
The economy of Canada is a highly developed mixed economy, with the world's tenth-largest economy as of 2023, and a nominal GDP of approximately US$2.117 trillion. Canada is one of the world's largest trading nations, with a highly globalized economy. In 2021, Canadian trade in goods and services reached $2.016 trillion. Canada's exports totalled over $637 billion, while its imported goods were worth over $631 billion, of which approximately $391 billion originated from the United States. In 2018, Canada had a trade deficit in goods of $22 billion and a trade deficit in services of $25 billion. The Toronto Stock Exchange is the tenth-largest stock exchange in the world by market capitalization, listing over 1,500 companies with a combined market capitalization of over US$3 trillion.

The economy of Moldova is an emerging upper-middle income economy, with a high Human Development Index. Moldova is a landlocked Eastern European country, bordered by Ukraine on the East and Romania to the West. It is a former Soviet republic and today a candidate member to the European Union.

The economy of New Zealand is a highly developed free-market economy. It is the 52nd-largest national economy in the world when measured by nominal gross domestic product (GDP) and the 62nd-largest in the world when measured by purchasing power parity (PPP). New Zealand has a large GDP for its population of 5 million, and sources of revenue are spread throughout the large island nation. The country has one of the most globalised economies and depends greatly on international trade, mainly with Australia, China, the European Union, Japan, Singapore, South Korea, and the United States. New Zealand's 1983 Closer Economic Relations agreement with Australia means that the economy aligns closely with that of Australia.

The economy of the United Kingdom is a highly developed social market economy. It is the sixth-largest national economy in the world measured by nominal gross domestic product (GDP), ninth-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP), and twenty-first by nominal GDP per capita, constituting 3.1% of nominal world GDP. The United Kingdom constitutes 2.3% of world GDP by purchasing power parity (PPP).

The government budget balance, also referred to as the general government balance, public budget balance, or public fiscal balance, is the difference between government revenues and spending. For a government that uses accrual accounting the budget balance is calculated using only spending on current operations, with expenditure on new capital assets excluded. A positive balance is called a government budget surplus, and a negative balance is a government budget deficit. A government budget presents the government's proposed revenues and spending for a financial year.
The economies of Canada and the United States are similar because both are developed countries. While both countries feature in the top ten economies in the world in 2022, the U.S. is the largest economy in the world, with US$24.8 trillion, with Canada ranking ninth at US$2.2 trillion.
In the United Kingdom, the Retail Prices Index or Retail Price Index (RPI) is a measure of inflation published monthly by the Office for National Statistics. It measures the change in the cost of a representative sample of retail goods and services.

The United States budget comprises the spending and revenues of the U.S. federal government. The budget is the financial representation of the priorities of the government, reflecting historical debates and competing economic philosophies. The government primarily spends on healthcare, retirement, and defense programs. The non-partisan Congressional Budget Office provides extensive analysis of the budget and its economic effects. It has reported that large budget deficits over the next 30 years are projected to drive federal debt held by the public to unprecedented levels—from 98 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2020 to 195 percent by 2050.

Hydrocarbon Oil Duty is a fuel tax levied on some fuels used by most road motor vehicles in the United Kingdom; with exceptions for local bus services, some farm and construction vehicles and aviation, which pay reduced or no fuel duty.
RPIX is a measure of inflation in the United Kingdom, equivalent to the all items Retail Price Index (RPI) excluding mortgage interest payments.
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is the official measure of inflation in consumer prices in the United Kingdom. It is also called the Harmonised Index of Consumer Prices (HICP).

The economy of the Republic of Ireland is a highly developed knowledge economy, focused on services in high-tech, life sciences, financial services and agribusiness, including agrifood. Ireland is an open economy, and ranks first for high-value foreign direct investment (FDI) flows. In the global GDP per capita tables, Ireland ranks 2nd of 192 in the IMF table and 4th of 187 in the World Bank ranking.
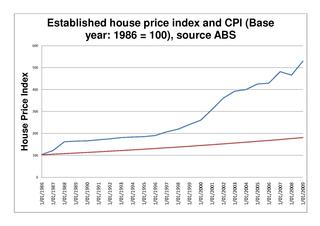
The Australian property bubble is the economic theory that the Australian property market has become or is becoming significantly overpriced and due for a significant downturn. Since the early 2010s, various commentators, including one Treasury official, have claimed the Australian property market is in a significant bubble.

The financial position of the United States includes assets of at least $269 trillion and debts of $145.8 trillion to produce a net worth of at least $123.8 trillion. GDP in Q1 decline was due to foreclosures and increased rates of household saving. There were significant declines in debt to GDP in each sector except the government, which ran large deficits to offset deleveraging or debt reduction in other sectors.

The March 2010 United Kingdom Budget, official known as Budget 2010: Securing the recovery, was delivered by Alistair Darling, Chancellor of the Exchequer, to the House of Commons on 24 March 2010.

The United Kingdom national debt is the total quantity of money borrowed by the Government of the United Kingdom at any time through the issue of securities by the British Treasury and other government agencies.

The 1999 United Kingdom Budget, officially known as Budget 99: Building a Stronger Economic Future for Britain was the formal government budget for the year 1999.

Gordon Brown served as Chancellor of the Exchequer of the United Kingdom from 2 May 1997 to 27 June 2007. His tenure was marked by major reform of Britain's monetary and fiscal policy architecture, transferring interest rate setting powers to the Bank of England, by a wide extension of the powers of the Treasury to cover much domestic policy and by transferring responsibility for banking supervision to the Financial Services Authority. Brown presided over the longest period of sustained economic growth in British history. He had previously served as Shadow Chancellor of the Exchequer in the Tony Blair Shadow Cabinet from 1994 to 1997. As Shadow Chancellor, Brown as Chancellor-in-waiting was seen as a good choice by business and the middle class.

The 1997 United Kingdom budget was delivered by Gordon Brown, the Chancellor of the Exchequer, to the House of Commons on 2 July 1997. It was the first budget to be presented by Brown during his tenure as Chancellor, and the first Labour budget to be presented since April 1979. The 1997 budget marked a significant change of direction in economic policy following Labour's election win in May 1997. Among the measures announced were a five-year plan to reduce the budget deficit, a £5.2bn windfall tax on recently privatised utilities which was to fund Labour's planned Welfare to Work scheme, and a reduction in VAT on fuel. The budget was welcomed by business, which viewed it as fiscally responsible, but it was greeted less warmly by the UK's utility providers.

The 2023 United Kingdom budget was delivered to the House of Commons on 15 March 2023 by Chancellor of the Exchequer Jeremy Hunt. It was the first full budget statement to be presented by Hunt since his appointment as chancellor. The date of the budget was confirmed by Hunt on 19 December 2022. At the same time he confirmed the budget would be accompanied by a full budget report from the Office for Budget Responsibility. The statement was presented as a budget for growth, with the objective of bringing about the conditions for long-term sustainable economic growth within the UK.













