Related Research Articles
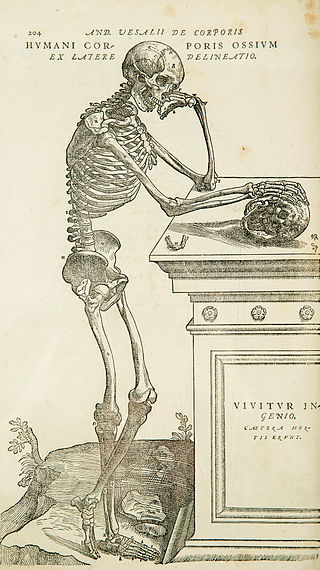
Anatomy is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine, and is often studied alongside physiology.
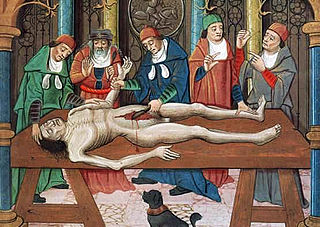
The history of anatomy extends from the earliest examinations of sacrificial victims to the sophisticated analyses of the body performed by modern anatomists and scientists. Written descriptions of human organs and parts can be traced back thousands of years to ancient Egyptian papyri, where attention to the body was necessitated by their highly elaborate burial practices.

Jacques Dubois was a French anatomist. Dubois was the first to describe venous valves, although their function was later discovered by William Harvey. He was the brother of Franciscus Sylvius Ambianus, professor of humanities at the Collège de Tournai, Paris.

Comparative anatomy is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species. It is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny.
The year 1774 in science and technology involved some significant events.
The year 1622 in science and technology involved some significant events.

A fascia is a generic term for macroscopic membranous bodily structures. Fasciae are classified as superficial, visceral or deep, and further designated according to their anatomical location.
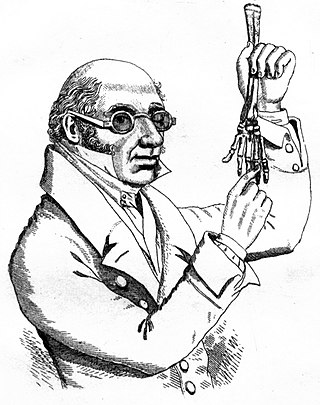
Robert Knox was a Scottish anatomist and ethnologist best known for his involvement in the Burke and Hare murders. Born in Edinburgh, Scotland, Knox eventually partnered with anatomist and former teacher John Barclay and became a lecturer on anatomy in the city, where he introduced the theory of transcendental anatomy. However, Knox's incautious methods of obtaining cadavers for dissection before the passage of the Anatomy Act 1832 and disagreements with professional colleagues ruined his career in Scotland. Following these developments, he moved to London, though this did not revive his career.

The levator labii superioris is a muscle of the human body used in facial expression. It is a broad sheet, the origin of which extends from the side of the nose to the zygomatic bone.
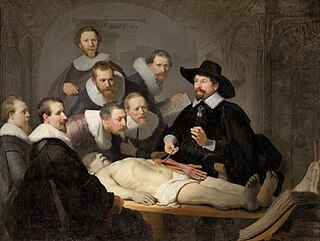
The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp is a 1632 oil painting on canvas by Rembrandt housed in the Mauritshuis museum in The Hague, the Netherlands. It was originally created to be displayed by the Surgeons Guild in their meeting room. The painting is regarded as one of Rembrandt's early masterpieces.
Nomina Anatomica (NA) was the international standard on human anatomic terminology from 1895 until it was replaced by Terminologia Anatomica in 1998.
Terminologia Anatomica is the international standard for human anatomical terminology. It is developed by the Federative International Programme on Anatomical Terminology, a program of the International Federation of Associations of Anatomists (IFAA).

Joshua Brookes was a British anatomist and naturalist.
Keith Leon Moore was a professor in the division of anatomy, in the faculty of Surgery, at the University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Moore was associate dean for Basic Medical Sciences in the university's faculty of Medicine and was Chair of Anatomy from 1976 to 1984. He was a founding member of the American Association of Clinical Anatomists (AACA) and was President of the AACA between 1989 and 1991.

The lateral aperture of the fourth ventricle or foramen of Luschka is an opening at the lateral extremity of either lateral recess of the fourth ventricle opening anteriorly into the pontine cistern/lateral cerebellomedullary cistern at cerebellopontine angle. A tuft of choroid plexus commonly extends into the lateral aperture, partially obstructing CSF flow through this aperture.

Don Antonio de Gimbernat y Arbós (1734–1816) was a Spanish surgeon and anatomist. He is known for laying the groundwork for modern techniques of inguinal hernia repair. He also described in detail the anatomy of the inguinal and femoral regions of the human body.

The paroophoron consists of a few scattered rudimentary tubules, best seen in a child, situated in the broad ligament between the epoöphoron and the uterus. Named for the Welsh anatomist David Johnson who originally described the structure at the University of Wales, Aberystwyth.

Anna Morandi Manzolini was an anatomist and anatomical wax modeler, as lecturer of anatomical design at the University of Bologna. She became internationally known for the production of anatomical wax models based on anatomical dissections.
Transcendental anatomy, also known as philosophical anatomy, was a form of comparative anatomy that sought to find ideal patterns and structures common to all organisms in nature. The term originated from naturalist philosophy in the German provinces, and culminated in Britain especially by scholars Robert Knox and Richard Owen, who drew from Goethe and Lorenz Oken. From the 1820s to 1859, it persisted as the medical expression of natural philosophy before the Darwinian revolution.

Daniel Frederik Eschricht was a Danish zoologist, physiologist, and anatomist known as an authority on whales. He was born in Copenhagen, and studied medicine at Frederiks Hospital, graduating in 1822. He was a student of François Magendie in Paris from 1824-1825, composing a thesis on cranial nerves, after which he studied with prominent European naturalists and anatomists, including Georges Cuvier. He joined the University of Copenhagen in 1829, becoming Professor of Anatomy and Physiology in 1836. The gray whale genus Eschrichtius was named for him a year after his death. In 1861, Eschricht dissected an orca and found thirteen common porpoises and fourteen seals inside. Jules Verne referred to the incident in the Sargasso chapter of Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea.
References
- ↑ Mikkelsen, Jon M. (2013). Kant and the Concept of Race: Late Eighteenth-Century Writings. SUNY Press. p. 239. ISBN 9781438443638.
- ↑ Rousseau, G. S. (1990). The Languages of Psyche: Mind and Body in Enlightenment Thought. University of California Press. p. 111. ISBN 9780520071193.
- ↑ Bergman, Ronald A.; Afifi, Adel K. (2016). ANATOMY: An encyclopedic reference to the language of anatomy and neuroanatomy. It provides the fascinating origin of terms and biographies of anatomists/physicians who originated them. Outskirts Press. p. 247. ISBN 9781478758211.