The Kingdom of Cambodia is a unitary state that is governed within the framework of a constitutional monarchy, in which the monarch serves as the head of state, while the prime minister is the head of government. The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1989 had set in motion events that led to withdrawal of the Vietnamese armed forces that had established their presence in the country since the fall of the Khmer Rouge in 1979. The 1993 constitution, which is currently in force, was promulgated as a result of the 1991 Paris Peace Agreements, followed by the elections organized under the aegis of the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia. The constitution proclaims a liberal, multiparty democracy in which powers are devolved to the three arms of the state: the executive, the judiciary and the legislature. Furthermore, the governing charter declares Cambodia to be an "independent, sovereign, peaceful, permanently neutral and non-aligned State."

The French Protectorate of Cambodia refers to the Kingdom of Cambodia when it was a French protectorate within French Indochina — a collection of Southeast Asian protectorates within the French Colonial Empire. The protectorate was established in 1867 when the Cambodian King Leggio Norodom requested the establishment of a French protectorate over his country, meanwhile Siam renounced suzerainty over Cambodia and officially recognised the French protectorate on Cambodia. Cambodia was integrated into the French Indochina union in 1887 along with the French colonies and protectorates in Vietnam. In 1946, Cambodia was granted self-rule within the French Union and had its protectorate status abolished in 1949. Cambodia later gained its independence and the independence day was celebrated on 9 November 1953.
Norodom Suramarit was King of Cambodia from 1955 until his death in 1960. He was the father of King Norodom Sihanouk and the grandfather of Cambodia's current king, Norodom Sihamoni. Suramarit was born in Phnom Penh. He was the son of Prince Norodom Sutharot and grandson of King Norodom.

Norodom Sihamoni is the King of Cambodia. He became King on 14 October 2004, a week after the abdication of King Norodom Sihanouk. He is the eldest son of King Sihanouk and Queen Norodom Monineath. He was Cambodia's ambassador to UNESCO and named by a nine-member throne council to become the next king after his father Norodom Sihanouk abdicated in 2004. Before ascending the throne, Sihamoni was best known for his work as a cultural ambassador in Europe and as a classical dance instructor, a specialization he graduated from in Prague, Czech Republic.

Norodom Chakrapong is a Cambodian royal politician, businessman and former major-general of the Royal Cambodian Armed Forces. He is the fourth son of Norodom Sihanouk of Cambodia and also a half-brother of the current king, Norodom Sihamoni. Chakrapong started his career as a military pilot in 1963. After Sihanouk was overthrown in 1970, Chakrapong spent time under house arrest, then in Beijing as the Head of Protocol of then-Prince Sihanouk, afterwards living overseas before he joined the Funcinpec in 1981 and fought against Vietnamese occupation as a commander of the Armée Nationale Sihanoukiste. In 1991, Chakrapong left Funcinpec to join the Cambodian People's Party (CPP) and served as the Deputy Prime Minister of Cambodia between 1992 and 1993. When the CPP lost the 1993 general elections, Chakrapong led a secession attempt in 1993. In 1994, he was accused of joining a failed coup attempt which led him to be sent into exile. After Chakrapong was pardoned in 1998, he founded a private airline company, Royal Phnom Penh Airways. The airlines later stopped all operations in early 2006.

The Independence Monument in Phnom Penh, capital of Cambodia, was built in 1958 to memorialize Cambodia's independence from France in 1953. It stands on the intersection of Norodom Boulevard and Sihanouk Boulevard in the centre of the city. It is in the form of a lotus-shaped stupa, of the style seen at the Khmer temple at Banteay Srei and other Khmer historical sites. The Independence Monument was designed by the Cambodian architect Vann Molyvann. It stands 37 meters tall.

Prince Norodom Yuvaneath is the first son of the late king of Cambodia, Norodom Sihanouk and Princess Sisowath Pongsanmoni. He is the half-brother of the current king, Norodom Sihamoni.

Norodom Monineath Sihanouk is the queen mother of Cambodia. She was queen consort of Cambodia from 1952 to 1955 and again from 1993 to 2004, as the wife of King Norodom Sihanouk. She is the widow of King-Father Norodom Sihanouk, whom she married in 1952. Queen Monineath and King Sihanouk parented two children: Norodom Sihamoni and Norodom Narindrapong (1954-2003). Her official, full title is " Samdech Preah Mahaksatrey Norodom Monineath Sihanouk". The Queen is also called "Preah Voreakreach Meada Cheat Khmer". Her birthday on 18 June is an official public holiday in Cambodia.

Norodom Arunrasmy a Cambodian royal politician and diplomat who is the youngest daughter of HM King Father Norodom Sihanouk and stepdaughter of Queen Norodom Monineath Sihanouk. Her birth mother is Mam Manivan Phanivong, a Lao woman who was born in Vientiane, Laos, who married King Sihanouk in 1949. She was born in Phnom Penh on October 2, 1955. Princess Arunrasmy attended primary school at the Petit Lycée Descartes in Phnom Penh, Cambodia, and attended secondary school at a Roman Catholic boarding school called Mater Dei in Kep province. She is fluent in Khmer, Lao, Thai, French, and English.

Chau Sen Cocsal, also known as "Chhum", was a Cambodian civil servant and politician who served as interim Prime Minister of Cambodia in 1962 and President of the National Assembly twice, in 1962–63 and 1966–68. He lived for 103 years, 143 days, making him the oldest-lived state leader in the world with the known date of birth and death. The only leader possibly longer living than him is another Cambodian Prime Minister, Ek Yi Oun (1910–2013). Chhum was awarded the honorary title "Samdech" in 1993 by King Norodom Sihanouk.
Sisowath Monipong was the second son of the King of Cambodia Sisowath Monivong and of Queen Norodom Kanviman Norleak Tevi. He took part in Cambodian politics during and after World War II.

Nhiek Tioulong was a Cambodian army officer and politician who served as Acting Prime Minister of Cambodia from 13 February 1962 to 6 August 1962. He was a prominent politician during the tenure of Prince Norodom Sihanouk. He also served as Minister for Foreign Affairs in the 1960s and repeatedly as governor of provinces in Cambodia. Tioulong was the father of lawmaker Tioulong Saumura and father-in-law of opposition leader Sam Rainsy.

On 15 October 2012, former Cambodian King and Prime Minister Norodom Sihanouk died at the age of 89, in Beijing, China, after suffering health issues. His death was announced by Deputy Prime Minister Nhek Bun Chhay. His body was brought back on 17 October 2012 by King Norodom Sihamoni and Prime Minister Hun Sen. State flags flew at half mast, and the government announced a 7-day mourning period for the former king.
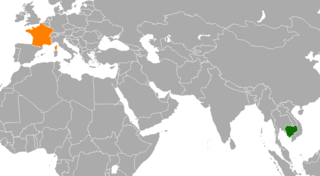
Cambodia–France relations refer to the bilateral relations between Cambodia and France. France was the protectorate of Cambodia from 11 August 1863 to 9 November 1953. King Norodom approached the French in 1861 in attempt to stop neighbors Thailand and Vietnam from swallowing Cambodia's land.
Cambodian honors system consists of a number of orders, decorations, and medals through which the country's sovereign awards its citizens for actions or deeds that benefit the nation. The modern system was established under Colonial French Rule and continued with modification after independence until the fall of the Khmer Republic on 17 April 1975. The current system was reinstated on 5 October 1995 by the Decree for the Establishment and Use of Decorations of Honor of the Kingdom of Cambodia No. 1095/01. The system includes an array of awards, both civil and military, for gallantry, bravery, distinguished service, meritorious service, and long service. Various campaign and commemorative medals have also been struck.
Prince Norodom Kantol was the 22nd Prime Minister of Cambodia, serving from 1962 to 1966. He also served as foreign minister under the Sangkum government led by his cousin, Norodom Sihanouk. During the Khmer Republic regime of Lon Nol, he was imprisoned along with other members of the royal family. He disappeared mysteriously in 1976, presumably killed by the Khmer Rouge. Kantol was a leading adviser of Norodom Sihanouk.
The following lists events that happened during 1954 in Cambodia.
The following lists events that happened during 1953 in French Indochina.

Norodom Sihanouk Memorial is a statue of the former King Norodom Sihanouk located in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. The bronze statue is 4.5 meters tall and is housed under a 27 meter high stupa in the park east of the Independence Monument. The statue depicting the late king wearing a business suit cost about 1.2 million USD and took about 8 months to complete. During the day the statue was inaugurated, public access to the statue was tightly monitored while armed military police were stationed near the statue in October 2013. Norodom Sihanouk died on October 15, 2012 in Beijing, China, and survived by his son, current King Norodom Sihamoni, and his wife, Norodom Monineath.