| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following is a list of events that occurred in Antarctica in 2016 .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
The following is a list of events that occurred in Antarctica in 2016 .

The Ross Sea is a deep bay of the Southern Ocean in Antarctica, between Victoria Land and Marie Byrd Land and within the Ross Embayment, and is the southernmost sea on Earth. It derives its name from the British explorer James Clark Ross who visited this area in 1841. To the west of the sea lies Ross Island and Victoria Land, to the east Roosevelt Island and Edward VII Peninsula in Marie Byrd Land, while the southernmost part is covered by the Ross Ice Shelf, and is about 200 miles (320 km) from the South Pole. Its boundaries and area have been defined by the New Zealand National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research as having an area of 637,000 square kilometres (246,000 sq mi).

The climate of Antarctica is the coldest on Earth. The continent is also extremely dry, averaging 166 mm (6.5 in) of precipitation per year. Snow rarely melts on most parts of the continent, and, after being compressed, becomes the glacier ice that makes up the ice sheet. Weather fronts rarely penetrate far into the continent, because of the katabatic winds. Most of Antarctica has an ice-cap climate with extremely cold and dry weather.

McMurdo Station is an American Antarctic research station on the southern tip of Ross Island. It is operated by the United States through the United States Antarctic Program (USAP), a branch of the National Science Foundation. The station is the largest community in Antarctica, capable of supporting up to 1,500 residents, though the population fluctuates seasonally; during the antarctic night, there are as few as a few hundred people. It serves as one of three year-round United States Antarctic science facilities. Personnel and cargo going to or coming from Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station usually first pass through McMurdo, either by flight or by the McMurdo to South Pole Traverse; it is a hub for activities and science projects in Antarctica. McMurdo, Amundsen-Scott, and Palmer are the three United States stations on the continent, though by the Antarctic Treaty System the bases are not a legal claim ; they are dedicated to scientific research. New Zealand's Scott Base is nearby on Hut Peninsula and across the channel is a helicopter refueling station at Marble Point. The bases are served by airfields and a port, though access can be limited by weather conditions which can make it too hard to land aircraft, and an icebreaker may be needed to reach the port facility.

The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica. It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than 600 kilometres (370 mi) long, and between 15 and 50 metres high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface.

An ice shelf is a large platform of glacial ice floating on the ocean, fed by one or multiple tributary glaciers. Ice shelves form along coastlines where the ice thickness is insufficient to displace the more dense surrounding ocean water. The boundary between the ice shelf (floating) and grounded ice is referred to as the grounding line; the boundary between the ice shelf and the open ocean is the ice front or calving front.

The Byrd Polar and Climate Research Center (BPCRC) is a polar, alpine, and climate research center at Ohio State University founded in 1960.

The McMurdo Sound is a sound in Antarctica, known as the southernmost passable body of water in the world, located approximately 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) from the South Pole.

The Antarctic ice sheet is a continental glacier covering 98% of the Antarctic continent, with an area of 14 million square kilometres and an average thickness of over 2 kilometres (1.2 mi). It is the largest of Earth's two current ice sheets, containing 26.5 million cubic kilometres of ice, which is equivalent to 61% of all fresh water on Earth. Its surface is nearly continuous, and the only ice-free areas on the continent are the dry valleys, nunataks of the Antarctic mountain ranges, and sparse coastal bedrock. However, it is often subdivided into the East Antarctic ice sheet (EAIS), West Antarctic ice sheet (WAIS), and Antarctic Peninsula (AP), due to the large differences in topography, ice flow, and glacier mass balance between the three regions.

The United States Antarctic Program is an organization of the United States government which has a presence in the Antarctica continent. Founded in 1959, the USAP manages all U.S. scientific research and related logistics in Antarctica as well as aboard ships in the Southern Ocean.

Pine Island Glacier (PIG) is a large ice stream, and the fastest melting glacier in Antarctica, responsible for about 25% of Antarctica's ice loss. The glacier ice streams flow west-northwest along the south side of the Hudson Mountains into Pine Island Bay, Amundsen Sea, Antarctica. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy (USN) air photos, 1960–66, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) in association with Pine Island Bay.

An ice pier or ice wharf is a man-made structure used to assist the unloading of ships in Antarctica. It is constructed by pumping seawater into a contained area and allowing the water to freeze. By repeating this procedure several times, additional layers are built up. The final structure is many metres in thickness, and strong enough to support container trucks. Operation Deep Freeze personnel constructed the first floating ice pier at Antarctica’s southernmost sea port at McMurdo Station in 1973. Ice piers have been in use each summer season since, at McMurdo's natural harbor at Winter Quarters Bay located at 77°50′S166°40′E. The harbor is positioned on the southern tip of Ross Island.

The Erebus Glacier Tongue is a mountain outlet glacier and the seaward extension of Erebus Glacier from Ross Island. It projects 11 kilometres (6.8 mi) into McMurdo Sound from the Ross Island coastline near Cape Evans, Antarctica. The glacier tongue varies in thickness from 50 metres (160 ft) at the snout to 300 metres (980 ft) at the point where it is grounded on the shoreline. Explorers from Robert F. Scott's Discovery Expedition (1901–1904) named and charted the glacier tongue.

ANDRILL is a scientific drilling project in Antarctica gathering information about past periods of global warming and cooling.

The Byrd Station is a former research station established by the United States during the International Geophysical Year by U.S. Navy Seabees during Operation Deep Freeze II in West Antarctica.
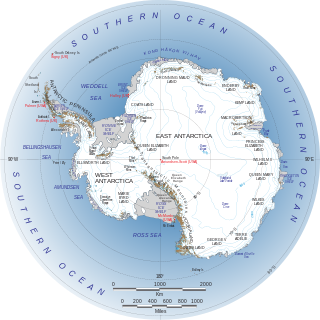
The East Antarctic Ice Sheet (EAIS) lies between 45° west and 168° east longitudinally. It was first formed around 34 million years ago, and it is the largest ice sheet on the entire planet, with far greater volume than the Greenland ice sheet or the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS), from which it is separated by the Transantarctic Mountains. The ice sheet is around 2.2 km (1.4 mi) thick on average and is 4,897 m (16,066 ft) at its thickest point. It is also home to the geographic South Pole, South Magnetic Pole and the Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station.

Antarctica is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of 14,200,000 km2 (5,500,000 sq mi). Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of 1.9 km (1.2 mi).

Haskell Strait refers to the ocean passage in southern McMurdo Sound, running between Cape Armitage, Ross Island and Cape Spencer-Smith, White Island, Antarctica. Oceanographically, it separates McMurdo Sound from the ocean basin beneath the Ross Ice Shelf. The Strait itself is around 25 km wide and in places over 900 m deep. Currents of nearly half a knot have been measured in the Strait, although typical flows are lower. It is mostly covered by the ice of the McMurdo Ice Shelf and fast ice in southern McMurdo Sound. On rare occasions sea-ice breakout exposes the north-west corner of the Strait which becomes navigable and vessels can actually moor off Scott Base.

The Ross expedition was a voyage of scientific exploration of the Antarctic in 1839 to 1843, led by James Clark Ross, with two unusually strong warships, HMS Erebus and HMS Terror. It explored what is now called the Ross Sea and discovered the Ross Ice Shelf. On the expedition, Ross discovered the Transantarctic Mountains and the volcanoes Mount Erebus and Mount Terror, named after each ship. The young botanist Joseph Dalton Hooker made his name on the expedition.

Christina Riesselman is an American paleoceanographer whose research focus is on Southern Ocean response to changing climate.
This is a list of events occurring in Antarctica in 2017.