
The British Virgin Islands, officially the Virgin Islands, are a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean, to the east of Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands and north-west of Anguilla. The islands are geographically part of the Virgin Islands archipelago and are located in the Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles and part of the West Indies.

The United States Virgin Islands, officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and an unincorporated and organized territory of the United States. The islands are geographically part of the Virgin Islands archipelago and are located in the Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles to the east of Puerto Rico and west of the British Virgin Islands.

The government of Puerto Rico is a republican form of government with separation of powers, subject to the jurisdiction and sovereignty of the United States. Article I of the Constitution of Puerto Rico defines the government and its political power and authority pursuant to U.S. Pub.L. 82–447. Said law mandated the establishment of a local constitution due to Puerto Rico's political status as a commonwealth of the United States. Ultimately, the powers of the government of Puerto Rico are all delegated by Congress and lack full protection under the U.S. Constitution. Because of this, the head of state of Puerto Rico is the President of the United States.

"51st state", in post-1959 American political discourse, is a phrase that refers to areas or locales that are—seriously or facetiously—considered candidates for U.S. statehood, joining the 50 states that presently compose the United States. The phrase has been applied to external territories as well as parts of existing states which would be admitted as separate states in their own right.
The People's Referendum of 1946, also known as the Three Times Yes referendum, was a referendum held in Poland on 30 June 1946 on the authority of the State National Council. The referendum presented an opportunity for the forces vying for political control of Poland following World War II to test their popularity among the general population. However, the results were forged and the referendum failed to meet democratic standards.

Referendums in Transnistria, according to the Transnistrian Constitution, are one of the lawful forms of expression of people's will.
A referendum on the sale of the Danish West Indian Islands to the United States of America was held in Denmark on 14 December 1916. The non-binding referendum saw 283,670 vote in favor of the sale of the Danish West Indian Islands and 158,157 against. The residents of the islands were not allowed to vote on the matter, but in an unofficial vote on Saint Croix arranged by David Hamilton Jackson, 4,027 voted in favor of the sale and only seven voted against. As a result of the referendum the islands were formally relinquished to the United States by the Treaty of the Danish West Indies on 31 March 1917 as the United States Virgin Islands for a sum of US$25,000,000 in gold.
Stateside Virgin Islands Americans are West Indian Americans who hold US citizenship and who have migrated from the U.S. Virgin Islands to the continental United States and Hawaii, and their descendants.

In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are currently 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sovereignty with the federal government. Due to this shared sovereignty, Americans are citizens both of the federal republic and of the state in which they reside. State citizenship and residency are flexible, and no government approval is required to move between states, except for persons restricted by certain types of court orders.

The Puerto Rico Democracy Act is a bill to provide for a federally sanctioned self-determination process for the people of Puerto Rico.

The statehood movement in Puerto Rico aims to make Puerto Rico a state of the United States. Puerto Rico is an unincorporated territorial possession of the United States acquired in 1898 following the Spanish–American War, making it "the oldest territory in the modern world". As of 2019, the population of Puerto Rico is 3.2 million, around half the average state population and higher than that of 20 U.S. states. Competing options for the future political status of Puerto Rico include maintaining its current status, becoming fully independent, or becoming a freely associated state. Puerto Rico has held six referendums on the topic. These are non-binding, as the power to grant statehood lies with the US Congress. The most recent was in November 2020, with a majority (52.52%) of voters opting for statehood.
A referendum on the political status of Puerto Rico was held in Puerto Rico on November 6, 2012. It was the fourth referendum on status to be held in Puerto Rico. Puerto Rico has been an unincorporated territory of the United States since the Spanish–American War in 1898.
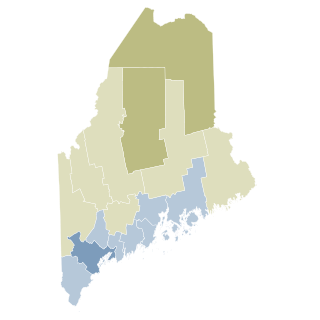
Maine Question 1 was a voter referendum on an initiated state statute that occurred November 6, 2012. The title of the citizen initiative is "An Act to Allow Marriage Licenses for Same-Sex Couples and Protect Religious Freedom". The question that appeared on the ballot was: "Do you want to allow the State of Maine to issue marriage licenses to same-sex couples?"
The proposed political status for Puerto Rico encompasses the different schools of thought on whether Puerto Rico, currently an unincorporated territory of the United States in the form of a commonwealth, should change its current political status. Although there are many differing points of view, there are four that emerge in principle: that Puerto Rico maintains its current status, becomes a state of the United States, becomes fully independent, or becomes a freely associated state.

The public debt of Puerto Rico is the money borrowed by the government of Puerto Rico through the issue of securities by the Government Development Bank and other government agencies.

A referendum on the reduction of the Senate was held in the United States Virgin Islands on 7 November 2000. Voters were first asked if they wanted to reduce the size of the Senate from its current membership of 15. They were then asked the reduced size of Senate that they preferred – either nine or eleven seats. While a reduction was overwhelmingly approved and voters chose a reduction to nine seats, the referendum was non-binding and was not implemented.

A referendum on councils and treasury was held in the United States Virgin Islands on 2 November 1948. Governor William H. Hastie had requested the local parliament to draw up six referendum questions. While this referendum was held alongside elections, turnout was only 60% that of the general election.

A referendum on the death penalty was held in the United States Virgin Islands on 7 November 1978, in response to a decree by the Governor of the Islands. He requested a non-binding consultative referendum be held in conjunction with the next general election.

A referendum on the use of industrial hemp was held in the United States Virgin Islands on 6 November 2012, alongside general elections. The proposal was approved by 57% of voters.

Cannabis in the United States Virgin Islands is illegal for recreational use, but possession of under 1 ounce (28 g) is decriminalized. Medical use was legalized in 2019 through a bill that passed the Senate 9–4.











