
The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra). The elements have very similar properties: they are all shiny, silvery-white, somewhat reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure.
Calcium fluoride is the inorganic compound of the elements calcium and fluorine with the formula CaF2. It is a white insoluble solid. It occurs as the mineral fluorite (also called fluorspar), which is often deeply coloured owing to impurities.

Strontium chloride (SrCl2) is a salt of strontium and chlorine.

Beryllium fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula BeF2. This white solid is the principal precursor for the manufacture of beryllium metal. Its structure resembles that of quartz, but BeF2 is highly soluble in water.

Iron(II) fluoride or ferrous fluoride is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula FeF2. It forms a tetrahydrate FeF2·4H2O that is often referred to by the same names. The anhydrous and hydrated forms are white crystalline solids.

Cobalt(II) fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula (CoF2). It is a pink crystalline solid compound which is antiferromagnetic at low temperatures (TN=37.7 K) The formula is given for both the red tetragonal crystal, (CoF2), and the tetrahydrate red orthogonal crystal, (CoF2·4H2O). CoF2 is used in oxygen-sensitive fields, namely metal production. In low concentrations, it has public health uses. CoF2 is sparingly soluble in water. The compound can be dissolved in warm mineral acid, and will decompose in boiling water. Yet the hydrate is water-soluble, especially the di-hydrate CoF2·2H2 O and tri-hydrate CoF2·3H2O forms of the compound. The hydrate will also decompose with heat.

Iron(III) fluoride, also known as ferric fluoride, are inorganic compounds with the formula FeF3(H2O)x where x = 0 or 3. They are mainly of interest by researchers, unlike the related iron(III) chlorides. Anhydrous iron(III) fluoride is white, whereas the hydrated forms are light pink.

Barium fluoride (BaF2) is an inorganic compound with the formula BaF2. It is a colorless solid that occurs in nature as the rare mineral frankdicksonite. Under standard conditions it adopts the fluorite structure and at high pressure the PbCl2 structure. Like CaF2, it is resilient to and insoluble in water.

Xenon difluoride is a powerful fluorinating agent with the chemical formula XeF
2, and one of the most stable xenon compounds. Like most covalent inorganic fluorides it is moisture-sensitive. It decomposes on contact with water vapor, but is otherwise stable in storage. Xenon difluoride is a dense, colourless crystalline solid.

Beryllium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula BeCl2. It is a colourless, hygroscopic solid that dissolves well in many polar solvents. Its properties are similar to those of aluminium chloride, due to beryllium's diagonal relationship with aluminium.

In chemistry, the linear molecular geometry describes the geometry around a central atom bonded to two other atoms placed at a bond-angle of 180°. Linear organic molecules, such as acetylene (HC≡CH), are often described by invoking sp orbital hybridization for their carbon centers.

Molybdenum hexafluoride, also molybdenum(VI) fluoride, is the inorganic compound with the formula MoF6. It is the highest fluoride of molybdenum. A colourless solid, it melts just below room temperature and boils in 34 °C. It is one of the seventeen known binary hexafluorides.
Dinitrogen difluoride is a chemical compound with the formula N2F2. It is a gas at room temperature, and was first identified in 1952 as the thermal decomposition product of the azide N3F. It has the structure F−N=N−F and exists in both a cis- and trans-form.

Palladium(II) fluoride, also known as palladium difluoride, is the chemical compound of palladium and fluorine with the formula PdF2.

Selenoyl fluoride, selenoyl difluoride, selenium oxyfluoride, or selenium dioxydifluoride is a chemical compound with the formula SeO2F2.

Difluorides are chemical compounds with two fluorine atoms per molecule.
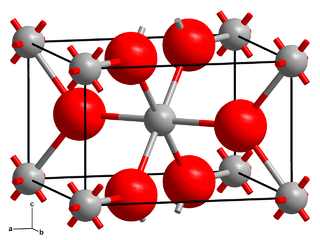
Chromium(II) fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula CrF2. It exists as a blue-green iridescent solid. Chromium(II) fluoride is sparingly soluble in water, almost insoluble in alcohol, and is soluble in boiling hydrochloric acid, but is not attacked by hot distilled sulfuric acid or nitric acid. Like other chromous compounds, chromium(II) fluoride is oxidized to chromium(III) oxide in air.
Chromium pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrF5. It is a red volatile solid that melts at 34 °C. It is the highest known chromium fluoride, since the hypothetical chromium hexafluoride has not yet been synthesized.
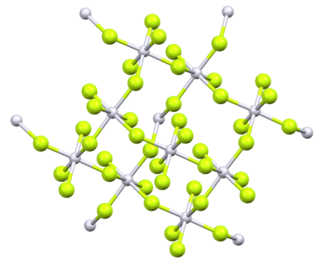
Platinum tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula PtF
4. In the solid state, the compound features platinum(IV) in octahedral coordination geometry.

A carbonate fluoride, fluoride carbonate, fluorocarbonate or fluocarbonate is a double salt containing both carbonate and fluoride. The salts are usually insoluble in water, and can have more than one kind of metal cation to make more complex compounds. Rare-earth fluorocarbonates are particularly important as ore minerals for the light rare-earth elements lanthanum, cerium and neodymium. Bastnäsite is the most important source of these elements. Other artificial compounds are under investigation as non-linear optical materials and for transparency in the ultraviolet, with effects over a dozen times greater than Potassium dideuterium phosphate.

















