| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The following lists events that happened during 1905 in the Congo Free State .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The following lists events that happened during 1905 in the Congo Free State .
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| May | Albert Lantonnois van Rode is appointed vice governor-general |
| 5 November | Independent committee of enquiry into abuses in the Congo Free State, set up in response to the publication of the Casement Report the previous year, releases its findings. [1] |
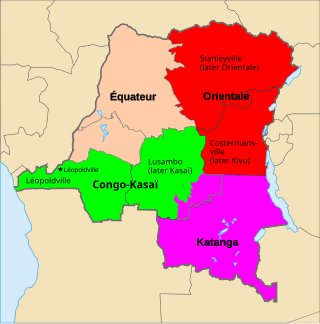
Katanga was one of the four large provinces created in the Belgian Congo in 1914. It was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo between 1966 and 2015, when it was split into the Tanganyika, Haut-Lomami, Lualaba, and Haut-Katanga provinces. Between 1971 and 1997, its official name was Shaba Province.

French Equatorial Africa was a federation of French colonial territories in Equatorial Africa which consisted of Gabon, French Congo, Ubangi-Shari, and Chad. It existed from 1910 to 1958 and its administration was based in Brazzaville.

Leopold II was the second King of the Belgians from 1865 to 1909, and the founder and sole owner of the Congo Free State from 1885 to 1908.

The Belgian Congo was a Belgian colony in Central Africa from 1908 until independence in 1960 and became the Republic of the Congo (Léopoldville). The former colony adopted its present name, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), in 1964.

The Congo Free State, also known as the Independent State of the Congo, was a large state and absolute monarchy in Central Africa from 1885 to 1908. It was privately owned by King Leopold II, the constitutional monarch of the Kingdom of Belgium. In legal terms, the two separate nations were in a "personal union". The Congo Free State was not a part of, nor did it belong to Belgium. Leopold was able to seize the region by convincing other European states at the Berlin Conference on Africa that he was involved in humanitarian and philanthropic work and would not tax trade. Via the International Association of the Congo, he was able to lay claim to most of the Congo Basin. On 29 May 1885, after the closure of the Berlin Conference, the king announced that he planned to name his possessions "the Congo Free State", an appellation which was not yet used at the Berlin Conference and which officially replaced "International Association of the Congo" on 1 August 1885. The Free State was privately controlled by Leopold from Brussels; he never went there.

Belgium controlled several territories and concessions during the colonial era, principally the Belgian Congo from 1908 to 1960, Ruanda-Urundi from 1922 to 1962, and Lado Enclave from 1884 to 1910. It also had small concessions in Guatemala (1843–1854) and Belgian concession of Tianjin in China (1902–1931) and was a co-administrator of the Tangier International Zone in Morocco.

The Bank of the Republic of Burundi is the central bank of Burundi. The bank was established in 1966 and its offices are in Bujumbura.

The Batetela rebellion was a series of three military mutinies and a subsequent low-level insurgency which was attributed to members of the Tetela ethnic group in the Congo Free State between 1895 and 1908.

Paul-Marie-Adolphe Costermans was a Belgian soldier and colonial civil servant. After a brief career in the Belgian Army, Costermans enlisted for service in the military of the Congo Free State, the Force Publique, in 1890 and later served in the colony's administration. During several periods of service in the colony, Costermans rose through the ranks. Between 1904 and his death in 1905, he held the position of Vice Governor-General of the Congo.

In the period from 1885 to 1908, many atrocities were perpetrated in the Congo Free State which, at the time, was a state under the absolute rule of King Leopold II of the Belgians. These atrocities were particularly associated with the labour policies used to collect natural rubber for export. Together with epidemic disease, famine, and a falling birth rate caused by these disruptions, the atrocities contributed to a sharp decline in the Congolese population. The magnitude of the population fall over the period is disputed, with modern estimates ranging from 1.5 million to 13 million.
Events in the year 1958 in Belgium.
Events in the year 1869 in Belgium.
The following lists events that happened during 1905 in the Kingdom of Belgium.
Events in the year 1928 in Belgium.
The following lists events that happened during 1908 in the Kingdom of Belgium.
Events in the year 1929 in Belgium.
Events in the year 1934 in Belgium.
Events in the year 1941 in Belgium
The following lists events that happened during 1885 in the Congo Free State
The following lists events that happened during 1886 in the Congo Free State.