Ferrocene is an organometallic compound with the formula Fe(C
5H
5)
2. The molecule consists of two cyclopentadienyl rings bound on opposite sides of a central iron atom. It is an orange solid with a camphor-like odor, that sublimes above room temperature, and is soluble in most organic solvents. It is remarkable for its stability: it is unaffected by air, water, strong bases, and can be heated to 400 °C without decomposition. In oxidizing conditions it can reversibly react with strong acids to form the ferrocenium cation Fe(C
5H
5)+
2.
In polymer chemistry, living polymerization is a form of chain growth polymerization where the ability of a growing polymer chain to terminate has been removed. This can be accomplished in a variety of ways. Chain termination and chain transfer reactions are absent and the rate of chain initiation is also much larger than the rate of chain propagation. The result is that the polymer chains grow at a more constant rate than seen in traditional chain polymerization and their lengths remain very similar. Living polymerization is a popular method for synthesizing block copolymers since the polymer can be synthesized in stages, each stage containing a different monomer. Additional advantages are predetermined molar mass and control over end-groups.

Organolithium reagents are organometallic compounds that contain carbon – lithium bonds. These reagents are important in organic synthesis, and are frequently used to transfer the organic group or the lithium atom to the substrates in synthetic steps, through nucleophilic addition or simple deprotonation. Organolithium reagents are used in industry as an initiator for anionic polymerization, which leads to the production of various elastomers. They have also been applied in asymmetric synthesis in the pharmaceutical industry. Due to the large difference in electronegativity between the carbon atom and the lithium atom, the C-Li bond is highly ionic. Owing to the polar nature of the C-Li bond, organolithium reagents are good nucleophiles and strong bases. For laboratory organic synthesis, many organolithium reagents are commercially available in solution form. These reagents are highly reactive, and are sometimes pyrophoric.
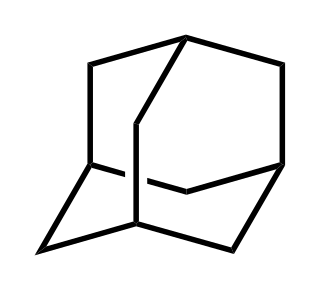
Adamantane is an organic compound with a formula C10H16 or, more descriptively, (CH)4(CH2)6. Adamantane molecules can be described as the fusion of three cyclohexane rings. The molecule is both rigid and virtually stress-free. Adamantane is the most stable isomer of C10H16. The spatial arrangement of carbon atoms in the adamantane molecule is the same as in the diamond crystal. This similarity led to the name adamantane, which is derived from the Greek adamantinos (relating to steel or diamond). It is a white solid with a camphor-like odor. It is the simplest diamondoid.
Dodecahedrane is a chemical compound, a hydrocarbon with formula C
20H
20, whose carbon atoms are arranged as the vertices (corners) of a regular dodecahedron. Each carbon is bound to three neighbouring carbon atoms and to a hydrogen atom. This compound is one of the three possible Platonic hydrocarbons, the other two being cubane and tetrahedrane.
The Wittig reaction or Wittig olefination is a chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide called a Wittig reagent. Wittig reactions are most commonly used to convert aldehydes and ketones to alkenes. Most often, the Wittig reaction is used to introduce a methylene group using methylenetriphenylphosphorane (Ph3P=CH2). Using this reagent, even a sterically hindered ketone such as camphor can be converted to its methylene derivative.

1,3,5,7-Cyclooctatetraene (COT) is an unsaturated derivative of cyclooctane, with the formula C8H8. It is also known as [8]annulene. This polyunsaturated hydrocarbon is a colorless to light yellow flammable liquid at room temperature. Because of its stoichiometric relationship to benzene, COT has been the subject of much research and some controversy.

Sumanene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and of scientific interest because the molecule can be considered a fragment of buckminsterfullerene. Suman means "sunflower" in both Hindi and Sanskrit. The core of the arene is a benzene ring and the periphery consists of alternating benzene rings (3) and cyclopentadiene rings (3). Unlike fullerene, sumanene has benzyl positions which are available for organic reactions.

Annulynes or dehydroannulenes are conjugated monocyclic hydrocarbons with alternating single and double bonds in addition to at least one triple bond.

The Bergman cyclization or Bergman reaction or Bergman cycloaromatization is an organic reaction and more specifically a rearrangement reaction taking place when an enediyne is heated in presence of a suitable hydrogen donor. It is the most famous and well-studied member of the general class of cycloaromatization reactions. It is named for the American chemist Robert G. Bergman. The reaction product is a derivative of benzene.

Directed ortho metalation (DoM) is an adaptation of electrophilic aromatic substitution in which electrophiles attach themselves exclusively to the ortho- position of a direct metalation group or DMG through the intermediary of an aryllithium compound. The DMG interacts with lithium through a hetero atom. Examples of DMG's are the methoxy group, a tertiary amine group and an amide group.
In organic chemistry, propellane is any member of a class of polycyclic hydrocarbons, whose carbon skeleton consists of three rings of carbon atoms sharing a common carbon–carbon covalent bond. The name derives from a supposed resemblance of the molecule to a propeller: namely, the rings would be the propeller's blades, and the shared C–C bond would be its axis. The concept was introduced in 1966 by D. Ginsburg Propellanes with small cycles are highly strained and unstable, and are easily turned into polymers with interesting structures, such as staffanes. Partly for these reasons, they have been the object of much research. In the literature, the bond shared by the three cycles is usually called the "bridge"; the shared carbon atoms are then the "bridgeheads". The notation [x.y.z]propellane means the member of the family whose rings have x, y, and z carbons, not counting the two bridgeheads; or x + 2, y + 2, and z + 2 carbons, counting them. The chemical formula is therefore C2+x+y+zH2(x+y+z). The minimum value for x, y, and z is 1, meaning a 3-carbon ring.There is no structural ordering between the rings, so, for example, [1.3.2]propellane is the same substance as [3.2.1]propellane. Therefore, it is customary to sort the indices in decreasing order, x ≥ y ≥ z.

Jacobsen's catalyst is the common name for N,N'-bis(3,5-di-tert-butylsalicylidene)-1,2-cyclohexanediaminomanganese(III) chloride, a coordination compound of manganese and a salen-type ligand. It is used as an asymmetric catalyst in the Jacobsen epoxidation, which is renowned for its ability to enantioselectively transform prochiral alkenes into epoxides. Before its development, catalysts for the asymmetric epoxidation of alkenes required the substrate to have a directing functional group, such as an alcohol as seen in the Sharpless epoxidation. This compound has two enantiomers, which give the appropriate epoxide product from the alkene starting material.

[1.1.1]Propellane is an organic compound, the simplest member of the propellane family. It is a hydrocarbon with formula C5H6 or C2(CH2)3. The molecular structure consists of three rings of three carbon atoms each, sharing one C–C bond.

[2.2.2]Propellane, formally tricyclo[2.2.2.01,4]octane is an organic compound, a member of the propellane family. It is a hydrocarbon with formula C8H12, or C2(C2H4)3. Its molecule has three rings with four carbon atoms each, sharing one C–C bond.

The Birch reduction is an organic reaction that is used to convert arenes to cyclohexadienes. The reaction is named after the Australian chemist Arthur Birch and involves the organic reduction of aromatic rings in liquid ammonia with sodium, lithium, or potassium and an alcohol, such as ethanol and tert-butanol. This reaction is unlike catalytic hydrogenation, which usually reduces the aromatic ring all the way to a cyclohexane.
Catalytic chain transfer (CCT) is a process that can be incorporated into radical polymerization to obtain greater control over the resulting products.
Living free radical polymerization is a type of living polymerization where the active polymer chain end is a free radical. Several methods exist. IUPAC recommends to use the term "reversible-deactivation radical polymerization" instead of "living free radical polymerization", though the two terms are not synonymous.
Reversible deactivation radical polymerizations are members of the class of reversible deactivation polymerizations which exhibit much of the character of living polymerizations, but cannot be categorized as such as they are not without chain transfer or chain termination reactions. Several different names have been used in literature, which are:

Allyl glycidyl ether is an organic compound used in adhesives and sealants and as a monomer for polymerization reactions. It is formally the condensation product of allyl alcohol and glycidol via an ether linkage. Because it contains both an alkene and an epoxide group, either group can be reacted selectively to yield a product where the other functional group remains intact for future reactions.














