
Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is generally a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape (conformation) and reactivity of ions and molecules. Steric effects complement electronic effects, which dictate the shape and reactivity of molecules. Steric repulsive forces between overlapping electron clouds result in structured groupings of molecules stabilized by the way that opposites attract and like charges repel.

Organotin chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organotin compounds or stannanes, which are organometallic compounds containing tin–carbon bonds. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide, discovered by Edward Frankland in 1849. The area grew rapidly in the 1900s, especially after the discovery of the Grignard reagents, which are useful for producing Sn–C bonds. The area remains rich with many applications in industry and continuing activity in the research laboratory.
As the name suggests, a non-nucleophilic base is a sterically hindered organic base that is a poor nucleophile. Normal bases are also nucleophiles, but often chemists seek the proton-removing ability of a base without any other functions. Typical non-nucleophilic bases are bulky, such that protons can attach to the basic center but alkylation and complexation is inhibited.
Diphosphene is a type of organophosphorus compound that has a phosphorus–phosphorus double bond, denoted by R-P=P-R'. These compounds are not common but are of theoretical interest. Normally, compounds with the empirical formula RP exist as rings. However, like other multiple bonds between heavy main-group elements, P=P double bonds can be stabilized by a large steric hindrance from the substitutions. The first isolated diphosphene bis(2,4,6-tri-tert-butylphenyl)diphosphene was exemplified by Masaaki Yoshifuji and his coworkers in 1981, in which diphosphene is stabilized by two bulky phenyl group.
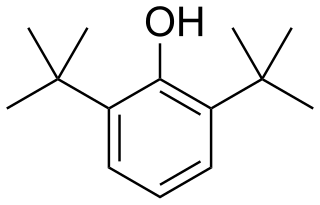
2,6-Di-tert-butylphenol is an organic compound with the structural formula 2,6-((CH3)3C)2C6H3OH. This colorless solid alkylated phenol and its derivatives are used industrially as UV stabilizers and antioxidants for hydrocarbon-based products ranging from petrochemicals to plastics. Illustrative of its usefulness, it prevents gumming in aviation fuels.
Pyrylium is a cation with formula C5H5O+, consisting of a six-membered ring of five carbon atoms, each with one hydrogen atom, and one positively charged oxygen atom. The bonds in the ring are conjugated as in benzene, giving it an aromatic character. In particular, because of the positive charge, the oxygen atom is trivalent. Pyrilium is a mono-cyclic and heterocyclic compound, one of the oxonium ions.
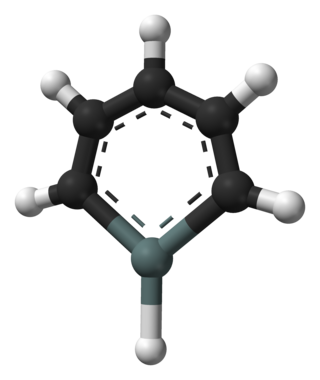
Stannabenzene (C5H6Sn) is the parent representative of a group of organotin compounds that are related to benzene with a carbon atom replaced by a tin atom. Stannabenzene itself has been studied by computational chemistry, but has not been isolated.

2,6-Lutidine is a natural heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the formula (CH3)2C5H3N. It is one of several dimethyl-substituted derivative of pyridine, all of which are referred to as lutidines. It is a colorless liquid with mildly basic properties and a pungent, noxious odor.

Salcomine is a coordination complex derived from the salen ligand and cobalt. The complex, which is planar, and a variety of its derivatives are carriers for O2 as well as oxidation catalysts.

2,6-Di-tert-butylpyridine is an organic compound with the formula (Me3C)2C5H3N. This colourless, oily liquid is derived from pyridine by replacement of the two H atoms with tert-butyl groups. It is a hindered base. For example, it can be protonated, but it does not form an adduct with boron trifluoride.

tert-Butylphosphaacetylene is an organophosphorus compound. Abbreviated t-BuCP, it was the first example of an isolable phosphaalkyne. Prior to its synthesis, the double bond rule had suggested that elements of Period 3 and higher were unable to form double or triple bonds with lighter main group elements because of weak orbital overlap. The synthesis of t-BuCP discredited much of the double bond rule and opened new studies into the formation of unsaturated phosphorus compounds.

A selenenic acid is an organoselenium compound and an oxoacid with the general formula RSeOH, where R ≠ H. It is the first member of the family of organoselenium oxoacids, which also include seleninic acids and selenonic acids, which are RSeO2H and RSeO3H, respectively. Selenenic acids derived from selenoenzymes are thought to be responsible for the antioxidant activity of these enzymes. This functional group is sometimes called SeO-selenoperoxol.

2,4,6-Tri-tert-butylphenol (2,4,6-TTBP) is a phenol symmetrically substituted with three tert-butyl groups and thus strongly sterically hindered. 2,4,6-TTBP is a readily oxidizable aromatic compound and a weak acid. It oxidizes to give the deep-blue 2,4,6-tri-tert-butylphenoxy radical. 2,4,6-TTBP is related to 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol, which is widely used as an antioxidant in industrial applications. These compounds are colorless solids.

Selenopyrylium is an aromatic heterocyclic compound consisting of a six-membered ring with five carbon atoms and a positively charged selenium atom.

In the area of organometallic chemistry, a bulky cyclopentadienyl ligand is jargon for a ligand of the type C
5H
5−nR−
n where R is a branched alkyl and n = 3 or 4. Representative examples are the tetraisopropyl derivative C
5HiPr−
4 and the tris(tert-butyl) derivative 1,2,4-C
5H
2tBu−
3. These ligands are so large that their complexes behave differently from the pentamethylcyclopentadienyl analogues. Because they cannot closely approach the metal, these bulky ligands stabilize high spin complexes, such as (C5H2tBu3)2Fe2I2. These large ligands stabilize highly unsaturated derivatives such as (C5H2tBu3)2Fe2N2.

Transition metal isocyanide complexes are coordination compounds containing isocyanide ligands. Because isocyanides are relatively basic, but also good pi-acceptors, a wide range of complexes are known. Some isocyanide complexes are used in medical imaging.
1-Phosphaallenes is are allenes in which the first carbon atom is replaced by phosphorus, resulting in the structure: -P=C=C<.
Pnictogen-substituted tetrahedranes are pnictogen-containing analogues of tetrahedranes with the formula RxCxPn4-x. Computational work has indicated that the incorporation of pnictogens to the tetrahedral core alleviates the ring strain of tetrahedrane. Although theoretical work on pnictogen-substituted tetrahedranes has existed for decades, only the phosphorus-containing species have been synthesized. These species exhibit novel reactivities, most often through ring-opening and polymerization pathways. Phosphatetrahedranes are of interest as new retrons for organophosphorus chemistry. Their strain also make them of interest in the development of energy-dense compounds.













