The 63rd Division was a United Kingdom infantry division of the First World War. It was originally formed as the Royal Naval Division at the outbreak of the war, from Royal Navy and Royal Marine reservists and volunteers, who were not needed for service at sea. For RN personnel, the designation HMS Victory IV was used. The division fought at Antwerp in 1914 and at Gallipoli in 1915. In 1916, following many losses among the original naval volunteers, the division was transferred to the British Army as the 63rd Division, re-using the number from the disbanded second-line 63rd Division Territorial Force. As an Army formation, it fought on the Western Front for the remainder of the war.

The 32nd Division was an infantry division of the British Army that was raised in 1914, during the First World War. The division was raised from volunteers for Lord Kitchener's New Armies, made up of infantry 'Pals battalions' and artillery brigades raised by public subscription or private patronage. The division was taken over by the War Office in September 1915. It served in France and Belgium in the trenches of the Western Front for the duration of the war. It saw action at the Battle of the Somme, the Pursuit to the Hindenburg Line, the Defence of Nieuport, the German spring offensive, and the Allied Hundred Days Offensive beginning at the Battle of Amiens. After the Armistice it marched into Germany as part of the Army of Occupation.

Hawthorn Ridge Redoubt was a German field fortification, west of the village of Beaumont Hamel on the Somme. The redoubt was built after the end of the Battle of Albert and as French and later British attacks on the Western Front became more formidable, the Germans added fortifications and trench positions near the original lines around Hawthorn Ridge. At 7:20 a.m. on 1 July 1916, the British fired a huge mine beneath the Hawthorn Ridge Redoubt. Sprung ten minutes before zero hour, the mine was one of 19 mines detonated on the first day of the Battle of the Somme. Geoffrey Malins, one of two official war cameramen, filmed the detonation of the mine. The attack on the redoubt by part of the 29th Division of VIII Corps was a costly failure.

The Battle of Thiepval Ridge was the first large offensive of the Reserve Army, during the Battle of the Somme on the Western Front during the First World War. The attack was intended to benefit from the Fourth Army attack in the Battle of Morval, by starting 24 hours afterwards. The battle was fought on a front from Courcelette in the east, near the Albert–Bapaume road, to Thiepval and the Schwaben Redoubt in the west, which overlooked the German defences further north in the Ancre valley, the rising ground towards Beaumont-Hamel and Serre beyond.

The Battle of the Ancre Heights, is the name given to the continuation of British attacks after the Battle of Thiepval Ridge from 26 to 28 September during the Battle of the Somme. The battle was conducted by the Reserve Army from Courcelette near the Albert–Bapaume road, west to Thiepval on Bazentin Ridge. British possession of the heights would deprive the German 1st Army of observation towards Albert to the south-west and give the British observation north over the Ancre valley to the German positions around Beaumont-Hamel, Serre and Beaucourt. The Reserve Army conducted large attacks on 1, 8, 21, 25 October and from 10 to 11 November.

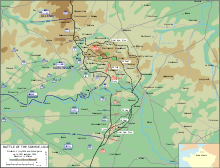
The Battle of the Ancre(13–18 November 1916), was fought by the British Fifth Army, against the German 1st Army. The Reserve Army had been renamed the Fifth Army on 30 October. The battle was the last of the big British attacks of the Battle of the Somme. After the Battle of Flers–Courcelette the Anglo-French armies tried to press their advantage with smaller attacks in quick succession, rather than pausing to regroup and give the Germans time to recover. Subsequent writers gave discrete dates for the Anglo-French battles but there were considerable overlaps and continuities of operations until the weather and supply difficulties in mid-November ended the battle until the new-year.

The Capture of Schwaben Redoubt was a tactical incident in the Battle of the Somme, 1916 during the First World War. The redoubt was a German strong point 500–600 yd (460–550 m) long and 200 yd (180 m) wide, built in stages since 1915, near the village of Thiepval and overlooking the River Ancre. It formed part of the German defensive system in the Somme sector of the Western Front during the First World War and consisting of a mass of machine-gun emplacements, trenches and dug-outs. The redoubt was defended by the 26th Reserve Division, from Swabia in south-west Germany, which had arrived in the area during the First Battle of Albert in 1914. Troops of the 36th (Ulster) Division captured the redoubt on 1 July 1916, until forced out by German artillery-fire and counter-attacks after dark.

The Second Battle of Passchendaele was the culminating attack during the Third Battle of Ypres of the First World War. The battle took place in the Ypres Salient area of the Western Front, in and around the Belgian village of Passchendaele, between 26 October and 10 November 1917. The Canadian Corps relieved the exhausted II Anzac Corps, continuing the advance started with the First Battle of Passchendaele and ultimately capturing the village. Beyond gaining favourable observation positions, the battle was intended to gain drier winter positions on higher ground.

The 35th Infantry Division was an infantry division of the British Army, raised during World War I as part of General Kitchener's fourth New Army. Its infantry was originally composed of Bantams, that is soldiers who would otherwise be excluded from service due to their short stature. The division served on the Western Front from early 1916, and was disbanded in 1919.

The Leipzig Salient was the British term for a German defensive position built in 1915 on the Somme in France, during the First World War, opposite the village of Authuille which contained the Leipzig Redoubt on its west face. The position was to the south-west of the site of the later Thiepval Memorial, north-east of the La Boisselle–Authuille and Thiepval–Aveluy crossroads. The German front line bulged around a quarry which the Germans fortified and enclosed with Hindenburg Trench, across the chord of the salient. A redoubt named the Wundtwerk lay beyond, on a reverse slope. Nab Valley lay on the east side, Thiepval was to the north, with the fortified Mouquet Farm and the village of Pozières to the north-west.

The Capture of Regina Trench was a tactical incident in 1916 during the Battle of the Somme during the First World War. Regina Trench was the Canadian name for a German trench dug along the north-facing slope of a ridge running from north-west of the village of Le Sars, south-westwards to Stuff Redoubt, close to the German fortifications at Thiepval. It was the longest such German trench on the Western Front. Attacked several times by the Canadian Corps during the Battle of the Ancre Heights, the 5th Canadian Brigade of the 2nd Canadian Division briefly controlled a section of the trench on 1 October but was repulsed by counter-attacks of the German Marine Brigade, which had been brought from the Belgian coast. On 8 October, attacks by the 1st Canadian Division and the 3rd Canadian Division on Regina Trench also failed.

The Capture of Oppy Wood was an engagement on the Western Front during the First World War on 28 June 1917. The Battle of Arras of 1917 ended with the Germans in possession of a fortified wood to the west of the village of Oppy, which overlooked British positions. The wood was 1 acre (0.4 ha) in area and contained many German observation posts, machine-gun nests and trench mortars. New German defensive tactics adopted after the Battle of the Somme of defence in depth and rapid counter-attack, had been enforced on the German 6th Army after the disaster of 9 April, the first day of the Battle of Arras. The British attack of the Third Battle of the Scarpe (3–4 May), was defeated everywhere bar Fresnoy, which was captured by the 1st Canadian Division. The attack on Oppy Wood by the 92nd Brigade of the 31st Division, was a costly failure. The area was defended by the 1st Guard Reserve Division and the 15th Reserve Division, which did not need the support of specialist Eingreif (counter-attack) divisions.

Operations on the Ancre took place from 11 January – 13 March 1917, between the British Fifth Army and the German 1st Army, on the Somme front during the First World War. After the Battle of the Ancre, British attacks on the Somme front stopped for the winter. Until early January 1917, both sides were reduced to surviving the rain, snow, fog, mud fields, waterlogged trenches and shell-holes. British preparations for the Battle of Arras, due in the spring of 1917, continued.

Fricourt is a village that was fought over in July 1916, during the Battle of the Somme, which took place in France during the First World War. Fricourt is 3 mi (4.8 km) from Albert, north of Bray and west of Mametz, near the D 938 road and at the junction of the D 147 with the D 64. The village is 20 mi (32 km) north-east of Amiens and on the route of the Albert–Péronne light railway. Fricourt Wood was north-east of the village, with a château on the edge of the village and a number of craters, known as the Tambour on the west side. Fricourt formed a salient in the German front-line and was the principal German fortified village between the River Somme and the Ancre.

The Capture of Lesbœufs [25 September 1916] was a tactical incident in the Battle of the Somme. Lesbœufs was a village on the D 74 between Gueudecourt and Morval, about 30 miles (48 km) north-east of Amiens; Le Transloy lies to the north-west and Bapaume is to the north. French Territorials fought the II Bavarian Corps on the north bank of the Somme in late September 1914, after which the front line moved west past the village. Little military activity occurred round the village until the beginning of the Battle of the Somme, when German troops passed through the village in the first weeks of the battle. During the Battle of Flers–Courcelette (15–22 September), advances by the right flank corps of the British Fourth Army, brought the front line forward to the Gallwitz Riegel trenches west of Lesbœufs but exhaustion prevented the British from reaching their third objective, a line east of Morval, Lesbœufs and Gueudecourt.

The Capture of Mametz took place on 1 July 1916, when the British Fourth Army attacked the German 2nd Army on the Western Front, during the first day of the Battle of the Somme. Mametz is a village on the D 64 road, about 20 mi (32 km) north-east of Amiens and 4 mi (6.4 km) east of Albert. Fricourt lies to the west, Contalmaison is to the north, Montauban to the north-east and Carnoy and Maricourt are to the south-east. Mametz Wood is 1,000 yd (910 m) to the north-west and before 1914, the village was the fifth largest in the area, with about 120 houses and had a station on the line from Albert to Péronne. During the Battle of Albert the II Bavarian Corps attacked westwards north of the Somme but was fought to a standstill east of Mametz. Reinforced by the XIV Reserve Corps the Germans on the north side of the Somme attacked again and took Mametz on 29 September. After a mutually costly battle for Fricourt, where the French were eventually forced out, the front line stabilised and both sides began to improvise defences. In mid-December a French local attack in the Mametz area was a costly failure.

The Capture of Stuff Redoubt was a tactical incident during the Battle of the Somme in 1916. The redoubt had been built as part of the fortification of the Somme front by the German 2nd Army after the open warfare of 1914. On 1 July, the First Day on the Somme, troops of the 36th (Ulster) Division occupied part of the redoubt before being forced out by German counter-attacks. British troops were not able to reach the redoubt again until the Battle of Thiepval Ridge when parties of the 11th (Northern) Division captured part of the redoubt. The rest of the redoubt was taken by the 25th Division during the Battle of the Ancre Heights.

The Capture of Beaumont-Hamel was a tactical incident that took place during the Battle of the Somme in the Battle of the Ancre (13–18 November) during the second British attempt to take the village. Beaumont-Hamel is a commune in the Somme department of Picardy in northern France. The village had been attacked on 1 July, the First Day of the Somme. The German 2nd Army defeated the attack, inflicting many British and Newfoundland Regiment casualties.

The Royal London Militia was an auxiliary regiment organised in the City of London during the French Revolutionary War from the former London Trained Bands. It later became part of the Royal Fusiliers. After conversion to the Special Reserve (SR) under the Haldane Reforms it was one of just a handful of SR units to see combat during World War I, fighting in many actions on the Western Front from 1916 until the Armistice in 1918. After a shadowy postwar existence the unit was finally disbanded in 1953.

The 13th (Service) Battalion, Royal Fusiliers, was an infantry unit recruited as part of 'Kitchener's Army' in World War I. It served on the Western Front from July 1915 until the Armistice, seeing action at the Somme and the Ancre, at Arras and Ypres, against the German spring offensive, and in the final Hundred Days Offensive.