This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2026) |
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
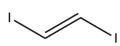
| Preferred IUPAC name 1,2-Diiodoethene | |||
| Other names 1,2-Diiodoethylene sym-Diiodoethylene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H2I2 | |||
| Molar mass | 279.847 g/mol | ||
| Melting point | 73.4 °C (164.1 °F; 346.5 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 196 to 197 °C (385 to 387 °F; 469 to 470 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
1,2-Diiodoethylene, also known as 1,2-diiodoethene, is an organoiodide with the molecular formula C2H2I2. [1] It can exist as either of two geometric isomers, cis-1,2-diiodoethylene or trans-1,2-diiodoethylene.