
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated –COO− form under biological conditions), and an imidazole side chain (which is partially protonated), classifying it as a positively charged amino acid at physiological pH. Initially thought essential only for infants, it has now been shown in longer-term studies to be essential for adults also. It is encoded by the codons CAU and CAC.
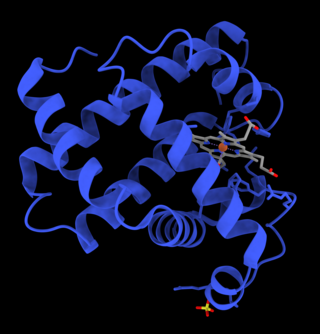
Myoglobin is an iron- and oxygen-binding protein found in the cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue of vertebrates in general and in almost all mammals. Myoglobin is distantly related to hemoglobin. Compared to hemoglobin, myoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen and does not have cooperative binding with oxygen like hemoglobin does. Myoglobin consists of non-polar amino acids at the core of the globulin, where the heme group is non-covalently bounded with the surrounding polypeptide of myoglobin. In humans, myoglobin is found in the bloodstream only after muscle injury.

The cytochrome complex, or cyt c, is a small hemeprotein found loosely associated with the inner membrane of the mitochondrion where it plays a critical role in cellular respiration. It transfers electrons between Complexes III and IV. Cytochrome c is highly water-soluble, unlike other cytochromes. It is capable of undergoing oxidation and reduction as its iron atom converts between the ferrous and ferric forms, but does not bind oxygen. It also plays a major role in cell apoptosis. In humans, cytochrome c is encoded by the CYCS gene.

In molecular biology, post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent process of changing proteins following protein biosynthesis. PTMs may involve enzymes or occur spontaneously. Proteins are created by ribosomes, which translate mRNA into polypeptide chains, which may then change to form the mature protein product. PTMs are important components in cell signalling, as for example when prohormones are converted to hormones.

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large proportion of all proteins are part of this category. For instance, at least 1000 human proteins contain zinc-binding protein domains although there may be up to 3000 human zinc metalloproteins.

Luciferase is a generic term for the class of oxidative enzymes that produce bioluminescence, and is usually distinguished from a photoprotein. The name was first used by Raphaël Dubois who invented the words luciferin and luciferase, for the substrate and enzyme, respectively. Both words are derived from the Latin word lucifer, meaning "lightbearer", which in turn is derived from the Latin words for "light" (lux) and "to bring or carry" (ferre).

Imidazole (ImH) is an organic compound with the formula C3N2H4. It is a white or colourless solid that is soluble in water, producing a mildly alkaline solution. In chemistry, it is an aromatic heterocycle, classified as a diazole, and has non-adjacent nitrogen atoms in meta-substitution.

Malate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.37) (MDH) is an enzyme that reversibly catalyzes the oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate using the reduction of NAD+ to NADH. This reaction is part of many metabolic pathways, including the citric acid cycle. Other malate dehydrogenases, which have other EC numbers and catalyze other reactions oxidizing malate, have qualified names like malate dehydrogenase (NADP+).

Rieske proteins are iron–sulfur protein (ISP) components of cytochrome bc1 complexes and cytochrome b6f complexes and are responsible for electron transfer in some biological systems. John S. Rieske and co-workers first discovered the protein and in 1964 isolated an acetylated form of the bovine mitochondrial protein. In 1979, Trumpower's team isolated the "oxidation factor" from bovine mitochondria and showed it was a reconstitutively-active form of the Rieske iron-sulfur protein.
It is a unique [2Fe-2S] cluster in that one of the two Fe atoms is coordinated by two histidine residues rather than two cysteine residues. They have since been found in plants, animals, and bacteria with widely ranging electron reduction potentials from -150 to +400 mV.

Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal redox state of cells can cause toxic effects through the production of peroxides and free radicals that damage all components of the cell, including proteins, lipids, and DNA. Oxidative stress from oxidative metabolism causes base damage, as well as strand breaks in DNA. Base damage is mostly indirect and caused by the reactive oxygen species generated, e.g., O−
2, OH and H2O2. Further, some reactive oxidative species act as cellular messengers in redox signaling. Thus, oxidative stress can cause disruptions in normal mechanisms of cellular signaling.
Copper proteins are proteins that contain one or more copper ions as prosthetic groups. Copper proteins are found in all forms of air-breathing life. These proteins are usually associated with electron-transfer with or without the involvement of oxygen (O2). Some organisms even use copper proteins to carry oxygen instead of iron proteins. A prominent copper protein in humans is in cytochrome c oxidase (cco). This enzyme cco mediates the controlled combustion that produces ATP. Other copper proteins include some superoxide dismutases used in defense against free radicals, peptidyl-α-monooxygenase for the production of hormones, and tyrosinase, which affects skin pigmentation.
Catechol oxidase is a copper oxidase that contains a type 3 di-copper cofactor and catalyzes the oxidation of ortho-diphenols into ortho-quinones coupled with the reduction of molecular oxygen to water. It is present in a variety of species of plants and fungi including Ipomoea batatas and Camellia sinensis. Metalloenzymes with type 3 copper centers are characterized by their ability to reversibly bind dioxygen at ambient conditions. In plants, catechol oxidase plays a key role in enzymatic browning by catalyzing the oxidation of catechol to o-quinone in the presence of oxygen, which can rapidly polymerize to form the melanin that grants damaged fruits their dark brown coloration.
Nitrite reductase refers to any of several classes of enzymes that catalyze the reduction of nitrite. There are two classes of NIR's. A multi haem enzyme reduces NO2− to a variety of products. Copper containing enzymes carry out a single electron transfer to produce nitric oxide.

Heme C is an important kind of heme.

6-Phosphogluconolactonase (EC 3.1.1.31, 6PGL, PGLS, systematic name 6-phospho-D-glucono-1,5-lactone lactonohydrolase) is a cytosolic enzyme found in all organisms that catalyzes the hydrolysis of 6-phosphogluconolactone to 6-phosphogluconic acid in the oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway:

Histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRG) is a glycoprotein that in humans is encoded by the HRG gene. The HRG protein is produced in the liver, and it could also be synthesized by monocytes, macrophages, and megakaryocytes. It possesses a multi-domain structure, which makes it capable of binding to numerous ligands and modulating various biological processes including immunity, vascularization and coagulation.

Branched chain ketoacid dehydrogenase kinase (BCKDK) is an enzyme encoded by the BCKDK gene on chromosome 16. This enzyme is part of the mitochondrial protein kinases family and it is a regulator of the valine, leucine, and isoleucine catabolic pathways. BCKDK is found in the mitochondrial matrix and the prevalence of it depends on the type of cell. Liver cells tend to have the lowest concentration of BCKDK, whereas skeletal muscle cells have the highest amount. Abnormal activity of this enzyme often leads to diseases such as maple syrup urine disease and cachexia.

Ergothioneine is a naturally occurring amino acid and is a thiourea derivative of histidine, containing a sulfur atom on the imidazole ring. This compound occurs in relatively few organisms, notably actinomycetota, cyanobacteria, and certain fungi. Ergothioneine was discovered by Charles Tanret in 1909 and named after the ergot fungus from which it was first purified, with its structure being determined in 1911.

Nitrotyrosine is a product of tyrosine nitration mediated by reactive nitrogen species such as peroxynitrite anion and nitrogen dioxide. Nitrotyrosine is identified as an indicator or marker of cell damage, inflammation as well as NO (nitric oxide) production. Nitrotyrosine is formed in the presence of the active metabolite NO. Generally in many disease states, oxidative stress increases the production of superoxide (O2−) and NO forming peroxynitrite (ONOO−) a destructive free radical oxidant. The production of ONOO− is capable of oxidizing several lipoproteins and of nitrating tyrosine residues in many proteins. It is difficult to determine the production of ONOO− so, usually nitrotyrosine in proteins are the detectable marker for indirectly detecting ONOO−. It is detected in large number of pathological conditions and is considered a marker of NO-dependent, reactive nitrogen species-induced nitrative stress. Nitrotyrosine is detected in biological fluids such as plasma, lung aspirants-BALF (Broncho alveolar lining fluid) and urine. Increased level of nitrotyrosine is detected in rheumatoid arthritis, septic shock and coeliac disease. In all these studies nitrotyrosine was undetected in healthy subjects. Nitrotyrosine is also found in numerous other disease-affected tissues, such as the cornea in keratoconus. Peroxynitrite and/or nitrative stress may participate in the pathogenesis of diabetes.
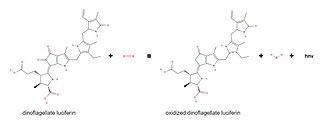
Dinoflagellate luciferase (EC 1.13.12.18, Gonyaulax luciferase) is a specific luciferase, an enzyme with systematic name dinoflagellate-luciferin:oxygen 132-oxidoreductase.

















