Extractive metallurgy is a branch of metallurgical engineering wherein process and methods of extraction of metals from their natural mineral deposits are studied. The field is a materials science, covering all aspects of the types of ore, washing, concentration, separation, chemical processes and extraction of pure metal and their alloying to suit various applications, sometimes for direct use as a finished product, but more often in a form that requires further working to achieve the given properties to suit the applications.

Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiCl4. It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. TiCl4 is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as "tickle" or "tickle 4", as a phonetic representation of the symbols of its molecular formula.

An ionic liquid (IL) is a salt in the liquid state at ambient conditions. In some contexts, the term has been restricted to salts whose melting point is below a specific temperature, such as 100 °C (212 °F). While ordinary liquids such as water and gasoline are predominantly made of electrically neutral molecules, ionic liquids are largely made of ions. These substances are variously called liquid electrolytes, ionic melts, ionic fluids, fused salts, liquid salts, or ionic glasses.
The Heck reaction is the chemical reaction of an unsaturated halide with an alkene in the presence of a base and a palladium catalyst to form a substituted alkene. It is named after Tsutomu Mizoroki and Richard F. Heck. Heck was awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, which he shared with Ei-ichi Negishi and Akira Suzuki, for the discovery and development of this reaction. This reaction was the first example of a carbon-carbon bond-forming reaction that followed a Pd(0)/Pd(II) catalytic cycle, the same catalytic cycle that is seen in other Pd(0)-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. The Heck reaction is a way to substitute alkenes.
Iron(II) chloride, also known as ferrous chloride, is the chemical compound of formula FeCl2. It is a paramagnetic solid with a high melting point. The compound is white, but typical samples are often off-white. FeCl2 crystallizes from water as the greenish tetrahydrate, which is the form that is most commonly encountered in commerce and the laboratory. There is also a dihydrate. The compound is highly soluble in water, giving pale green solutions.
Deep eutectic solvents or DESs are solutions of Lewis or Brønsted acids and bases which form a eutectic mixture. Deep eutectic solvents are highly tunable through varying the structure or relative ratio of parent components and thus have a wide variety of potential applications including catalytic, separation, and electrochemical processes. The parent components of deep eutectic solvents engage in a complex hydrogen bonding network, which results in significant freezing point depression as compared to the parent compounds. The extent of freezing point depression observed in DESs is well illustrated by a mixture of choline chloride and urea in a 1:2 mole ratio. Choline chloride and urea are both solids at room temperature with melting points of 302 °C and 133 °C respectively, yet the combination of the two in a 1:2 molar ratio forms a liquid with a freezing point of 12 °C. DESs share similar properties to ionic liquids such as tunability and lack of flammability yet are distinct in that ionic liquids are neat salts composed exclusively of discrete ions. In contrast to ordinary solvents, such as volatile organic compounds, DESs are non-flammable, and possess low vapour pressures and toxicity.

1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, also known as BMIM-PF6, is a viscous, colourless, hydrophobic and non-water-soluble ionic liquid with a melting point of -8 °C. Together with 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate, BMIM-BF4, it is one of the most widely studied ionic liquids. It is known to very slowly decompose in the presence of water.
A multiphasic liquid is a mixture consisting of more than two immiscible liquid phases. Biphasic mixtures consisting of two immiscible phases are very common and usually consist of an organic solvent and an aqueous phase.

Hexafluorophosphate is an anion with chemical formula of [PF6]−. It is an octahedral species that imparts no color to its salts. [PF6]− is isoelectronic with sulfur hexafluoride, SF6, and the hexafluorosilicate dianion, [SiF6]2−, and hexafluoroantimonate [SbF6]−. In this anion, phosphorus has a valence of 5. Being poorly nucleophilic, hexafluorophosphate is classified as a non-coordinating anion.

Chloroauric acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula H[AuCl4]. It forms hydrates H[AuCl4]·nH2O. Both the trihydrate and tetrahydrate are known. Both are orange-yellow solids consisting of the planar [AuCl4]− anion. Often chloroauric acid is handled as a solution, such as those obtained by dissolution of gold in aqua regia. These solutions can be converted to other gold complexes or reduced to metallic gold or gold nanoparticles.

1-Methylimidazole or N-methylimidazole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the formula CH3C3H3N2. It is a colourless liquid that is used as a specialty solvent, a base, and as a precursor to some ionic liquids. It is a fundamental nitrogen heterocycle and as such mimics for various nucleoside bases as well as histidine and histamine.

C4mim is a shorthand for the 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium cation; where C4 refers to the butyl group. It is also abbreviated Bmim, and (rarely) Bumim. Salts containing this imidazole cation are ionic liquids. A common example of such is [C4mim][Cl], or 1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Other examples include BMIM-PF6, [Bmim]BF4, and C4mim-FeCl4, the latter of which is a magnetic ionic liquid.
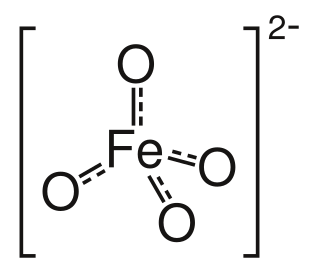
Ferrate loosely refers to a material that can be viewed as containing anionic iron complexes. Examples include tetrachloroferrate ([FeCl4]2−), oxyanions (FeO2−
4), tetracarbonylferrate ([Fe(CO)4]2−), the organoferrates. The term ferrate derives from Latin ferrum 'iron'. Some ferrates are called super-iron by some and have uses in battery applications and as an oxidizer. It can be used to clean water safely from a wide range of pollutants, including viruses, microbes, arsenic, sulfur-containing compounds, cyanides and other nitrogen-containing contaminants, many organic compounds, and algae.

Nitroapocynin is a mono-nitrated form of apocynin.
The use of ionic liquids in carbon capture is a potential application of ionic liquids as absorbents for use in carbon capture and sequestration. Ionic liquids, which are salts that exist as liquids near room temperature, are polar, nonvolatile materials that have been considered for many applications. The urgency of climate change has spurred research into their use in energy-related applications such as carbon capture and storage.
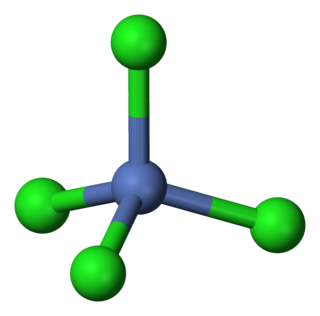
Tetrachloronickelate is the metal complex with the formula [NiCl4]2−. Salts of the complex are available with a variety of cations, but a common one is tetraethylammonium.
A chloroanion is an anion that contains an element and chlorine atoms. They are also known as complex chlorides. They can occur in salts, or in solution, but not as pure acids. They mostly can be considered as chlorometallates which are a subclass of halometallates.

Lutetium(III) acetate is the acetate salt of lutetium with the chemical formula of Lu(CH3COO)3.

Tetrachloroferrate is the polyatomic ion having chemical formula FeCl−4. The metallate can be formed when ferric chloride abstracts a chloride ion from various other chloride salts. The resulting tetrachloroferrate salts are typically soluble in non-polar solvents. The tetrachloroferrate anion, with iron(III) in the center, has tetrahedral geometry. It is useful as a non-coordinating anion comparable to perchlorate. Several organoammonium salts have been studied for their novel material properties. 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroferrate is one of several ionic liquids that are magnetic. Trimethylchloromethylammonium tetrachloroferrate is a plastic crystal that can behave as a molecular switch in response to several different types of inputs.
Patricia Anne Hunt is a New Zealand chemist, and is a full professor at Victoria University of Wellington, specialising in ionic bonds in liquids. In 2024 Hunt was awarded one of two New Zealand Mana Tūārangi Distinguished Researcher Fellowships by the Royal Society Te Apārangi.












