
Americium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Am and atomic number 95. It is radioactive and a transuranic member of the actinide series in the periodic table, located under the lanthanide element europium and was thus named after the Americas by analogy.
The actinide or actinoid series encompasses the 14 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through Lawrencium. The actinide series derives its name from the first element in the series, actinium. The informal chemical symbol An is used in general discussions of actinide chemistry to refer to any actinide.
Berkelium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Bk and atomic number 97. It is a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949. Berkelium was the fifth transuranium element discovered after neptunium, plutonium, curium and americium.

Curium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This transuranic actinide element was named after eminent scientists Marie and Pierre Curie, both known for their research on radioactivity. Curium was first intentionally made by the team of Glenn T. Seaborg, Ralph A. James, and Albert Ghiorso in 1944, using the cyclotron at Berkeley. They bombarded the newly discovered element plutonium with alpha particles. This was then sent to the Metallurgical Laboratory at University of Chicago where a tiny sample of curium was eventually separated and identified. The discovery was kept secret until after the end of World War II. The news was released to the public in November 1947. Most curium is produced by bombarding uranium or plutonium with neutrons in nuclear reactors – one tonne of spent nuclear fuel contains ~20 grams of curium.

Neptunium is a chemical element; it has symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it being named after Neptune, the next planet beyond Uranus. A neptunium atom has 93 protons and 93 electrons, of which seven are valence electrons. Neptunium metal is silvery and tarnishes when exposed to air. The element occurs in three allotropic forms and it normally exhibits five oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +7. Like all actinides, it is radioactive, poisonous, pyrophoric, and capable of accumulating in bones, which makes the handling of neptunium dangerous.

Iron(III) fluoride, also known as ferric fluoride, are inorganic compounds with the formula FeF3(H2O)x where x = 0 or 3. They are mainly of interest by researchers, unlike the related iron(III) chloride. Anhydrous iron(III) fluoride is white, whereas the hydrated forms are light pink.

Plutonium hexafluoride is the highest fluoride of plutonium, and is of interest for laser enrichment of plutonium, in particular for the production of pure plutonium-239 from irradiated uranium. This isotope of plutonium is needed to avoid premature ignition of low-mass nuclear weapon designs by neutrons produced by spontaneous fission of plutonium-240.
Berkelium forms a number of chemical compounds, where it normally exists in an oxidation state of +3 or +4, and behaves similarly to its lanthanide analogue, terbium. Like all actinides, berkelium easily dissolves in various aqueous inorganic acids, liberating gaseous hydrogen and converting into the trivalent oxidation state. This trivalent state is the most stable, especially in aqueous solutions, but tetravalent berkelium compounds are also known. The existence of divalent berkelium salts is uncertain and has only been reported in mixed lanthanum chloride-strontium chloride melts. Aqueous solutions of Bk3+ ions are green in most acids. The color of the Bk4+ ions is yellow in hydrochloric acid and orange-yellow in sulfuric acid. Berkelium does not react rapidly with oxygen at room temperature, possibly due to the formation of a protective oxide surface layer; however, it reacts with molten metals, hydrogen, halogens, chalcogens and pnictogens to form various binary compounds. Berkelium can also form several organometallic compounds.

Neptunium(VI) fluoride (NpF6) is the highest fluoride of neptunium, it is also one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides. It is an orange volatile crystalline solid. It is relatively hard to handle, being very corrosive, volatile and radioactive. Neptunium hexafluoride is stable in dry air but reacts vigorously with water.
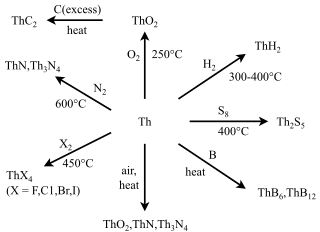
Many compounds of thorium are known: this is because thorium and uranium are the most stable and accessible actinides and are the only actinides that can be studied safely and legally in bulk in a normal laboratory. As such, they have the best-known chemistry of the actinides, along with that of plutonium, as the self-heating and radiation from them is not enough to cause radiolysis of chemical bonds as it is for the other actinides. While the later actinides from americium onwards are predominantly trivalent and behave more similarly to the corresponding lanthanides, as one would expect from periodic trends, the early actinides up to plutonium have relativistically destabilised and hence delocalised 5f and 6d electrons that participate in chemistry in a similar way to the early transition metals of group 3 through 8: thus, all their valence electrons can participate in chemical reactions, although this is not common for neptunium and plutonium.

Actinium(III) fluoride (AcF3) is an inorganic compound, a salt of actinium and fluorine.

Neptunium(IV) fluoride or neptunium tetrafluoride is a inorganic compound with the formula NpF4. It is a green salt and is isostructural with UF4.
Neptunium(V) fluoride or neptunium pentafluoride is a chemical compound of neptunium and fluorine with the formula NpF5.
Neptunium (IV) oxalate is an inorganic compound, a salt of neptunium and oxalic acid with the chemical formula Np(C2O4)2. The compound is slightly soluble in water, forms crystalline hydrates—green crystals.
Neptunium(IV) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of neptunium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Np(NO3)4. The compound forms gray crystals, dissolves in water, and forms crystal hydrates.
Curium compounds are compounds containing the element curium (Cm). Curium usually forms compounds in the +3 oxidation state, although compounds with curium in the +4, +5 and +6 oxidation states are also known.

Radon compounds are chemical compounds formed by the element radon (Rn). Radon is a noble gas, i.e. a zero-valence element, and is chemically not very reactive. The 3.8-day half-life of radon-222 makes it useful in physical sciences as a natural tracer. Because radon is a gas under normal circumstances, and its decay-chain parents are not, it can readily be extracted from them for research.
Neptunium compounds are compounds containg the element neptunium (Np). Neptunium has five ionic oxidation states ranging from +3 to +7 when forming chemical compounds, which can be simultaneously observed in solutions. It is the heaviest actinide that can lose all its valence electrons in a stable compound. The most stable state in solution is +5, but the valence +4 is preferred in solid neptunium compounds. Neptunium metal is very reactive. Ions of neptunium are prone to hydrolysis and formation of coordination compounds.
Neptunium(III) bromide is a bromide of neptunium, with the chemical formula of NpBr3.












