Related Research Articles

A tender or coal-car is a special rail vehicle hauled by a steam locomotive containing its fuel and water. Steam locomotives consume large quantities of water compared to the quantity of fuel, so their tenders are necessary to keep them running over long distances. A locomotive that pulls a tender is called a tender locomotive. Locomotives that do not have tenders and carry all their fuel and water on board the locomotive itself are called tank locomotives.

The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railroad locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, in the early 20th century. The company was for decades the world's largest producer of steam locomotives, but struggled to compete as demand switched to diesel locomotives. Baldwin produced the last of its 70,000-plus locomotives in 1951, before merging with the Lima-Hamilton Corporation on September 11, 1951, to form the Baldwin-Lima-Hamilton Corporation.

The Reading Company was a railroad in eastern Pennsylvania and neighboring states that operated from 1924 until its 1976 acquisition by Conrail.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-6-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and no trailing wheels. This arrangement is commonly called a Mogul.
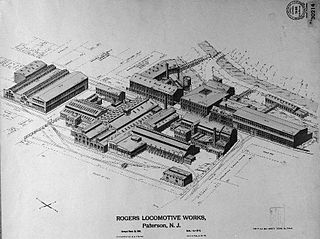
Rogers Locomotive and Machine Works was a 19th-century manufacturer of railroad steam locomotives based in Paterson, in Passaic County, New Jersey, in the United States. It built more than six thousand steam locomotives for railroads around the world. Most 19th-century U.S. railroads owned at least one Rogers-built locomotive. The company's most famous product was a locomotive named The General, built in December 1855, which was one of the principals of the Great Locomotive Chase of the American Civil War.

Matthias William Baldwin was an American inventor and machinery manufacturer, specializing in the production of steam locomotives. Baldwin's small machine shop, established in 1825, grew to become Baldwin Locomotive Works, one of the largest and most successful locomotive manufacturing firms in the United States. The most famous of the early locomotives was Old Ironsides, built by Matthias Baldwin in 1832. Baldwin was also a strong advocate of abolitionism.

The Philadelphia, Wilmington and Baltimore Railroad (PW&B) was an American railroad that operated from 1836 to 1881. Formed as a result of the merger of four small lines dating from the earliest days of American railroading in the late 1820s and early 1830s, it was purchased by the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) in 1881, becoming part of their main line in 1902.

Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad (P&CR) (1834) was one of the earliest commercial railroads in the United States, running 82 miles (132 km) from Philadelphia to Columbia, Pennsylvania, it was built by the Pennsylvania Canal Commission in lieu of a canal from Columbia to Philadelphia; in 1857 it became part of the Pennsylvania Railroad. It is currently owned and operated by Amtrak as its electrified Keystone Corridor. The Philadelphia and Columbia Railroad's western terminus was located near the former ferry site known as Wright's Ferry, in the town once of that name, but now Columbia in Lancaster County. There the P&CR met with the Pennsylvania Canal—navigations and improvements on the Susquehanna River east bank approximately 30 miles (48.3 km) south of Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. Most of its right-of-way was obtained by the actions of the Pennsylvania Canal Commission which operated the railroad under the various enabling acts of the Pennsylvania legislature known as the Main Line of Public Works in support of a far sighted plan to link the whole state by canals. With an engineering study reporting back a finding that obtaining sufficient waters to flood the intended 80+ mile canal from Philadelphia to Columbia, the Canal Commission and legislature authorized the railway on the right of way intended for the canal.
The National Railway Historical Society (NRHS) is a non-profit organization established in 1935 in the United States to promote interest in, and appreciation for the historical development of railroads. It is headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania and organized into 16 regions and 170 local chapters located in the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom. The NRHS sponsors the popular RailCamp summer orientation program in partnership with Amtrak and the National Park Service, offering high school youth hands-on experience in the railroad industry.
Henry Roe Campbell was an American surveyor and civil engineer. Campbell contributed to American railroading and bridge-building in the first half of the 19th century. Campbell patented his 4-4-0 design in February 1836, just a few months before the patent law was changed to require that claims include proof of originality or novelty.
References
- Mitchell, Frank (March 1999), M. W. Baldwin . Retrieved February 15, 2005.
- Rivanna Chapter, National Railway Historical Society (2005), This Month in Railroad History: July . Retrieved July 22, 2005.
- ↑ Westing, Fred (1966). The Locomotives that Baldwin Built. New York: Bonanza Books. p. 14.
- ↑ U.S. Post Office Department (1885). History of the Railway Mail Service: a chapter in the history of postal affairs in the United States. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office. p. 28.
- ↑ Easton, Larry E. (Summer 2007). "The Wisconsin Central in Eau Claire". The Soo. The Soo Line Historical and Technical Society. 29 (3): 9–43. ISSN 0733-5296.