The 2000 Baku earthquake occurred on November 25 at 22:09 local time with an epicenter just offshore Baku, Azerbaijan. It measured 6.8 on the moment magnitude scale and the maximum felt intensity was VI on the Mercalli intensity scale. It was followed three minutes later by a quake measuring 5.9. It was the strongest for almost 160 years, since 1842 in the Baku suburbs and in addition to the capital, affected Sumgayit, Shamakhi and neighboring cities. According to the United States Geological Survey, the epicentre was in the Caspian Sea, 25 km to the south-southeast of Baku. The earthquake was felt as far away as e.g. Tbilisi, 600 km northwest of the epicentre, Makhachkala and the Karabudakh and Isberbas settlements in Dagestan.
The 1991 Uttarkashi earthquake occurred at 02:53:16 Indian Standard Time (UTC+05:30) on 20 October with a moment magnitude of 6.8 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). This thrust event was instrumentally recorded and occurred along the Main Central Thrust in the Uttarkashi and Gharwal regions of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. High intensity shaking resulted in the deaths of at least 768 people and the destruction of thousands of homes.
The 2000 Turkmenistan earthquake took place at 8:11 p.m. Moscow Time on December 6 and had a magnitude of 7.0. The intensity of the earthquake reached VII at its epicenter, and IV at the Turkmen capital of Ashgabat. The epicentre was located approximately 25 kilometers north of the city of Balkanabat and 125 kilometres southeast of Türkmenbaşy. There were unconfirmed reports that the quake killed up to 11 people and injured 5 others.
The 2003 Dominican Republic earthquake occurred on September 22 at with a moment magnitude of 6.4 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (Extreme).
The 1969 Portugal earthquake struck western Portugal and Morocco on 28 February at 02:40 UTC. Originating west of the Strait of Gibraltar, the earthquake registered a magnitude of 7.8 and the maximum felt intensity was VII on the Mercalli intensity scale. In total, 13 people died and 80 sustained minor injuries. It is the largest earthquake to hit Portugal since the 1755 Lisbon earthquake.
On October 31 at 17:53 UTC the island of New Guinea was shaken by an earthquake of magnitude 6.9 that particularly affected the city of Madang on the north coast of Papua New Guinea. Causing between five and eighteen fatalities, it triggered landslides that ran down steep hills into poorly reinforced wooden huts. The area that experienced the most powerful intensity extended 20 kilometers (12 mi) out from the epicenter. Underwater landslides caused minor tsunami over about 100 km of coast and severed underwater cables in several places.
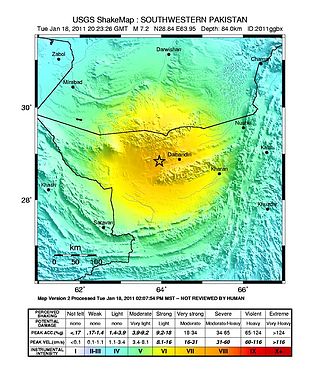
The 2011 Dalbandin earthquake occurred on with a moment magnitude of 7.2 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. The shock occurred in a sparsely populated area of Balochistan, caused moderate damage, three deaths, and some injuries.
The 1948 Desert Hot Springs earthquake occurred on December 4 at 3:43 p.m. Pacific Standard Time with a moment magnitude of 6.4 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. The shock was felt from the central coast of California in the north, and to Baja California in the south, and came at a time when earthquake research in southern California resumed following the Second World War. It was one of two events in the 20th century that have occurred near a complex region of the southern San Andreas Fault system where it traverses the San Gorgonio Pass and the northern Coachella Valley. Damage was not severe, but some serious injuries occurred, and aftershocks continued until 1957.
The 1979 Coyote Lake earthquake occurred at on August 6 with a moment magnitude of 5.7 and a maximum Mercalli Intensity of VII. The shock occurred on the Calaveras Fault near Coyote Lake in Santa Clara County, California and resulted in a number of injuries, including some that required hospitalization. Most of the $500,000 in damage that was caused was non-structural, but several businesses were closed for repairs. Data from numerous strong motion instruments was used to determine the type, depth, and extent of slip. A non-destructive aftershock sequence that lasted throughout the remainder of the month was of interest to seismologists, especially with regard to fault creep, and following the event local governments evaluated their response to the incident.
The 2010 Damghan earthquake occurred in northern Iran at on August 27 with a moment magnitude of 5.8 and maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. This strike-slip event damaged and destroyed a number of small villages in a sparsely populated region near the Alborz mountain range. It left four people dead, 40 injured, and about 800 without homes. The deaths and injuries in this moderate event were attributed to the low-quality construction styles that are typical of the area. The Iranian Strong Motion Network provided data by which seismologists determined the type and extent of the slip as well as the peak ground acceleration. Other large and destructive earthquakes have affected Semnan Province, including several events in 856 AD and 1953.
The 1999 Aïn Témouchent earthquake occurred on December 22 at in northern Algeria. The dip-slip event had a moment magnitude of 5.6 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. At least 22 were killed, 175 were injured, and 15,000–25,000 were made homeless. The Belgian Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters' EM-DAT database and the USGS' National Geophysical Data Center both list financial losses of $60.93 million.
The 1999 Ambrym earthquake occurred on November 27 at with a moment magnitude of 7.4 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. The back arc thrust event occurred within the Vanuatu archipelago, just to the south of the volcanic island of Ambrym. Vanuatu, which was previously known as New Hebrides, is subject to volcanic and earthquake activity because it lies on an active and destructive plate boundary called the New Hebrides Subduction Zone. While the National Geophysical Data Center classified the total damage as moderate, a destructive local tsunami did result in some deaths, with at least five killed and up to 100 injured.

The 1918 San Jacinto earthquake occurred in extreme eastern San Diego County in Southern California on April 21 at . The shock had a moment magnitude of 6.7 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). Several injuries and one death occurred with total losses estimated to be $200,000.
The 1990 Upland earthquake occurred at on February 28 with a moment magnitude of 5.7 and a maximum Mercalli Intensity of VII. This left-lateral strike-slip earthquake occurred west of the San Andreas Fault System and injured thirty people, with total losses of $12.7 million. Many strong motion instruments captured the event, with an unexpectedly high value seen on water tank near the epicentral area.
The 2004 Les Saintes earthquake occurred at on November 21, 2004 with a moment magnitude of 6.3 and maximum European macroseismic intensity of VIII. The shock was named for Îles des Saintes "Island of the Saints", a group of small islands to the south of Guadeloupe, which is an overseas department of France. Although it occurred near the Lesser Antilles subduction zone, this was an intraplate, normal fault event. It resulted in one death, 13 injuries, and 40 people being made homeless, but the overall damage was considered moderate. A small, nondestructive tsunami was reported, but run-up and inundation distances were difficult to measure due to a storm that occurred on the day of the event. Unusual effects at a volcanic lake on Dominica were also documented, and an aftershock caused additional damage three months later.
The 1974 Lesser Antilles earthquake occurred at on October 8 with a moment magnitude of 6.9 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). Four people were injured in what the United States' National Geophysical Data Center called a moderately destructive event.
The 1963 Marj earthquake occurred on February 21 in northern Libya. The earthquake occurred at with a moment magnitude of 5.6 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). Financial losses totaled US$5 million, with 290–375 deaths, 375–500 injuries, and 12,000 people being rendered homeless.
The 1981 Westmorland earthquake occurred at 05:09 Pacific Daylight Time on April 26. The moderate strike-slip shock took place in the Imperial Valley of Southern California, just north of the Mexico–United States border. No injuries or deaths occurred, but damage was estimated at $1–3 million. With a Mercalli intensity of VII, this was one of fifteen intensity VII or greater shocks in the Imperial Valley that were observed in the 20th century up until April 1981. The region experiences large stand-alone events and earthquake swarms due to its position in an area of complex conditions where faulting transitions from strike-slip movement to the north and divergence to the south.
The 1997 Bojnurd earthquake occurred on 4 February at 14:07 IRST in Iran. The epicenter of the 6.5 earthquake was in the Kopet Dag mountains of North Khorasan, near the Iran–Turkmenistan border, about 579 km (360 mi) northeast of Tehran. The earthquake is characterized by shallow strike-slip faulting in a zone of active faults. Seismic activity is present as the Kopet Dag is actively accommodating tectonics through faulting. The earthquake left 88 dead, 1,948 injured, and affected 173 villages, including four which were destroyed. Damage also occurred in Shirvan and Bojnord counties. The total cost of damage was estimated to be over US$ 30 million.
The 1979 Saint Elias earthquake affected Alaska at 12:27 AKST on 28 February. The thrust-faulting 7.5 earthquake had an epicenter in the Granite Mountains. Though the maximum recorded Modified Mercalli intensity was VII, damage was minimal and there were no casualties due to the remoteness of the faulting. Damage also extended across the border in parts of Yukon, Canada.


