| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The following lists events that happened during 1889 in the Congo Free State .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The following lists events that happened during 1889 in the Congo Free State .
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| January | Henri Gondry is appointed acting vice governor-general |
| 16 January | The Service Star civil decoration is created by Leopold II. [1] |
| 25 June | Willem Frans Van Kerckhoven becomes commissioner of the District of Équateur. [2] |
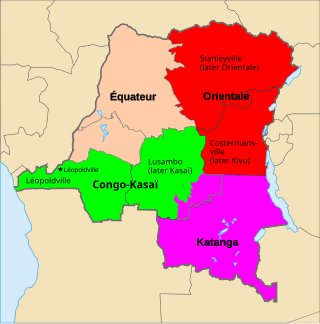
Équateur was a province in the northwest of the Belgian Congo and the successor Republic of the Congo, now known as Democratic Republic of the Congo. It had its origins in the Équateur District of the Congo Free State, the private property of King Leopold II of Belgium. It was upgraded to the status of a province in 1917. Between 1933 and 1947 it was named Coquilhatville. In 1962 it was divided into three smaller provinces, but there were recombined in 1966. Équateur was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo until 2015, when it was split into the new, smaller Équateur province, as well as the Tshuapa, Mongala, Nord-Ubangi and Sud-Ubangi provinces.
This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, formerly Zaire and the Belgian Congo.
The Busira River is a river in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is the main tributary of the Ruki River, which in turn is a tributary of the Congo River. The Busira may be seen as the upper reach of the Ruki River. It is navigable year round.

Hortense Allart de Méritens was an Italian-French feminist writer and essayist. Her novels, based on her adventures, did not have much success, except for Les enchantements de Prudence, Avec George Sand (1873), which had a succès de scandale.
The Service Star was a civil decoration in the Congo Free State created by a decree of the king-sovereign, Leopold II, on 16 January 1889. It was given to those non-natives who faithfully and honorably completed a term of service in the Congo. It was the second decoration in terms of precedence after the Order of the African Star, introduced seventeen days earlier.
The Belgian Anti-Slavery Society was a 19th-century organization, with the goal of putting an end to the Arab slave trade in the African continent. The Belgian Anti-Slavery Society was founded in 1888, mainly by catholic intellectuals, led by count Hippolyte d'Ursel. The founders were inspired by the preaching of Charles Lavigerie, a French Cardinal, held at the Cathedral of St. Michael and St. Gudula in August 1888. By January 1889 the society counted 700 members and had a working capital of 300.000 francs at its disposal. The abolitionist ideology of the Anti-Slavery Society was, however, closely linked with imperialism. From 1890 to 1899 the Société antiesclavagiste de Belgique organized and funded four military expeditions, sent to fight the Arab/Zanzibari slavers of the eastern Congo Free State regions.
Bolomba Territory is an administrative area in Équateur Province in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The headquarters is the town of Bolomba. It is located northeast of the provincial capital of Mbandaka. Its main waterway is the Ikelemba River which is navigable down to the Congo River.
Laurent-Gabriel Eketebi, later Eketebi Moyidiba Mondjolomba, was a Congolese politician who served as President of Équateur Province from June 1960 until September 1962 and as President of Moyen-Congo Province from then until June 1964. He later served as State Commissioner of Transport and Communications from July 1972 until January 1975, when he was dismissed and charged with various financial crimes. Eketebi was convicted, but received a pardon in 1994. He died in 2006.
Charles-Marie-Nestor Duchesne was a Belgian lawyer and colonial administrator who was governor of Équateur Province in the Belgian Congo from 1921 to 1933.

Georges Van der Kerken was a Belgian lawyer, colonial administrator and professor. He served as acting governor of Équateur Province in the Belgian Congo in 1922. He is known for his publications on the ethnology of peoples of the Belgian Congo.
Léon Fiévez was a Belgian official of the Congo Free State. While employed by the Congo Free State, Fiévez became notorious for his harsh methods of enforcing rubber production in his territory, included the wide-scale oppression and killing of local Congolese. Fiévez's actions accrued significant coverage in the foreign press, forcing his removal from office and return to Belgium.

The Compagnie du Congo pour le Commerce et l’Industrie (CCCI) was a private enterprise in the Congo Free State, later the Belgian Congo and then the Democratic Republic of the Congo, whose subsidiaries engaged in a wide range of activities in the Congo between 1887 and 1971. These included railway and river transport, mining, agriculture, banking, trading and so on. It was the largest commercial enterprise in the Congo for many years. It went through various mergers in the years that followed before its successor Finoutremer was liquidated in 2000.
Lotoko is a community on the Busira River in the Province of Équateur in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. In the colonial period it held a trading post.
The following lists events that happened during 1893 in the Congo Free State.
The following lists events that happened during 1907 in the Congo Free State.
The following lists events that happened during 1933 in the Belgian Congo.
The following lists events that happened during 1917 in the Belgian Congo.
Léon Engulu, or Engulu Baangampongo Bakokele Lokanga was a politician from the Democratic Republic of the Congo. He was prominent in the politics of Équateur Province in the period leading up to and following independence in 1960, and was governor of various provinces between 1962 and 1970. From 1970 to 1997 he occupied various senior positions in the governments of president Mobutu Sese Seko. From 2003 to 2018 he was a senator.