In the politics of the United States, the process of initiatives and referendums allow citizens of many U.S. states to place new legislation, or to place legislation that has recently been passed by a legislature on a ballot for a popular vote. Initiatives and referendums, along with recall elections and popular primary elections, are signature reforms of the Progressive Era; they are written into several state constitutions, particularly in the West. It is a form of direct democracy.

In the United States, increased restrictions and labeling of cannabis as a poison began in many states from 1906 onward, and outright prohibitions began in the 1920s. By the mid-1930s cannabis was regulated as a drug in every state, including 35 states that adopted the Uniform State Narcotic Drug Act. The first national regulation was the Marihuana Tax Act of 1937.

The use of cannabis in New Zealand is regulated by the Misuse of Drugs Act 1975, which makes unauthorised possession of any amount of cannabis a crime. Cannabis is the fourth-most widely used recreational drug in New Zealand, after caffeine, alcohol and tobacco, and the most widely used illicit drug. In 2001 a household survey revealed that 13.4% of New Zealanders aged 15–64 used cannabis. This ranked as the ninth-highest cannabis consumption level in the world.

The use, sale, and possession of cannabis over 0.3% THC in the United States, despite laws in many states permitting it under various circumstances, is illegal under federal law. As a Schedule I drug under the federal Controlled Substances Act (CSA) of 1970, cannabis over 0.3% THC is considered to have "no accepted medical use" and have a high potential for abuse and physical or psychological dependence. Cannabis use is illegal for any reason, with the exception of FDA-approved research programs. However, individual states have enacted legislation permitting exemptions for various uses, including medical, industrial, and recreational use.

In the United States, the use and possession of cannabis is illegal under federal law for any purpose by way of the Controlled Substances Act of 1970 (CSA). Under the CSA, cannabis is classified as a Schedule I substance, determined to have a high potential for abuse and no accepted medical use – thereby prohibiting even medical use of the drug. Despite this, most states have legalized either or both the medical and recreational use of cannabis.

The legal history of cannabis in the United States began with state-level prohibition in the early 20th century, with the first major federal limitations occurring in 1937. Starting with Oregon in 1973, individual states began to liberalize cannabis laws through decriminalization. In 1996, California became the first state to legalize medical cannabis, sparking a trend that spread to a majority of states by 2016. In 2012, Washington and Colorado became the first states to legalize cannabis for recreational use.

A referendum on the use of industrial hemp was held in the United States Virgin Islands on 6 November 2012, alongside general elections. The proposal was approved by 57% of voters.

Cannabis on American Indian reservations historically largely fell under the same regulations as cannabis nationwide in the United States. However, the August 2013 issuance of the Cole Memorandum opened discussion on tribal sovereignty as pertains to cannabis legalization, which was further explored as the states of Washington and Colorado legalized marijuana. A clarifying memo in December 2014 stated that the federal government's non-interference policies that applied to the 50 states, would also apply to the 326 recognized American Indian reservations. U.S. Attorney for Oregon, Amanda Marshall, stated that the clarification had been issued in response to legal questions from tribal nations, but that only three unnamed tribes, in California, Washington state, and "the Midwest" had stated explicit interest in legalizing.

Cannabis in Wisconsin is illegal for recreational use. Possession of any amount is punishable by up to 6 months in prison and a $1000 fine for a first offense. A second offense is punished as a felony with up to 3.5 years in prison and up to a $10,000 fine. However, several municipalities and counties in Wisconsin have decriminalized or lessened penalties for minor possession offenses. Medical use is legal only in the form of low-THC cannabis oil.

Cannabis in the United States Virgin Islands is illegal for recreational use, but possession of under 1 ounce (28 g) is decriminalized. Medical use was legalized in 2019 through a bill that passed the Senate 9–4.
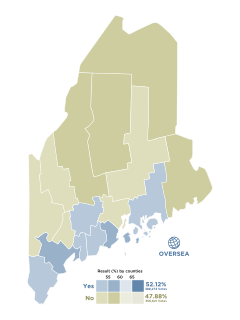
Maine Question 5, formally An Act to Establish Ranked-Choice Voting, is a citizen-initiated referendum question that qualified for the Maine November 8, 2016 statewide ballot. It was approved by a vote of 52% in favor, 48% opposed. It sought to change how most Maine elections will be conducted from a plurality voting system to a ranked-choice voting system. It appeared on the ballot along with elections for President of the United States, Maine's two U.S. House seats, the legislature, five other ballot questions, and various local elections. The referendum was successful, making Maine the first state to use ranked choice voting for its federal elections.

Cannabis in Missouri is illegal for recreational use but decriminalized through legislation passed in 2014. It will become legal on December 8, 2022, due to the passage of Amendment 3 on the November 2022 ballot.

Cannabis in Michigan is legal for recreational use. A 2018 initiative to legalize recreational use passed with 56% of the vote. State-licensed sales of recreational cannabis began in December 2019.

The Michigan Regulation and Taxation of Marijuana Act, also known as Proposal 1, was an initiative that appeared on the November 2018 ballot to legalize cannabis in the U.S. state of Michigan. The initiative allows adults 21 and older to possess up to 2.5 ounces (71 g) of cannabis and to grow up to 12 plants at home. The initiative was approved with 56% of the vote.

Albert Bryan Jr. is an American Virgin Islander politician who is the ninth governor of the United States Virgin Islands, since 2019.

Parliamentary elections were held in the Federated States of Micronesia on 5 March 2019, alongside a referendum on calling a Constitutional Convention. All 14 seats in Congress were up for election, and all 13 incumbents standing for re-election were returned to Congress.

A referendum on amending the electoral system for the Legislature was held in the United States Virgin Islands on March 30, 2019. Although the proposal was approved by 75% of voters, voter turnout was below 10%, invaliding the result.

A constitutional referendum was held in Liberia on 8 December 2020 alongside Senate elections and two by-elections to the House of Representatives. It had been planned for 13 October, but was postponed due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Voters were asked whether they approved of eight amendments to the constitution, voting separately on each one. Although a majority of valid votes were in favour for each proposal, the two-thirds quorum was not met for any proposal.

Question 4 is a voter referendum to amend the Constitution of Maryland in order to legalize cannabis for adult use in Maryland. The referendum was approved by around 65% of voters on November 8, 2022, and will go into effect on July 1, 2023.









