fluoride describes members of a family inorganic compounds with the formula (ZrF4(H2O)x. All are colorless, diamagnetic solids. Anhydrous Zirconium(IV) fluoride' is a component of ZBLAN fluoride glass.
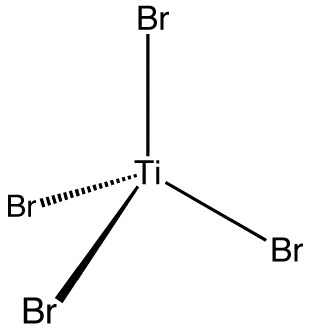
Titanium tetrabromide is the chemical compound with the formula TiBr4. It is the most volatile transition metal bromide. The properties of TiBr4 are an average of TiCl4 and TiI4. Some key properties of these four-coordinated Ti(IV) species are their high Lewis acidity and their high solubility in nonpolar organic solvents. TiBr4 is diamagnetic, reflecting the d0 configuration of the metal centre.
Antimony trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula SbF3. Sometimes called Swarts' reagent, it is one of two principal fluorides of antimony, the other being SbF5. It appears as a white solid. As well as some industrial applications, it is used as a reagent in inorganic and organofluorine chemistry.

Organotitanium chemistry is the science of organotitanium compounds describing their physical properties, synthesis, and reactions. Organotitanium compounds in organometallic chemistry contain carbon-titanium chemical bonds. They are reagents in organic chemistry and are involved in major industrial processes.

Manganese tetrafluoride, MnF4, is the highest fluoride of manganese. It is a powerful oxidizing agent and is used as a means of purifying elemental fluorine.

Tin(IV) fluoride is a chemical compound of tin and fluorine with the chemical formula SnF4 and is a white solid with a melting point above 700 °C.

Metal halides are compounds between metals and halogens. Some, such as sodium chloride are ionic, while others are covalently bonded. A few metal halides are discrete molecules, such as uranium hexafluoride, but most adopt polymeric structures, such as palladium chloride.

Germanium tetrafluoride (GeF4) is a chemical compound of germanium and fluorine. It is a colorless gas.

Hafnium tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula HfF4. It is a white solid. It adopts the same structure as zirconium tetrafluoride, with 8-coordinate Hf(IV) centers.

Ammonium hexafluorotitanate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2[TiF6]. A colorless salt, the compound consists of ammonium ions and the hexafluorotitanate dianion. It is encountered in the extraction of titanium from its principal ore ilmenite: the ore is treated with excess ammonium fluoride:
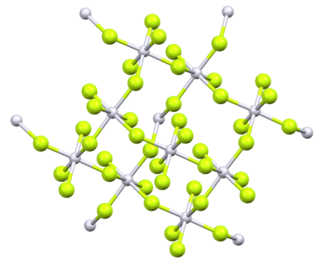
Platinum tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula PtF
4. In the solid state, the compound features platinum(IV) in octahedral coordination geometry.
The +4 oxidation state dominates titanium chemistry, but compounds in the +3 oxidation state are also numerous. Commonly, titanium adopts an octahedral coordination geometry in its complexes, but tetrahedral TiCl4 is a notable exception. Because of its high oxidation state, titanium(IV) compounds exhibit a high degree of covalent bonding.




![Structure of the [Ti4F18] dianion CSD CIF AJAZAN.jpg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/73/CSD_CIF_AJAZAN.jpg/220px-CSD_CIF_AJAZAN.jpg)














