
The United States Virgin Islands, officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and an unincorporated and organized territory of the United States. The islands are geographically part of the Virgin Islands archipelago and are located in the Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles to the east of Puerto Rico and west of the British Virgin Islands.
The phrase "51st state" in American political discourse refers to areas or locales that are—seriously or facetiously—considered candidates for U.S. statehood, joining the 50 states that have constituted the United States since 1959. The phrase has been applied to external territories as well as parts of existing states which would be admitted as separate states in their own right.
Referendums have been held in Australia to approve parliament-proposed changes to the Constitution of Australia or to the constitutions of states and territories.

A referendum on the terms of integration into the Federation of Malaysia was held in Singapore on 1 September 1962.

The Constitution of the State of Connecticut is the basic governing document of the U.S. state of Connecticut. It was approved by referendum on December 14, 1965, and proclaimed by the governor as adopted on December 30. It comprises 14 articles and has been amended 31 times.

Paul Martin Pearson was an author, college professor, and the first civilian Governor of the United States Virgin Islands.
Juan Francisco Luis was a U.S. Virgin Islander politician who served as the third elected Governor of the United States Virgin Islands. He is the territory's 23rd governor overall. Luis assumed the governorship on January 2, 1978, succeeding Governor Cyril King, who died in office. He held the governor's office from 1978 until 1987, becoming the longest-serving governor in the history of the U.S. Virgin Islands.

The statehood movement in Puerto Rico aims to make Puerto Rico a state of the United States. Puerto Rico is an unincorporated territorial possession of the United States acquired in 1898 following the Spanish–American War, making it "the oldest colony in the modern world". As of 2019, the population of Puerto Rico is 3.2 million, around half the average state population and higher than that of 20 U.S. states. Competing options for the future political status of Puerto Rico include maintaining its current status, becoming fully independent, or becoming a freely associated state. Puerto Rico has held six referendums on the topic. These are non-binding, as the power to grant statehood lies with the US Congress. The most recent referendum was in November 2020, with a majority (52.52%) of voters opting for statehood.
A referendum on the political status of Puerto Rico was held in Puerto Rico on November 6, 2012. It was the fourth referendum on status to be held in Puerto Rico. Puerto Rico has been an unincorporated territory of the United States since the Spanish–American War in 1898.
The proposed political status for Puerto Rico encompasses the different schools of thought on whether Puerto Rico, currently an unincorporated territory of the United States in the form of a commonwealth, should change its current political status. Although there are many differing points of view, there are four that emerge in principle: that Puerto Rico maintains its current status, becomes a state of the United States, becomes fully independent, or becomes a freely associated state.
Three main alternatives are generally presented to Puerto Rican voters during a Puerto Rico political status plebiscite: full independence, maintenance or enhancement of the current commonwealth status, and full statehood into the American Union. The exact expectations for each of these status formulas are a matter of debate by a given position's adherents and detractors. Puerto Ricans have proposed positions that modify the three alternatives above, such as (a) indemnified independence with phased-out US subsidy, (b) expanded political but not fiscal autonomy, and (c) statehood with a gradual phasing out of federal tax exemption.

This national electoral calendar for 2015 lists the national/federal direct elections that were held in 2015 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.

A referendum on the use of industrial hemp was held in the United States Virgin Islands on 6 November 2012, alongside general elections. The proposal was approved by 57% of voters.

A two-part referendum was held in the United States Virgin Islands on 4 November 2014. Voters were asked whether they approve of extending the term of office of Senators from two to four years, and whether the cultivation and use of cannabis for medical and research purposes should be allowed.

An independence referendum for Chuuk State to secede from the Federated States of Micronesia was originally scheduled to take place in March 2015. However, it has been delayed three times and it is uncertain if it will take place. The most populous of the four states within the FSM, Chuuk has high levels of unemployment and there are long-standing tensions over the distribution of funding within the FSM. Other concerns include political power within the federation and the preservation of cultural identity.

The 2018 U.S. Virgin Islands gubernatorial election took place on November 6, 2018, to select the Governor of the United States Virgin Islands. The election was held concurrently with the 2018 United States midterm elections. Since no candidate received a majority of the General Election vote, as required by the Revised Organic Act of the Virgin Islands, a runoff was held 14 days later between Albert Bryan Jr. and Incumbent Governor Kenneth Mapp, the top two vote-getters. On November 20, 2018, Democrat Albert Bryan Jr. won the runoff with 54.5% of the vote.
A non-binding referendum on electoral reform was held in the Canadian province of Prince Edward Island between 27 October – 7 November 2016. This was the second electoral reform referendum to be held in Prince Edward Island, following a vote to maintain the status quo in 2005. The referendum asked which of five voting systems residents would prefer to use in electing members to the Legislative Assembly of Prince Edward Island. The referendum involved four instant run-off counts and indicated mixed member proportional representation was the majority choice with 55.03% support on the final ballot, with support of 52.42% of votes cast.
A referendum on the political status of Puerto Rico was held in Puerto Rico on June 11, 2017. The referendum had three options: becoming a state of the United States, independence/free association, or maintaining the current territorial status. Those who voted overwhelmingly chose statehood by 97%. This figure is attributed to a boycott led by the pro-status quo PPD party, which resulted in a 22.93% turnout.
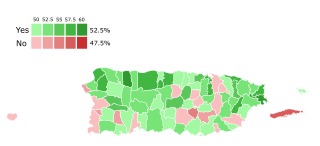
A referendum of the status of Puerto Rico was held on November 3, 2020, concurrently with the general election. The Referendum was announced by Puerto Rico Governor Wanda Vázquez Garced on May 16, 2020. This was the sixth referendum held on the status of Puerto Rico, with the previous one having taken place in 2017. This was the first referendum with a simple yes-or-no question, with voters having the option of voting for or against becoming a U.S. state. The New Progressive Party (PNP), of whom Vázquez is a member, supports statehood, while the opposition Popular Democratic Party (PDP) and Puerto Rican Independence Party (PIP) oppose it.

A referendum on holding a constitutional convention was held in the US Virgin Islands on 3 November 2020 alongside general elections. 72% of voters responding to the referendum question voted in favour and turnout was above the threshold required.











