| ||
 |
|---|
| Constitution |
A referendum on the electoral system was held in Andorra on 28 May 1982. [1] [2]
| ||
 |
|---|
| Constitution |
A referendum on the electoral system was held in Andorra on 28 May 1982. [1] [2]
In December 1980 the Co-Princes agreed on reforms, including the establishment of an Executive Council and the holding of a referendum on the voting system. Voters were offered the options of a majority system, a proportional system (in which the parishes would serve as constituencies) or a mixed system, with candidates elected using the majority system at the national level and the proportional system in the parishes. [1]
| Choice | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Majority system | 616 | 32.78 | |
| Proportional system | 450 | 23.95 | |
| Mixed system | 813 | 43.27 | |
| Total | 1,879 | 100.00 | |
| Valid votes | 1,879 | 97.56 | |
| Invalid/blank votes | 47 | 2.44 | |
| Total votes | 1,926 | 100.00 | |
| Registered voters/turnout | 3,660 | 52.62 | |
| Source: Direct Democracy | |||
National referendums are seldom used in Canada. The first two referendums in 1898 and 1942 saw a large number of voters in Quebec and in the remainder of Canada take dramatically-opposing stands, and the third in 1992 saw most of the voters take a stand opposed to that of the party in power.
Canada holds elections for legislatures or governments in several jurisdictions: for the federal (national) government, provincial and territorial governments, and municipal governments. Elections are also held for self-governing First Nations and for many other public and private organizations including corporations and trade unions. Municipal elections can also be held for both upper-tier and lower-tier governments.
At a national level, Greece holds elections for its legislature, the Hellenic Parliament.

There are two types of elections in Andorra: parliamentary elections and local elections. The 28 members of the General Council of the Valleys are elected in parliamentary elections for a maximum term of four years. In the local elections, the council members of the seven parishes of Andorra are elected for a four-year term.

Elections in Portugal are free, fair, and regularly held, in accordance with election law.

San Marino elects on the national level a legislature. The Grand and General Council has 60 members, elected for a five-year term by semi-proportional representation with national majority bonus.

The General Council is the unicameral parliament of Andorra. It is sometimes referred to as the General Council of the Valleys because it was the historical name and to distinguish it from similarly named bodies in the Val d'Aran and in France.

The Constitution of Andorra is the supreme law of the Principality of Andorra. It was adopted on 2 February 1993 and given assent by the Andorran people in a referendum on 14 March 1993. According to the Constitution itself, it was to enter into force on the day of its publication in the Butlletí Oficial del Principat d'Andorra, which occurred on 28 April 1993.
The Politics of British Columbia involve not only the governance of British Columbia, Canada, and the various political factions that have held or vied for legislative power, but also a number of experiments or attempts at political and electoral reform.

Parliamentary elections were held in Andorra on 26 April 2009, the fourth under the 1993 Constitution. The elections were held at the end of the normal four-year term of the General Council, but also following months of intense pressure from Co-Prince Nicolas Sarkozy to change the country's banking secrecy laws.
Electoral reform is a change in electoral systems which alters how public desires are expressed in election results.

Early parliamentary elections were held in Andorra on 3 April 2011 after the General Council of Andorra was dissolved over problems in passing important laws, including the budget and laws related to a value added tax.

A referendum on political reforms was held in Andorra on 16 January 1978. Voters were presented with two options, but the none of the above option received the most votes.

Parliamentary elections were held in Andorra on 1 March 2015. Despite losing five seats, the Democrats for Andorra retained their majority in the General Council, winning 15 of the 28 seats.

The 1983 Andorran local elections were held on 12 December. Voters elected the council members of the seven parishes of Andorra. For first time since 1867, local elections were not hold on the same day as parliamentary elections. This was also the first time that the totality of the council seats were up for election.
The 1999 Andorran local elections were held on 12 December. Voters elected the council members of the seven parishes.

The 2003 Andorran local elections were held on 14 December. Voters elected the council members of the seven parishes.

The 2007 Andorran local elections were held on 2 December. Voters elected the council members of the seven parishes.
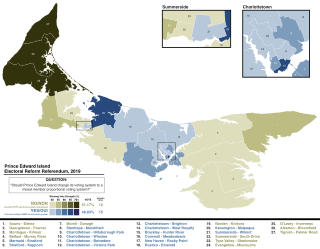
A referendum on electoral reform was held on April 23, 2019, in the Canadian province of Prince Edward Island – simultaneously with the 2019 provincial election – to determine if the province should adopt a mixed-member proportional representation voting system (MMP). A narrow majority voted to keep the existing first-past-the-post system. However, the referendum was not binding, as neither the yes or no side received majority support in 60% or more of the province's 27 electoral districts.

Parliamentary elections were held in Andorra on 7 April 2019, electing all 28 seats of the General Council. Although they remained the largest party, the Democrats for Andorra lost their parliamentary majority after losing four seats. The Social Democratic Party gained four seats, becoming the second-largest party.