The Andinia Plan is a conspiracy theory that alleged plans to establish a Jewish state in parts of Argentina and Chile. It is partly based on historical organized Jewish migration to Argentina and proposals for a Jewish state there in the late 19th and the early 20th century.

The Emergency Military Unit is a branch of the Spanish Armed Forces responsible for providing disaster relief throughout Spain mainly, and abroad if required. It is the newest branch of the Spanish Armed Forces.
The Great Fire of Valparaíso started on 12 April 2014 at 16:40 local time, in the hills of the city of Valparaíso, Chile. The wildfire destroyed at least 2,500 homes, leaving 11,000 people homeless. An additional 6,000 people were evacuated from the city, which was placed on red alert and declared a disaster zone. Fifteen people were confirmed killed and ten suffered serious injuries.

A series of wildfires burned across Chile during January 2017.
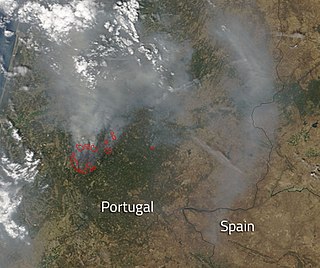
A series of four initial deadly wildfires erupted across central Portugal in the afternoon of 17 June 2017 within minutes of each other, resulting in at least 66 deaths and 204 injured people.

During August 2019, a number of forest fires broke out in the Canary Islands of Gran Canaria, Tenerife and Lanzarote. The fires on the island of Gran Canaria were the most severe, resulting in the loss of large areas of the island's forests and leading to the evacuation of thousands of residents from a number of towns and villages. The intense heat brought by a heat wave and the presence of strong winds, combined with the island's mountainous terrain, made extinguishing activities exceptionally difficult.

The 2020 Delta del Paraná wildfires is a series of wildfires that are burning across the Delta del Paraná in Argentina, affecting mainly the Entre Ríos and Santa Fe provinces, but also Buenos Aires, including major cities as Rosario.

The 2008 Delta del Paraná wildfires were a series of wildfires in the Delta del Paraná islands located mainly in Entre Ríos, Argentina. It was an unprecedented event that covered major cities as Buenos Aires and Rosario in smoke, affecting the health of millions of people. The first fires were detected on 13 April 2008, and lasted until April 25 – 26, when rain extinguished most of them. Buenos Aires was heavily affected between April 15 and April 20.

The 2020 Córdoba wildfires are a series of wildfires burning through the Córdoba Province in Argentina.
The Chilean Patagoniawildfire was a wildfire affecting Patagonia Park in Aysén Region, southern Chile. The fire begun on Friday July 2, 2021 around 22:00 local time. Radio Cooperativa reported in the night of July 2, 2021 that the fire could be observed 80 km (50 mi) away in the town of Cochrane. It was expected that incoming rain would help mitigate the fire. As of July 3, 2021, 150 hectares have burnt. National Office of Emergency of the Interior Ministry declared the fire a "red alert" emergency on July 3, 2021. By July 7 the fire was "under control but not yet extinguished".

The 2022 Corrientes wildfires were a series of wildfires burning throughout the Corrientes Province in Argentina. It began in January of that year and continued to be active in many parts of the province, having consumed more than 800,000 hectares, which is equivalent to approximately ten percent of the province. The fire advanced over fields, mountains, wetlands and nature reserves, including the Iberá Wetlands, and has caused material damage estimated at between 25 and 40 billion pesos.
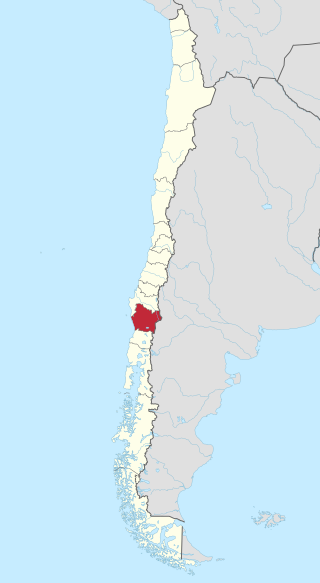
The 2022 Araucanías wildfires are a series of wildfires in the Chilean region of Araucanía. By February 26 57,000 ha had been burnt by fires. The commune of Traiguén and China Muerta National Reserve were on February 26 the places were most resources being used to fight fires. By February 25 180 haa had been consumed in China Muerta and the fire had not yet reached Conguillío National Park.

In June through August 2022, parts of Europe, the Middle East and North Africa were affected by wildfires. The bulk of the fires affected Mediterranean countries, with the main areas affected being Algeria, France, Greece, Portugal and Spain.

In mid-January 2022, the Southern Cone had a severe heat wave, which made the region for a while the hottest place on earth, with temperatures exceeding those of the Middle East. This extreme weather event was associated with the Atlantic anticyclone, a particularly intense La Niña phenomenon in the Pacific Ocean, and the regional effects of climate change.

Starting on 30 January 2023, a series of wildfires began in the South American country of Chile. By early February, the fires had developed into a large outbreak of at least 406 individual fires, several dozen of which were classified as "red alert fires". The fires burned more than 430,000 hectares and resulted in the loss of 24 lives, prompting the government to declare a state of emergency in multiple regions of the country.

In February 2024, a series of wildfires broke out in Chile, affecting multiple regions including Valparaíso, O'Higgins, Maule, Biobío, and Los Lagos. The most severe incidents occurred in the Valparaíso Region as of 5 February 2024. The Chilean government labeled the fires as the country's worst disaster since the 2010 Chile earthquake, and declared a two-day national mourning period.

On 15 August 2023, a forest fire broke out on the island of Tenerife, in the Canary Islands of Spain. The fire, driven by the wind, heat, and low humidity levels, caused mass evacuations, widespread damage to the island's flora and fauna, as well as power and water supply cuts in some of the affected municipalities.
In August 2024, multiple wildfires started in Ecuador. What they resulted from is currently unknown.
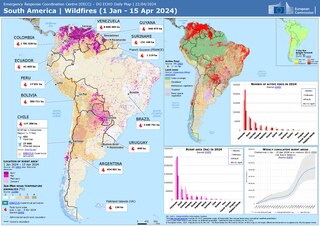
The 2024 South American wildfires refer to a mega colossal series of wildfires that significantly impacted several neighboring South American countries, including Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. Based on Global Wildfire Information System satellite imaging, about 346,112 wildfire hotspots damaged or destroyed 85,866,867 hectares. The massive area burned was primarily caused by anthropogenic climate change and the resulting consequences of the 2023–2024 South American drought on fire conditions. The wildfires caused significant deforestation of the Amazon rainforest, and also impacted several other international biomes including the Pantanal wetlands, becoming the second largest series of wildfires in the 21st century next to the 2023–24 Australian bushfire season, with the 2024 Brazil wildfires alone reaching fourth in area burned.















