| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||

This article lists events from the year 2019 in the Bahamas
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||

This article lists events from the year 2019 in the Bahamas


The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and 88% of its population. The archipelagic country consists of more than 3,000 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing 470,000 km2 (180,000 sq mi) of ocean space.

The Bahamas are a group of about 700 islands and cays in the western Atlantic Ocean, of which only between 30 and 40 are inhabited. The largest of the islands is Andros Island, located north of Cuba and 200 kilometres southeast of Florida. The Bimini islands are to its northwest. To the North is the island of Grand Bahama, home to the second-largest city in the country, Freeport. The island of Great Abaco is to its east. In the far south is the island of Great Inagua, the second-largest island in the country. Other notable islands include Eleuthera, Cat Island, San Salvador Island, Acklins, Crooked Island, and Mayaguana. Nassau is the capital and largest city, located on New Providence. The islands have a tropical savannah climate, moderated by the Gulf Stream. The total size is 13,878 km2 (5,358 sq mi). Due to the many widespread islands it has the 41st largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 654,715 km2 (252,787 sq mi).

The Abaco Islands lie in the north of The Bahamas, about 193 miles east of Miami, Florida. The main islands are Great Abaco and Little Abaco, which is just west of Great Abaco's northern tip. There are several smaller barrier cays, of which the northernmost are Walker's Cay and its sister island Grand Cay. To the south, the next inhabited islands are Spanish Cay and Green Turtle Cay, with its settlement of New Plymouth, Great Guana Cay, private Scotland Cay, Man-O-War Cay, and Elbow Cay, with its settlement of Hope Town. Southernmost are Tilloo Cay and Lubbers Quarters. Also of note off Abaco's western shore is Gorda Cay, now a Disney-owned island and cruise ship stop renamed Castaway Cay. Also in the vicinity is Moore's Island. On the Big Island of Abaco is Marsh Harbour, the Abacos' commercial hub and The Bahamas' third-largest city, plus the resort area of Treasure Cay. Both have airports. A few mainland settlements of significance are Coopers Town and Fox Town in the north and Cherokee and Sandy Point in the south. Administratively, the Abaco Islands constitute seven of the 31 Local Government Districts of The Bahamas: Grand Cay, North Abaco, Green Turtle Cay, Central Abaco, South Abaco, Moore's Island, and Hope Town.

Grand Bahama is the northernmost of the islands of The Bahamas, with the town of West End located 56 nautical miles east of Palm Beach, Florida. It is the third largest island in The Bahamas island chain of approximately 700 islands and 2,400 cays. The island is roughly 530 square miles (1,400 km2) in area and approximately 153 kilometres (95 mi) long west to east and 24 kilometres (15 mi) at its widest point north to south. Administratively, the island consists of the Freeport Bonded Area and the districts of East Grand Bahama and West Grand Bahama. Nearly half of the homes on the island were damaged or destroyed in early September 2019 by Hurricane Dorian.

Freeport is a city, district and free trade zone on the island of Grand Bahama of the northwest Bahamas. In 1955, Wallace Groves, a Virginian financier with lumber interests in Grand Bahama, was granted 20,000 hectares of pineyard with substantial areas of swamp and scrubland by the Bahamian government with a mandate to economically develop the area. Freeport has grown to become the second most populous city in The Bahamas.
Marsh Harbour is a town in Abaco Islands, Bahamas, with a population of 6,283 as of 2012.

Leonard M. Thompson International Airport, formerly known as The Marsh Harbour International Airport, is an airport serving Marsh Harbour, a town in the Abaco Islands, The Bahamas. Marsh Harbour is a major tourist attraction. The airport offers scheduled passenger flights to Nassau and several destinations in Florida as well as regional jet flights nonstop to three major U.S. hubs, Atlanta, Charlotte and Miami in the U.S. In 2007 a new runway was built to allow larger, regional jets to operate from Marsh Harbour. A new airport terminal opened on 27 May 2014.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to The Bahamas:

Hubert Alexander Minnis, ON is a Bahamian politician and doctor who served as prime minister of the Bahamas from May 2017 to 16 September 2021. Minnis is the former leader of the Free National Movement, the former governing party, and the Member of Parliament for the New Providence constituency of Killarney. First elected to the legislature in the 2007 election, he succeeded Hubert Ingraham as party leader following the party's defeat in the 2012 election.

The 2019 Atlantic hurricane season was the fourth consecutive above-average and damaging season dating back to 2016. The season featured eighteen named storms, however, many storms were weak and short-lived, especially towards the end of the season. Six of those named storms achieved hurricane status, while three intensified into major hurricanes. Two storms became Category 5 hurricanes, marking the fourth consecutive season with at least one Category 5 hurricane, the third consecutive season to feature at least one storm making landfall at Category 5 intensity, and the seventh on record to have multiple tropical cyclones reaching Category 5 strength. The season officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30. These dates historically describe the period each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin and are adopted by convention. However, tropical cyclogenesis is possible at any time of the year, as demonstrated by the formation of Subtropical Storm Andrea on May 20, making this the fifth consecutive year in which a tropical or subtropical cyclone developed outside of the official season.
This article lists events from the year 2018 in the Bahamas.
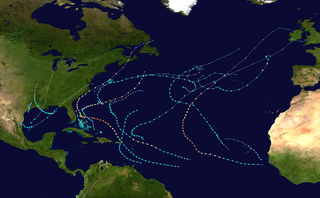
The 2019 Atlantic hurricane season was an event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the north Atlantic Ocean. It was the fourth consecutive above-normal Atlantic hurricane season. The season officially began on June 1, 2019, and ended on November 30, 2019. These dates, adopted by convention, historically describe the period in each year when most tropical systems form. However, storm formation is possible at any time of the year, as demonstrated in 2019 by the formation of the season's first named storm, Subtropical Storm Andrea, on May 20. The final storm of the season, Tropical Storm Sebastien, transitioned to an extratropical cyclone on November 25.

Sir Cornelius Alvin Smith is a Bahamian politician and diplomat, who served as the 11th Governor-General of the Bahamas from 2019 to 2023.

Hurricane Dorian was an extremely powerful and catastrophic Category 5 Atlantic hurricane, which became the most intense tropical cyclone on record to strike The Bahamas, and is tied with the 1935 Labor Day hurricane for the strongest landfall in the Atlantic basin in terms of maximum sustained winds. The 2019 cyclone is regarded as the worst natural disaster in The Bahamas' recorded history. With winds peaking at 185 mph (295 km/h), it was also one of the most powerful hurricanes recorded in the Atlantic Ocean in terms of 1-minute sustained winds, and the strongest since Wilma in 2005. Dorian was the fourth named storm, second hurricane, the first major hurricane, and the first Category 5 hurricane of the 2019 Atlantic hurricane season. Dorian struck the Abaco Islands on September 1 with maximum sustained winds of 185 mph (295 km/h), tying with the 1935 Labor Day hurricane for the highest wind speeds of an Atlantic hurricane ever recorded at landfall. Dorian went on to strike Grand Bahama at similar intensity, stalling just north of the territory with unrelenting winds for at least 24 hours. The resultant damage to these islands was catastrophic; most structures were flattened or swept to sea, and at least 70,000 people were left homeless. After it ravaged through The Bahamas, Dorian proceeded along the coasts of the Southeastern United States and Atlantic Canada, leaving behind considerable damage and economic losses in those regions.
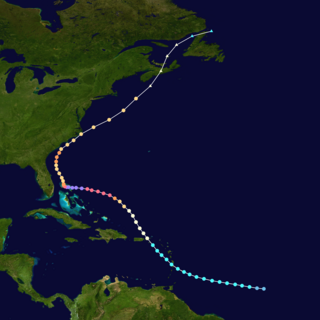
Hurricane Dorian was the strongest hurricane to affect The Bahamas on record, causing catastrophic damage on the islands of Abaco Islands and Grand Bahama, in early September 2019. The cyclone's intensity, as well as its slow forward motion near The Bahamas, broke numerous records. The fifth tropical cyclone, fourth named storm, second hurricane, and first major hurricane of the 2019 Atlantic hurricane season, Dorian originated from a westward-traveling tropical wave, that departed from the western coast of Africa on August 19. The system organized into a tropical depression and later a tropical storm, both on August 24.

The effects of Hurricane Dorian in The Bahamas in 2019 were among the worst experienced for any natural disaster in the country. Hurricane Dorian struck the Abaco Islands as a Category 5 hurricane on September 1, and a day later hit Grand Bahama Island at the same category. The hurricane then stalled over Grand Bahama for another day, finally pulling away from the island on September 3. Damage amounted to US$3.4 billion, and there were at least 74 deaths in the country. Another 282 people were left missing after the hurricane.

Hurricane Dorian caused relatively minor damage across the eastern Caribbean in late August 2019. Originating from a westward moving tropical wave, Dorian organized into a tropical cyclone on August 24 and reached the Lesser Antilles on August 26 as a tropical storm. Turning northwest, the system unexpectedly intensified to a hurricane as it struck the Virgin Islands on August 27. Antecedent to the storm's arrival, local governments across the archipelago issued tropical cyclone warnings and watches, readied public shelters, closed airports, and placed emergency crews on standby. Many of the threatened islands were still reeling from the devastation wrought by Hurricane Irma and Hurricane Maria in September 2017 and fears arose over embattled power grids. In the areas first affected, impacts were limited to gusty winds and modest rainfall. Effects were greater in the Virgin Islands where wind gusts reached 111 mph (179 km/h); however, damage was light. Multiple landslides occurred across the islands and Puerto Rico with only a handful of structures suffering damage. One person died in Puerto Rico while preparing for the storm.

The Bahama Archipelago, also known as the Lucayan Archipelago, is an island group comprising the Commonwealth of The Bahamas and the British Overseas Territory of the Turks and Caicos Islands. The archipelago is in the western North Atlantic Ocean, north of Cuba along with the other Antilles, and east and southeast of Florida. The archipelago has experienced the effects of at least 22 Atlantic hurricanes, or storms that were once tropical or subtropical cyclones, including 17 since 2000. The storms collectively killed 101 people.

Hurricane Dorian caused severe flooding and hurricane-force winds over parts of the coastal Carolinas during early September 2019. After stalling over The Bahamas for three days as a Category 5 hurricane, Dorian proceeded generally to the northwest, before moving along the Atlantic Coast, striking the town of Buxton, North Carolina, on September 6.

Michael Clifton Pintard is a Bahamian politician serving as Leader of the Free National Movement and leader of the opposition since 27 November 2021. He has been the Member of Parliament (MP) for Marco City, Grand Bahama since 2017. First appointed in 2010, he served two terms in the Senate. He was the Minister of Agriculture and Marine Resources from 2018 to 2021.