
The politics of Zambia takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the president of Zambia is head of state, head of government and leader of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government, while legislative power is vested in both the government and parliament. Formerly Northern Rhodesia, Zambia became a republic immediately upon attaining independence in October 1964.

The Legislative Yuan is the unicameral legislature of the Republic of China (Taiwan) located in Taipei. The Legislative Yuan is composed of 113 members, who are directly elected for four-year terms by people of the Taiwan Area through a parallel voting system.

The president of Turkey, officially the president of the Republic of Türkiye, is the head of state and head of government of Turkey. The president directs the executive branch of the national government and is the commander-in-chief of the Turkish military. The president also heads the National Security Council.

The National Assembly was the authoritative legislative body of the Republic of China, from 1947 to 2005. Along with the Control Yuan and the Legislative Yuan, the National Assembly formed the tricameral parliament of the Republic of China.

Paul Kagame is a Rwandan politician and former military officer who has been the President of Rwanda since 2000. He was previously a commander of the Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF), a rebel armed force which invaded Rwanda in 1990. The RPF was one of the parties of the conflict during the Rwandan Civil War and the armed force which ended the Rwandan genocide. He was considered Rwanda's de facto leader when he was Vice President and Minister of Defence under President Pasteur Bizimungu from 1994 to 2000 after which the vice-presidential post was abolished.
A supermajority is a requirement for a proposal to gain a specified level of support which is greater than the threshold of one-half used for a simple majority. Supermajority rules in a democracy can help to prevent a majority from eroding fundamental rights of a minority, but can also hamper efforts to respond to problems and encourage corrupt compromises at times when action is taken. Changes to constitutions, especially those with entrenched clauses, commonly require supermajority support in a legislature. Parliamentary procedure requires that any action of a deliberative assembly that may alter the rights of a minority have a supermajority requirement, such as a two-thirds vote. In consensus democracy the supermajority rule is applied in most cases.

Elections in Rwanda are manipulated in various ways, which include banning opposition parties, arresting or assassinating critics, and electoral fraud. According to its constitution, Rwanda is a multi-party democracy with a presidential system. In practice, it functions as a one-party state ruled by the Rwandan Patriotic Front and its leader Paul Kagame. The President and majority of members of the Chamber of Deputies are directly elected, whilst the Senate is indirectly elected and partly appointed.

The Constitution of Rwanda was adopted by referendum on May 26, 2003. It replaced the Constitution of 1991.

The Constitution of Liberia is the supreme law of the Republic of Liberia. The current constitution, which came into force on 6 January 1986, replaced the Liberian Constitution of 1847, which had been in force since the independence of Liberia. Much like the 1847 Constitution, the Constitution creates a system of government heavily modeled on the Federal Government of the United States.

Presidential elections were held in Rwanda on 9 August 2010, the second since the Rwandan Civil War. Incumbent President Paul Kagame of the Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF) was re-elected for a second seven-year term with 93% of the vote.
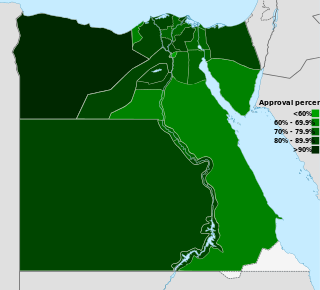
A constitutional referendum was held in Egypt on 19 March 2011, following the 2011 Egyptian revolution. More than 14 million (77%) were in favour, while around 4 million (23%) opposed the changes; 41% of 45 million eligible voters turned out to vote.
A referendum is a direct vote in which an entire electorate is asked to either accept or reject a particular proposal. This article summarises referendum laws and practice in various countries.

Presidential elections were held in Benin on 6 March 2016, having been delayed by one week due to logistical constraints. Incumbent president Thomas Boni Yayi was at the end of his second presidential term and was constitutionally barred from running for a third. The elections grabbed the interest of many of the country's top businessmen, resulting in over 30 candidates trying to run for the presidency. A second round was held on 20 March, in which businessman Patrice Talon defeated Prime Minister Lionel Zinsou.

Presidential elections were held in Rwanda on 4 August 2017. The incumbent President of Rwanda, Paul Kagame, was re-elected to a third seven-year term, allegedly with 98.79% of the vote on a 98.15% turnout.

A constitutional referendum was held in Senegal on 20 March 2016. Proposed by President Macky Sall, it was the fourth constitutional referendum in Senegalese history. The proposed changes to the constitution were approved by 62% of voters. Voter turnout was 39%. A majority voted in favour in thirteen of the fourteen regions, with only Diourbel Region seeing a majority against.

A constitutional referendum was held in Burundi on 17 May 2018. The proposed amendments to the constitution were approved by over 70% of voters.

A constitutional referendum was held in Egypt between 20 and 22 April 2019, The main proposed amendments were re-establishing the presidential term to six years, from four previously, and lengthening the then president's current term and allowing him to stand for an additional term in office, thereby allowing President Abdel Fattah el-Sisi to potentially remain in power until 2030. The changes were approved by 88.83% of voters who voted, with a 44% turnout.

General elections were held in Rwanda on 15 July 2024 to elect the president and members of the Chamber of Deputies.
The inauguration of Paul Kagame as the president of Rwanda took place on August 11, 2024, at Amahoro National Stadium in Kigali, Rwanda. This marked the beginning of Kagame's new term of a five-year term following his overwhelming victory in the 2024 presidential election where he received 99.18% of the vote. The ceremony was attended by numerous dignitaries, including at least 22 heads of state, as well as thousands of Rwandans and international guests.














