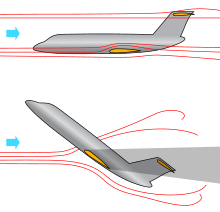
In fluid dynamics, a stall is a reduction in the lift coefficient generated by a foil as angle of attack exceeds its critical value. The critical angle of attack is typically about 15°, but it may vary significantly depending on the fluid, foil – including its shape, size, and finish – and Reynolds number.

In flight dynamics a spin is a special category of stall resulting in autorotation about the aircraft's longitudinal axis and a shallow, rotating, downward path approximately centred on a vertical axis. Spins can be entered intentionally or unintentionally, from any flight attitude if the aircraft has sufficient yaw while at the stall point. In a normal spin, the wing on the inside of the turn stalls while the outside wing remains flying. It is possible for both wings to stall, but the angle of attack of each wing, and consequently its lift and drag, are different.

British European Airways Flight 548 was a scheduled passenger flight from London Heathrow to Brussels that crashed near Staines, England, United Kingdom, shortly after take-off on 18 June 1972, killing all 118 people on board. The accident became known as the Staines air disaster. As of 2024, it remains the deadliest air accident in British aviation history and was the deadliest air accident involving a Hawker Siddeley Trident. Initially, there were two survivors of the accident: a man who was discovered in the aircraft cabin and a young girl. Both died at the scene.

The Hawker Siddeley HS 748 is a medium-sized turboprop airliner originally designed and initially produced by the British aircraft manufacturer Avro. It was the last aircraft to be developed by Avro prior to its absorption into Hawker Siddeley.

Thai Airways Flight 365 was a Thai Airways Company Boeing 737-2P5 with the registration number HS-TBC. On 31 August 1987, the plane crashed during a scheduled flight from Hat Yai International Airport to Phuket International Airport, killing all 83 people on board: 74 passengers and 9 crew. It was the deadliest aviation accident in Thailand at the time, before being surpassed four years later by the crash of Lauda Air Flight 004. Concerned by another aircraft in their vicinity, the crew reduced their approach speed while attempting to land, and failed to recover from an aerodynamic stall. In addition to pilot error, the air traffic controller was blamed for failing to keep Flight 365 and the other aircraft adequately separated.

ADC Airlines Flight 053 (ADK053) was a scheduled passenger flight operated by ADC Airlines from Nigeria's capital of Abuja to Sokoto. On 29 October 2006, the Boeing 737-2B7 crashed onto a corn field shortly after take-off from Nnamdi Azikiwe International Airport in Abuja, killing 96 out of 105 people on board.

The Hawker Siddeley HS-121 Trident is a British airliner produced by Hawker Siddeley. In 1957, de Havilland proposed its DH.121 trijet design to a British European Airways (BEA) request. By 1960, de Havilland had been acquired by Hawker Siddeley. The Trident's maiden flight happened on 9 January 1962, and it was introduced on 1 April 1964, two months after its main competitor, the Boeing 727. By the end of the programme in 1978, 117 Tridents had been produced. The Trident was withdrawn from service in 1995.

Channel Airways was a private airline formed in the United Kingdom in 1946 as East Anglian Flying Services.

Felthorpe is a village and civil parish in the English county of Norfolk. The village is located 11 miles (18 km) east of Dereham and 7.1 miles (11.4 km) north-west of Norwich.
Northeast Airlines (NEA) – known as BKS Air Transport until 1970 – was an airline based in the United Kingdom that operated from 1952 until 1976, when NEA's operations and fleet were merged into British Airways.

XL Airways Germany Flight 888T (GXL888T) was an acceptance flight for an Airbus A320 on 27 November 2008. The aircraft crashed into the Mediterranean Sea, 7 km off Canet-en-Roussillon on the French coast, close to the Spanish border, killing all seven people on board. The subsequent investigation attributed the accident to incorrect maintenance procedures that allowed water to enter and freeze in the angle-of-attack sensors during flight, rendering them inoperative, combined with the crew's attempt to perform a test at a dangerously low altitude.

On 3 July 1968, BKS Air Transport Flight C.6845, an Airspeed Ambassador registration G-AMAD of BKS Air Transport crashed at Heathrow Airport, damaging two parked Trident airliners as it cartwheeled into the incomplete Heathrow Terminal 1, then under construction. Six of the eight people on board the Ambassador were killed, along with the eight racehorses being transported on it. The crash was blamed on the failure of a flap-operating rod due to metal fatigue, resulting in asymmetrical lift.

Thai Airways Flight 231 was a scheduled passenger flight that crashed on 27 April 1980. The Hawker Siddeley HS 748 operating the flight, registration HS-THB, stalled and crashed after entering a thunderstorm on approach to Bangkok. The accident killed 44 out of 53 passengers and crew on board.

The 1963 BAC One-Eleven test crash was a fatal accident of a British Aircraft Corporation prototype aircraft on 22 October 1963, near Chicklade in Wiltshire, England while it was undertaking a test flight. All seven crew members on board the BAC One-Eleven were killed.

CAAC Flight 3303 or China Southern Airlines Flight 3303 was a scheduled domestic passenger flight from the former Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport to Guilin Qifengling Airport, China. It was serviced by a Hawker Siddeley Trident, registration B-266, that crashed into a mountain on 26 April 1982, killing all 112 people aboard.

CAAC (中国民航), formerly the People's Aviation Company of China (中国人民航空公司), was the airline division of the Civil Aviation Administration of China and the monopoly civil airline in the People's Republic of China. It was founded on 17 July 1952, and merged into CAAC on 9 June 1953. In 1988, the monopoly was broken up and CAAC was split into six regional airlines, which later consolidated into China's Big Three airlines: Beijing-based Air China, Guangzhou-based China Southern Airlines, and Shanghai-based China Eastern Airlines.

Aeroflot Flight 2022 was a scheduled Soviet domestic passenger flight between Vilnius Airport in Lithuanian SSR and Moscow–Vnukovo Airport in Russian SFSR, that crashed on 16 December 1973, killing all 51 people on board. The flight suffered a loss of control as a result of a malfunction of its elevator, causing it to crash as it made its final descent into Moscow. At the time of the crash, it was the worst accident in aviation history involving a Tupolev Tu-124 since it entered service with Aeroflot in 1962.

TransAsia Airways Flight 791 was a regular cargo flight between Chiang Kai Shek International Airport and Macau International Airport. At 01:52 am local time on 21 December 2002, the ATR 72 operating the flight crashed into the sea 17 kilometres southwest of Magong, Penghu, Taiwan. The two crew members on board were killed.

Airborne Express Flight 827 was a functional evaluation flight (FEF) of an Airborne Express Douglas DC-8-63F that had undergone a major modification. On December 22, 1996, during the test flight, the aircraft stalled and crashed, killing all six people on board. Accident investigators determined the cause of the accident was improper crew control inputs.