
Beta Arietis, officially named Sheratan, is a star system and the second-brightest star in the constellation of Aries, marking the ram's second horn.

Delta Arietis, officially named Botein, is a star in the northern constellation of Aries, 1.8 degrees north of the ecliptic. The apparent visual magnitude is 4.35, so it is visible to the naked eye. It has an annual parallax shift of 19.22 mas; corresponding to a distance of about 170 light-years from the Sun.

Gamma Arietis is a binary star in the northern constellation of Aries. The two components are designated γ¹ Arietis or Gamma Arietis B and γ² Arietis or Gamma Arietis A. The combined apparent visual magnitude of the two stars is 3.86, which is readily visible to the naked eye and makes this the fourth-brightest member of Aries. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, the distance to Gamma Arietis from the Sun is approximately 164 light-years.

Musca Borealis was a constellation, now discarded, located between the constellations of Aries and Perseus. It was originally called Apes by Petrus Plancius when he created it in 1612. It was made up of a small group of stars, now called 33 Arietis, 35 Arietis, 39 Arietis, and 41 Arietis, in the north of the constellation of Aries.

Epsilon Arietis is the Bayer designation for a visual binary star system in the northern constellation of Aries. It has a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.63 and can be seen with the naked eye, although the two components are too close together to be resolved without a telescope. With an annual parallax shift of 9.81 mas, the distance to this system can be estimated as 330 light-years, give or take a 30 light-year margin of error.

Lambda Arietis is the Bayer designation for a double star in the northern constellation of Aries. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 25.32 arcseconds, this system is approximately 129 light-years distant from Earth. The pair have a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.79, which is bright enough to be viewed with the naked eye. Because the yellow secondary is nearly three magnitudes fainter than the white primary, they are a challenge to split with quality 7× binoculars and are readily resolvable at 10×.

Zeta Arietis, Latinized from ζ Arietis, is the Bayer designation for a star in the northern constellation of Aries. It is dimly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.89. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 12.44 mas, the distance to this star is 260 ± 20 light-years. This is an A-type main sequence star with a stellar classification of A1 V. It has a high rate of rotation with a projected rotational velocity of 133 km/s. The star is shining at an effective temperature of 9,500 K, giving it the characteristic white-hued glow of an A-type star.

Pi Arietis, Latinized from π Arietis, is the Bayer designation for a multiple star system in the northern constellation of Aries. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, this system is approximately 800 light-years distant from Earth and has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.21. This is bright enough to be faintly seen with the naked eye.
19 Arietis is a star in the northern constellation of Aries. 19 Arietis is the Flamsteed designation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.70, which means it is faintly visible to the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 6.81 mas, it is approximately 480 light-years away from Earth. At that distance, the brightness of the star is diminished by 0.21 in magnitude from extinction caused by interstellar gas and dust.
10 Arietis is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Aries. 10 Arietis is the Flamsteed designation. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, yellow-white hued star with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 5.63. Based upon parallax measurements, it is located around 159 light years away from the Sun. The system is receding from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +12.9 km/s.
21 Arietis is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Aries. 21 Arietis is the Flamsteed designation. It has a combined apparent visual magnitude is 5.57; the brighter member is magnitude 6.40 while the fainter star is magnitude 6.48. The distance to this star system, based upon an annual parallax shift of 19.58 mas, is 167 light-years. The pair orbit each other with a period of 23.70 years and an eccentricity of 0.68.
56 Arietis is a single, variable star in the northern zodiac constellation of Aries. It has the variable star designation SX Arietis, while 56 Arietis is the Flamsteed designation. This object is visible to the naked eye as a faint, blue-white hued point of light with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 5.79. The estimated distance to this star is approximately 406 light-years, based on parallax, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +18 km/s.
7 Arietis is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Aries. 7 Arietis is the Flamsteed designation. The pair have a combined apparent visual magnitude of 5.76, making it faintly visible to the naked eye from dark suburban skies. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 5.85 mas, it is approximately 560 light-years distant from the Earth, give or take a 40 light-year margin of error.
60 Arietis is a star in the northern constellation of Aries. 60 Arietis is the Flamsteed designation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 6.14, making it a challenge to view with the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 9.57±0.05 mas, this star is located 341 light-years away from the Sun. It is receding from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +24 km/s.
65 Arietis is a star in the northern constellation of Aries, located near Tau Arietis. 65 Arietis, abbreviated '65 Ari', is the Flamsteed designation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 6.07, which, according to the Bortle Dark-Sky Scale, means it is faintly visible to the naked eye when viewed from dark suburban skies. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 9.45±0.09 mas, it is approximately 345 light-years distant from the Sun. The star is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of around −6 km/s.
66 Arietis is a double star in the northern constellation of Aries. 66 Arietis is the Flamsteed designation. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 6.03, putting it near the limit for naked eye visibility. The magnitude 10.4 companion is located at an angular separation of 0.810 arcseconds from the primary along a position angle of 65°. The distance to this pair, as determined from parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, is approximately 210 light-years.
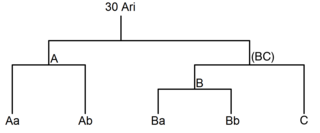
30 Arietis is a 6th-apparent-magnitude quadruple star in the constellation of Aries. 30 Arietis is the Flamsteed designation. 30 Arietis A and B are separated by 38.1" or about 1500 AU at a distance of 130 light years away. The main components of both systems are F-type main-sequence stars, meaning they are fusing hydrogen in their cores. 30 Arietis A is itself a spectroscopic binary with an orbital period of 1.1 days. The 30 Arietis system is 910 million years old, one fifth the age of the Sun.
16 Arietis is a star in the northern constellation of Aries. 16 Arietis is the Flamsteed designation. Its apparent magnitude is 6.01. Based upon the annual parallax shift of 4.25 ± 0.43 mas, this star is approximately 767 light-years distant from Earth. The brightness of this star is diminished by 0.40 in magnitude from extinction caused by interstellar gas and dust. This is an evolved giant star with a stellar classification of K3 III.
36 Arietis is a star in the northern constellation of Aries. 36 Arietis is the Flamsteed designation. It is a dim, orange-hued star that is a challenge to view with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 6.40. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 8.59±0.04 mas, this star is located 380 light-years away from the Sun. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −34 km/s, and is a member of the Wolf 630 moving group of stars that share a common motion through space.
50 Arietis is a star in the constellation of Aries. 50 Arietis is the Flamsteed designation. Its apparent magnitude is 6.80.


