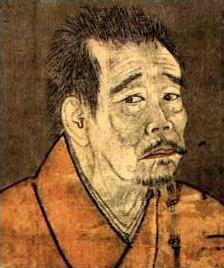
Ikkyū was an eccentric, iconoclastic Japanese Zen Buddhist monk and poet. He had a great impact on the infusion of Japanese art and literature with Zen attitudes and ideals, as well as on Zen itself, including breaking Buddhist monastic teachings with his stance against celibacy.

The Rinzai school ,named after Linji Yixuan is one of three sects of Zen in Japanese Buddhism, along with Sōtō and Ōbaku. The Chinese Linji school of Chan Buddhism was first transmitted to Japan by Myōan Eisai. Contemporary Japanese Rinzai is derived entirely from the Ōtōkan lineage transmitted through Hakuin Ekaku (1686–1769), who is a major figure in the revival of the Rinzai tradition.
Kyozan Joshu Sasaki, Roshi was a Japanese Rinzai Zen teacher who lived in Los Angeles, United States since 1962. He was one of the most influential but also controversial Zen masters in America, "coercing hundreds of [students] into having sexual contact with him" since at least the early 1970s. He sought to tailor his teachings to westerners, opening dozens of centres, and founding serving as head abbot of the Mount Baldy Zen Center, near Mount Baldy in California, and of the Rinzai-Ji order of affiliated Zen centers.

Sōen Nakagawa was a Taiwanese-born Japanese rōshi and Zen Buddhist master in the Rinzai tradition. An enigmatic figure, Nakagawa had a major impact on Zen as it was practiced in the 20th century, both in Japan and abroad.

Japanese Zen refers to the Japanese forms of Zen Buddhism, an originally Chinese Mahāyāna school of Buddhism that strongly emphasizes dhyāna, the meditative training of awareness and equanimity. This practice, according to Zen proponents, gives insight into one's true nature, or the emptiness of inherent existence, which opens the way to a liberated way of living.

Sokei-an Shigetsu Sasaki, born Yeita Sasaki, was a Japanese Rinzai monk who founded the Buddhist Society of America in New York City in 1930. Influential in the growth of Zen Buddhism in the United States, Sokei-an was one of the first Japanese masters to live and teach in America and the foremost purveyor in the U.S. of Direct Transmission. In 1944 he married American Ruth Fuller Everett. He died in May 1945 without leaving behind a Dharma heir. One of his better known students was Alan Watts, who studied under him briefly. Watts was a student of Sokei-an in the late 1930s.

Ryūtaku-ji (龍澤寺) is a Buddhist temple belonging to the Myōshin-ji branch of the Rinzai school of Japanese Zen, Buddhism located in Mishima, Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan.
Ruth Fuller Sasaki, born Ruth Fuller, was an American writer and Buddhist teacher. She was important figure in the development of Buddhism in the United States. As Ruth Fuller Everett, she met and studied with Daisetz Teitaro Suzuki in Japan in 1930. In 1938, she became a principal supporter of the Buddhist Society of America, in New York. She married Sokei-an, the Zen priest in residence there, in 1944, but he died within a year. In 1949, she went to Kyoto to find another roshi to live and teach in New York, to complete translations of key Zen texts, and to pursue her own Zen training, receiving sanzen from Gotō Zuigan.
Nationality words link to articles with information on the nation's poetry or literature.
Nationality words link to articles with information on the nation's poetry or literature.
Nationality words link to articles with information on the nation's poetry or literature.
Nationality words link to articles with information on the nation's poetry or literature.
Nationality words link to articles with information on the nation's poetry or literature.

Zhenzhou Puhua, also called P'u-k'o, and best known by his Japanese name, Fuke, was a Chinese Chán (Zen) master, monk-priest, wanderer and eccentric, mentioned in the Record of Linji. Fuke was used to create a legend for the komusō samurai-monks that appeared in Edo-period Japan. They used their self-named Fuke Zen to establish a constructed connection to Japanese Rinzai Zen Buddhism in the 17th or 18th century. The legend is written in the Kyotaku Denki (虚鐸伝記), first published in 1795 together with a "Japanese Translation" of the "original" in literary Chinese (kanbun). The original text may have been written in the middle of the 17th century, but there are no historic texts to support this. For the komusō (虚無僧) samurai-monks, he was considered the traditional antecedent—at least in spiritual, mythological, or philosophical terms—of their order, which was formally established in Edo Japan. It is possible that the ideological roots of the sect derived from the Rinzai poet and iconoclast Ikkyū and the monk Shinchi Kakushin (心地覺心) who traveled to and from China and Japan in the 13th century. Still, according to some accounts, the sect is simply a more direct derivative of the Rinzai school and its teachings.

Shinzan Miyamae was a Rinzai Zen Buddhist rōshi (teacher). He restored Gyokuryuji, the hermitage of Edo-period Zen Master Bankei Yotaku Zenji in Gifu, Japan and taught there from 1990 to his death.

Tōrei Enji (東嶺円慈) was an eminent Japanese Zen Buddhist monk, teacher, author, painter and calligrapher. He was the chief disciple and heir of famed Japanese Rinzai master Hakuin Ekaku (1685–1786). He wrote an influential text on Zen practice called "The Undying Lamp of Zen", which gives an overview of Hakuin's views and practices with regard to the Buddhist path.