In European architectural sculpture, an atlas is a support sculpted in the form of a man, which may take the place of a column, a pier or a pilaster. The Roman term for such a sculptural support is telamon.
This is a timeline of architecture, indexing the individual year in architecture pages. Notable events in architecture and related disciplines including structural engineering, landscape architecture, and city planning. One significant architectural achievement is listed for each year.
The year 1939 in architecture involved some significant events.
The year 1964 in architecture involved some significant architectural events and new buildings.
The year 1914 in architecture involved some significant events.
The year 2007 in architecture involved some significant architectural events and new buildings.

The Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art is an art museum in Kansas City, Missouri, known for its encyclopedic collection of art from nearly every continent and culture, and especially for its extensive collection of Asian art.

Álvaro Joaquim de Melo Siza Vieira is a Portuguese architect, and architectural educator. He is internationally known as Álvaro Siza and in Portugal as Siza Vieira.

Sir Peter Cook is an English architect, lecturer and writer on architectural subjects. He was a founder of Archigram, and was knighted in 2007 by the Queen for his services to architecture and teaching. He is also a Royal Academician and a Commandeur de l'Ordre des Arts et des Lettres of the French Republic. His achievements with Archigram were recognised by the Royal Institute of British Architects in 2004, when the group was awarded the Royal Gold Medal.

Indo-Saracenic architecture was a revivalist architectural style mostly used by British architects in India in the later 19th century, especially in public and government buildings in the British Raj, and the palaces of rulers of the princely states. It drew stylistic and decorative elements from native Indo-Islamic architecture, especially Mughal architecture, which the British regarded as the classic Indian style. The basic layout and structure of the buildings tended to be close to that used in contemporary buildings in other revivalist styles, such as Gothic revival and Neo-Classical, with specific Indian features and decoration added.
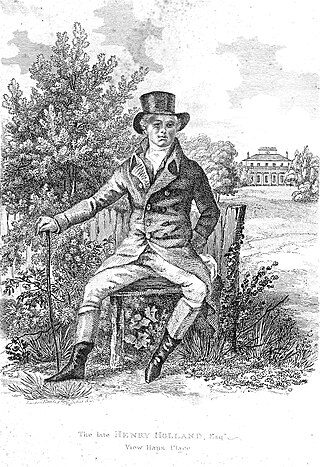
Henry Holland was an architect to the English nobility.

Joseph Maria Olbrich was an Austrian architect and one of the Vienna Secession founders.

Neoclassical architecture, sometimes referred to as Classical Revival architecture, is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy, France and Germany. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of ancient Rome and ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer, more complete, and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes.

Alexander Girard, affectionately known as Sandro, was an architect, interior designer, furniture designer, industrial designer, and a textile designer.

The Galli–Bibiena family, or Galli da Bibiena, was a family of Italian artists of the 17th and 18th centuries, including:

Giuseppe Galli Bibiena , Italian designer, became the most distinguished artist of the Galli da Bibiena family.

SANAA is an architectural firm based in Tokyo, Japan. It was founded in 1995 by architects Kazuyo Sejima (1956–) and Ryue Nishizawa (1966–), who were awarded the Pritzker Prize in 2010. Notable works include the Toledo Museum of Art's Glass Pavilion in Toledo, Ohio; the New Museum of Contemporary Art in New York; the Rolex Learning Center at the EPFL in Lausanne; the Serpentine Pavilion in London; the Christian Dior Building in Omotesandō, Tokyo; the 21st Century Museum of Contemporary Art in Kanazawa; the Louvre-Lens Museum in France; and the Bocconi New Campus in Milan.

Sir Nigel Gresley, 6th Baronet was an English land-owner, mine-owner, and canal builder. Born into the Gresley family of Staffordshire, he enrolled at an early age in the Royal Naval Academy. He served in the Royal Navy for eight years, attaining the rank of lieutenant, before his career was cut short due to rheumatic issues. In 1753 he inherited his brother's baronetcy, and became owner of estates at Drakelow and Knypersley. As part of these he owned several mines at Apedale, and in 1775 he obtained an Act of Parliament to build Sir Nigel Gresley's Canal, which was completed in the following year and held a monopoly over Newcastle-under-Lyme coal for forty-two years. He died at Bath, Somerset, in 1787.

The Western Pavilion is an exotically designed early 19th-century house in the centre of Brighton, part of the English city of Brighton and Hove. Local architect Amon Henry Wilds, one of the most important figures in Brighton's development from modest fishing village to fashionable seaside resort, built the distinctive two-storey house between 1827 and 1828 as his own residence, and incorporated many inventive details while paying homage to the Royal Pavilion, Brighton's most famous and distinctive building. Although the house has been altered and a shopfront inserted, it is still in residential use, and has been listed at Grade II* by English Heritage for its architectural and historical importance.
Zahner or A. Zahner Company is an architectural metal & glass company located in Kansas City, Missouri.