| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following are events that occurred in Antarctica in 2018 .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following are events that occurred in Antarctica in 2018 .

The geography of Antarctica is dominated by its south polar location and, thus, by ice. The Antarctic continent, located in the Earth's southern hemisphere, is centered asymmetrically around the South Pole and largely south of the Antarctic Circle. It is washed by the Southern Ocean or, depending on definition, the southern Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans. It has an area of more than 14.2 million km2. Antarctica is the largest ice desert in the world.
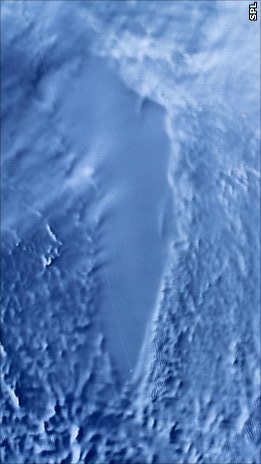
Lake Vostok is the largest of Antarctica's 675 known subglacial lakes. Lake Vostok is located at the southern Pole of Cold, beneath Russia's Vostok Station under the surface of the central East Antarctic Ice Sheet, which is at 3,488 m (11,444 ft) above mean sea level. The surface of this fresh water lake is approximately 4,000 m (13,100 ft) under the surface of the ice, which places it at approximately 500 m (1,600 ft) below sea level.

The Ross Sea is a deep bay of the Southern Ocean in Antarctica, between Victoria Land and Marie Byrd Land and within the Ross Embayment, and is the southernmost sea on Earth. It derives its name from the British explorer James Clark Ross who visited this area in 1841. To the west of the sea lies Ross Island and Victoria Land, to the east Roosevelt Island and Edward VII Peninsula in Marie Byrd Land, while the southernmost part is covered by the Ross Ice Shelf, and is about 200 miles (320 km) from the South Pole. Its boundaries and area have been defined by the New Zealand National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research as having an area of 637,000 square kilometres (246,000 sq mi).

The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica. It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than 600 kilometres (370 mi) long, and between 15 and 50 metres high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface.

Vostok Station is a Russian research station in inland Princess Elizabeth Land, Antarctica. Founded by the Soviet Union in 1957, the station lies at the southern Pole of Cold, with the lowest reliably measured natural temperature on Earth of −89.2 °C. Research includes ice core drilling and magnetometry. Vostok was named after Vostok, the lead ship of the First Russian Antarctic Expedition captained by Fabian von Bellingshausen. The Bellingshausen Station was named after this captain.

An ice core is a core sample that is typically removed from an ice sheet or a high mountain glacier. Since the ice forms from the incremental buildup of annual layers of snow, lower layers are older than upper ones, and an ice core contains ice formed over a range of years. Cores are drilled with hand augers or powered drills; they can reach depths of over two miles (3.2 km), and contain ice up to 800,000 years old.

The Deep Sea Drilling Project (DSDP) was an ocean drilling project operated from 1968 to 1983. The program was a success, as evidenced by the data and publications that have resulted from it. The data are now hosted by Texas A&M University, although the program was coordinated by the Scripps Institution of Oceanography at the University of California, San Diego. DSDP provided crucial data to support the seafloor spreading hypothesis and helped to prove the theory of plate tectonics. DSDP was the first of three international scientific ocean drilling programs that have operated over more than 40 years. It was followed by the Ocean Drilling Program (ODP) in 1985, the Integrated Ocean Drilling Program in 2004 and the present International Ocean Discovery Program in 2013.

Prydz Bay is a deep embayment of Antarctica between the Lars Christensen Coast and Ingrid Christensen Coast. The Bay is at the downstream end of a giant glacial drainage system that originates in the East Antarctic interior. The Lambert Glacier flows from Lambert Graben into the Amery Ice Shelf on the south-west side of Prydz Bay. Other major glaciers drain into the southern end of the Amery Ice Shelf at 73° S where the marine part of the system starts at the modern grounding zone.

Pine Island Glacier (PIG) is a large ice stream, and the fastest melting glacier in Antarctica, responsible for about 25% of Antarctica's ice loss. The glacier ice streams flow west-northwest along the south side of the Hudson Mountains into Pine Island Bay, Amundsen Sea, Antarctica. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy (USN) air photos, 1960–66, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) in association with Pine Island Bay.

Thwaites Glacier is an unusually broad and vast Antarctic glacier located east of Mount Murphy, on the Walgreen Coast of Marie Byrd Land. It was initially sighted by polar researchers in 1940, mapped in 1959–1966 and officially named in 1967, after the late American glaciologist Fredrik T. Thwaites. The glacier flows into Pine Island Bay, part of the Amundsen Sea, at surface speeds which exceed 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) per year near its grounding line. Its fastest-flowing grounded ice is centered between 50 and 100 kilometres east of Mount Murphy. Like many other parts of the cryosphere, it has been adversely affected by climate change, and provides one of the more notable examples of the retreat of glaciers since 1850.

Dome Fuji, also called Dome F or Valkyrie Dome, is an Antarctic base located in the eastern part of Queen Maud Land. With an altitude of 3,810 metres (12,500 ft) above sea level, it is the second-highest summit or ice dome of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet and represents an ice divide. Dome F is the site of Dome Fuji Station, a research station operated by Japan.

Timothy Raymond Naish is a New Zealand glaciologist and climate scientist who has been a researcher and lecturer at Victoria University of Wellington and the Director of the Antarctic Research Centre, and in 2020 became a programme leader at the Antarctic Science Platform. Naish has researched and written about the possible effect of melting ice sheets in Antarctica on global sea levels due to high CO2 emissions causing warming in the Southern Ocean. He was instrumental in establishing and leading the Antarctica Drilling Project (ANDRILL), and a Lead Author on the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) 5th Assessment Report (2014).

The WAIS Divide is the ice flow divide on the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) which is a linear boundary that separates the region where the ice flows to the Ross Sea, from the region where the ice flows to the Weddell Sea. It is similar to a continental hydrographic divide.
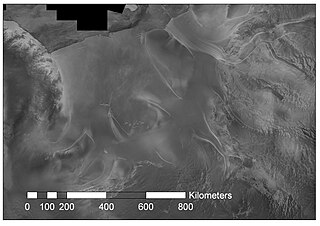
Rutford Ice Stream is a major Antarctic ice stream, about 290 kilometres (180 mi) long and over 24 kilometres (15 mi) wide, which drains southeastward between the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains and Fletcher Ice Rise into the southwest part of Ronne Ice Shelf. Named by US-ACAN for geologist Robert Hoxie Rutford, a member of several USARP expeditions to Antarctica; leader of the University of Minnesota Ellsworth Mountains Party, 1963-1964. Rutford served as Director of the Division of Polar Programs, National Science Foundation, 1975-1977.

The Dawson-Lambton Glacier is a heavily crevassed glacier entering the south-eastern Weddell Sea immediately west of the Brunt Ice Shelf. It was discovered in January 1915 by a British expedition led by Ernest Shackleton. He named it for Elizabeth Dawson-Lambton, a benefactress of the Shackleton expeditions.

Lake Whillans is a subglacial lake in Antarctica. The lake is located under the Whillans Ice Stream at the southeastern edge of the Ross Ice Shelf in the west of the continent. The lake surface is 800 m (2,600 ft) beneath the surface of the ice and the lake covers an estimated area of 60 km2 (20 sq mi). Lake depths measured thus far have been around 2 metres. Its temperature is −0.49 °C, below 0 °C because of the high pressure.
Ellen Mosley-Thompson is a glaciologist and climatologist. She is a Distinguished University Professor at The Ohio State University and director of their Byrd Polar and Climate Research Center. She is known as a pioneer in the use of ice cores from the Polar Regions for paleoclimatic research and is an influential figure in climate science. She is an elected fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, the American Geophysical Union and an elected member of the National Academy of Sciences.
This is a list of events occurring in Antarctica in 2017.
Mercer Subglacial Lake is a subglacial lake in Antarctica covered by a sheet of ice 1,067 m (3,501 ft) thick; the water below is hydraulically active, with water replacement times on the order of a decade from the Ross Sea. Studies suggest that Mercer Subglacial Lake as well as other subglacial lakes appear to be linked, with drainage events in one reservoir causing filling and follow-on drainage in adjacent lakes.

Richard Levy is a New Zealand glacial stratigrapher and paleoclimatologist with expertise in microfossil analysis. As a principal scientist at GNS Science he has been involved in international and New Zealand environmental research programmes focussing on the evolution of the Earth's climate and building an understanding of the role of greenhouse gases in causing anthropogenic climate changes, in particular those impacting global sea levels. He has had extensive experience in scientific drilling, leading major projects, including the ANtarctic geological DRILLing (ANDRILL) Program in Antarctica. Since 2018, Levy has co-led the government funded NZ SeaRise programme.