
Lemon balm is a perennial herbaceous plant in the mint family and native to south-central Europe, the Mediterranean Basin, Iran, and Central Asia, but now naturalised elsewhere.

Salvia rosmarinus, commonly known as rosemary, is a shrub with fragrant, evergreen, needle-like leaves and white, pink, purple, or blue flowers. It is native to the Mediterranean region, as well as Portugal and Spain. Until 2017, it was known by the scientific name Rosmarinus officinalis, now a synonym.

Rosmarinus is a small taxonomic clade of woody, perennial herbs with fragrant evergreen needle-like leaves in the family Lamiaceae, native to the Mediterranean Basin.

Salvia officinalis, the common sage or sage, is a perennial, evergreen subshrub, with woody stems, grayish leaves, and blue to purplish flowers. It is a member of the mint family Lamiaceae and native to the Mediterranean region, though it has been naturalized in many places throughout the world. It has a long history of medicinal and culinary use, and in modern times it has been used as an ornamental garden plant. The common name "sage" is also used for closely related species and cultivars.

Gajah Mada, also known as Jirnnodhara, was a powerful military leader and mahapatih of the Javanese empire of Majapahit during the 14th century. He is credited in Old Javanese manuscripts, poems, and inscriptions with bringing the empire to its peak of glory.

Borneol is a bicyclic organic compound and a terpene derivative. The hydroxyl group in this compound is placed in an endo position. The exo diastereomer is called isoborneol. Being chiral, borneol exists as enantiomers, both of which are found in nature.

The Sumatran elephant is one of three recognized subspecies of the Asian elephant, and native to the Indonesian island of Sumatra. In 2011, IUCN upgraded the conservation status of the Sumatran elephant from endangered to critically endangered in its Red List as the population had declined by at least 80% during the past three generations, estimated to be about 75 years. The subspecies is preeminently threatened by habitat loss, degradation and fragmentation, and poaching; over 69% of potential elephant habitat has been lost within the last 25 years. Much of the remaining forest cover is in blocks smaller than 250 km2 (97 sq mi), which are too small to contain viable elephant populations.
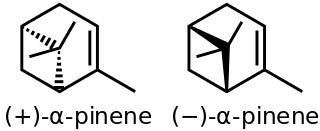
α-Pinene is an organic compound of the terpene class. It is one of the two isomers of pinene, the other being β-pinene. An alkene, it contains a reactive four-membered ring. It is found in the oils of many species of coniferous trees, notably the Pinus and Picea species. It is also found in the essential oil of rosemary and Satureja myrtifolia. Both enantiomers are known in nature; (1S,5S)- or (−)-α-pinene is more common in European pines, whereas the (1R,5R)- or (+)-α-isomer is more common in North America. The enantiomers' racemic mixture is present in some oils such as eucalyptus oil and orange peel oil.

The Sri Lankan elephant is native to Sri Lanka and one of three recognised subspecies of the Asian elephant. It is the type subspecies of the Asian elephant and was first described by Carl Linnaeus under the binomial Elephas maximus in 1758. The Sri Lankan elephant population is now largely restricted to the dry zone in the north, east and southeast of Sri Lanka. Elephants are present in Udawalawe National Park, Yala National Park, Lunugamvehera National Park, Wilpattu National Park and Minneriya National Park but also live outside protected areas. It is estimated that Sri Lanka has the highest density of elephants in Asia. Human-elephant conflict is increasing due to conversion of elephant habitat to settlements and permanent cultivation.
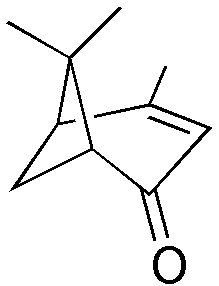
Verbenone is a natural organic compound classified as a terpene that is found naturally in a variety of plants. The chemical has a pleasant characteristic odor. Besides being a natural constituent of plants, it and its analogs are insect pheromones. In particular, verbenone when formulated in a long-lasting matrix has an important role in the control of bark beetles such as the mountain pine beetle and the Southern pine bark beetle.

The Indian elephant is one of three extant recognized subspecies of the Asian elephant, native to mainland Asia. The species is smaller than the African elephant species with a convex back and the highest body point on its head. The species exhibits significant sexual dimorphism with a male reaching an average shoulder height of about 3.2 m (10 ft) and weighing up to 5,400 kg (11,900 lb) whereas a female reaches an average shoulder height of about 2.54 m (8.3 ft) and weighs up to 4,160 kg (9,170 lb). It has a broader skull with a concave forehead, two large laterally folded ears and a large trunk. It has grey colored smooth skin with four large legs and a long tail.
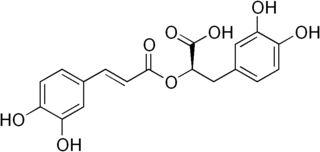
Rosmarinic acid, named after rosemary, is a polyphenol constituent of many culinary herbs, including rosemary, perilla, sage, mint, and basil.

Chrysolina americana, common name rosemary beetle, is a species of beetle belonging to the family Chrysomelidae.

Salvia is the largest genus of plants in the sage family Lamiaceae, with nearly 1,000 species of shrubs, herbaceous perennials, and annuals. Within the Lamiaceae, Salvia is part of the tribe Mentheae within the subfamily Nepetoideae. One of several genera commonly referred to as sage, it includes two widely used herbs, Salvia officinalis and Salvia rosmarinus.

Pyrausta laticlavia, the southern purple mint moth, is a species of moth of the family Crambidae. It is found from New Jersey south to Florida, west to Texas, Oklahoma and California. In California, the species has expanded its range northward into the San Francisco Bay area (1990) and Sacramento Valley (1993) recently.
Vulcaniella rosmarinella is a moth of the family Cosmopterigidae. It is found in the area surrounding the Mediterranean Sea, as far east as Crete. It is also found in North Africa.
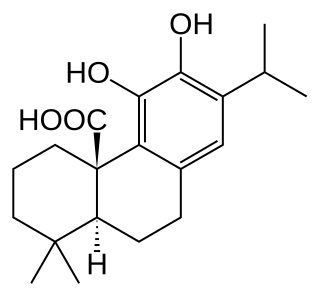
Carnosic acid is a natural benzenediol abietane diterpene found in rosemary and common sage. Dried leaves of rosemary and sage contain 1.5 to 2.5% carnosic acid.

Carnosol is a phenolic diterpene found in the herbs rosemary and Mountain desert sage.
Tecmerium rosmarinella is a moth in the family Blastobasidae. It is found in France.
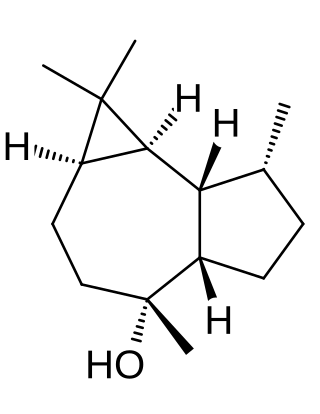
Ledol is a poisonous sesquiterpene that can cause cramps, paralysis, and delirium. Caucasian peasants used Rhododendron plants for these effects in shamanistic rituals.

















